Web-optimized vector database (written in Rust).
- Rust API (using native filesystem, or a transient in-memory filesystem)
- Web API (Using the Private Origin File System)
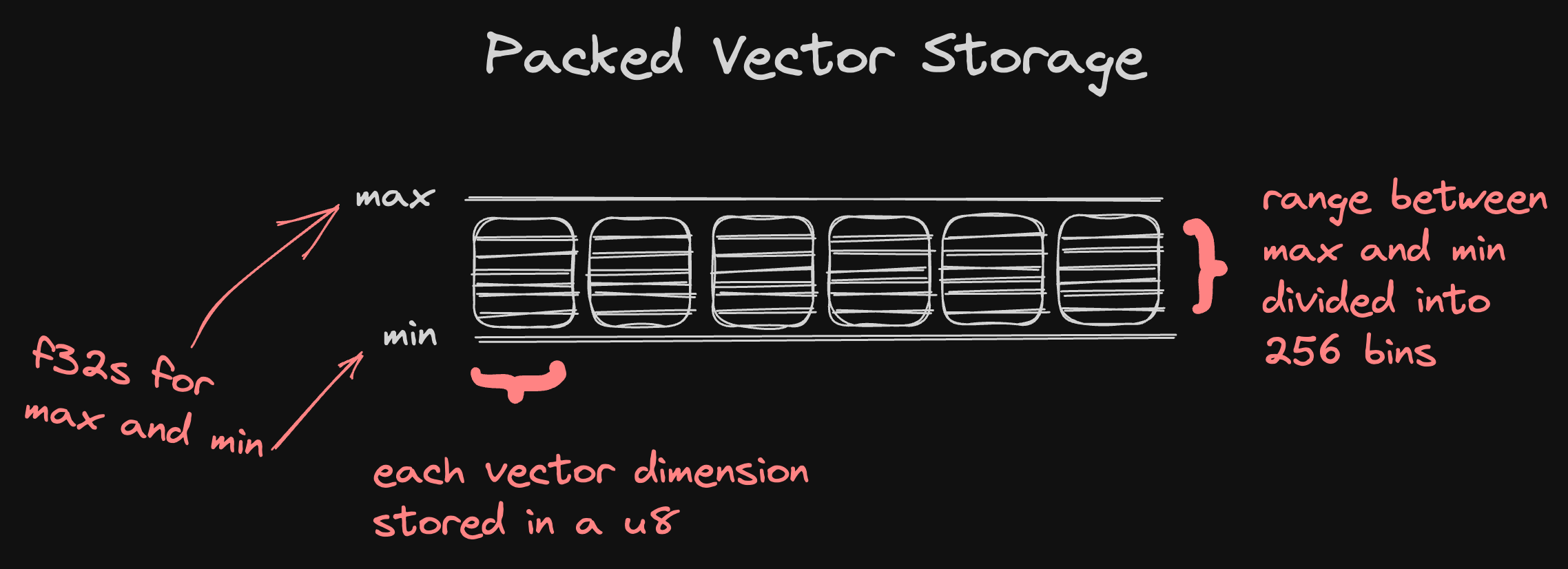
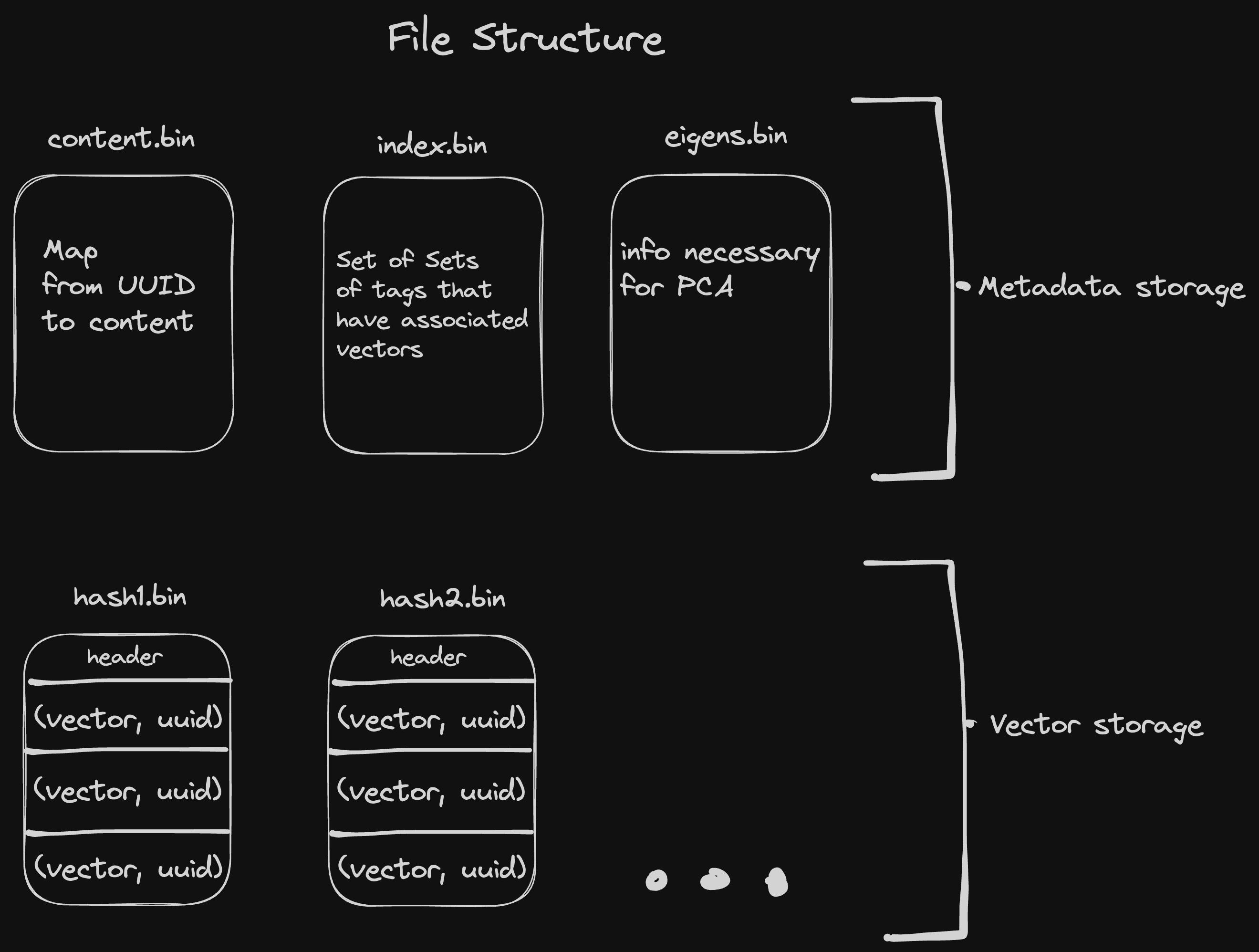
- Very efficient vector storage format
- For a vector with 1536 dimensions, our representation consumes 1.5 KB, while naively encoding with JSON would consume 20.6 KB.
- PCA for vector compression when storage space is low
npm install victor-db
import { Db } from "victor";
const db = await Db.new();
const content = "My content!";
const tags = ["these", "are", "tags"];
const embedding = new Float64Array(/* your embedding here */);
// write to victor
await db.insert(content, embedding, tags);
// read the 10 closest results from victor that are tagged with "tags"
// (only 1 will be returned because we only inserted one embedding)
const result = await db.search(embedding, ["tags"], 10);
assert(result[0].content == content);
// clear database
await db.clear();See www/ for a more complete example, including fetching embeddings from OpenAI.
cargo add victor-db
use std::path::PathBuf;
use victor_db::native::Db;
let _ = std::fs::create_dir("./victor_test_data");
let mut victor = Db::new(PathBuf::from("./victor_test_data"));
victor.clear_db().await.unwrap();
victor
.write(
"Test Vector 1",
vec![1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
vec!["Test".to_string()],
)
.await;
victor
.write(
"Test Vector 2",
vec![0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
vec!["Test".to_string()],
)
.await;
// read the 10 closest results from victor that are tagged with "tags"
// (only 2 will be returned because we only inserted two embeddings)
let nearest = victor
.find_nearest_neighbors(vec![0.9, 0.0, 0.0], vec!["Test".to_string()], 10)
.await
.first()
.unwrap()
.content
.clone();
assert_eq!(nearest, "Test Vector 1".to_string());This example is also in the /examples directory. If you've cloned this repository, you can run it with cargo run --example native_filesystem.
-
Victor is written in Rust, and compiled to wasm with wasm-pack.
Install wasm pack with
cargo install wasm-packornpm i -g wasm-pack(https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-pack/installer/) -
Build Victor with
wasm-pack build -
Set up the example project, which is in
www/.If you use nvm, you can just run
cd www/ && nvm useThen,
npm i. -
From
www/, start the example project withnpm run start.
Relevant code at src/packed_vector.rs.