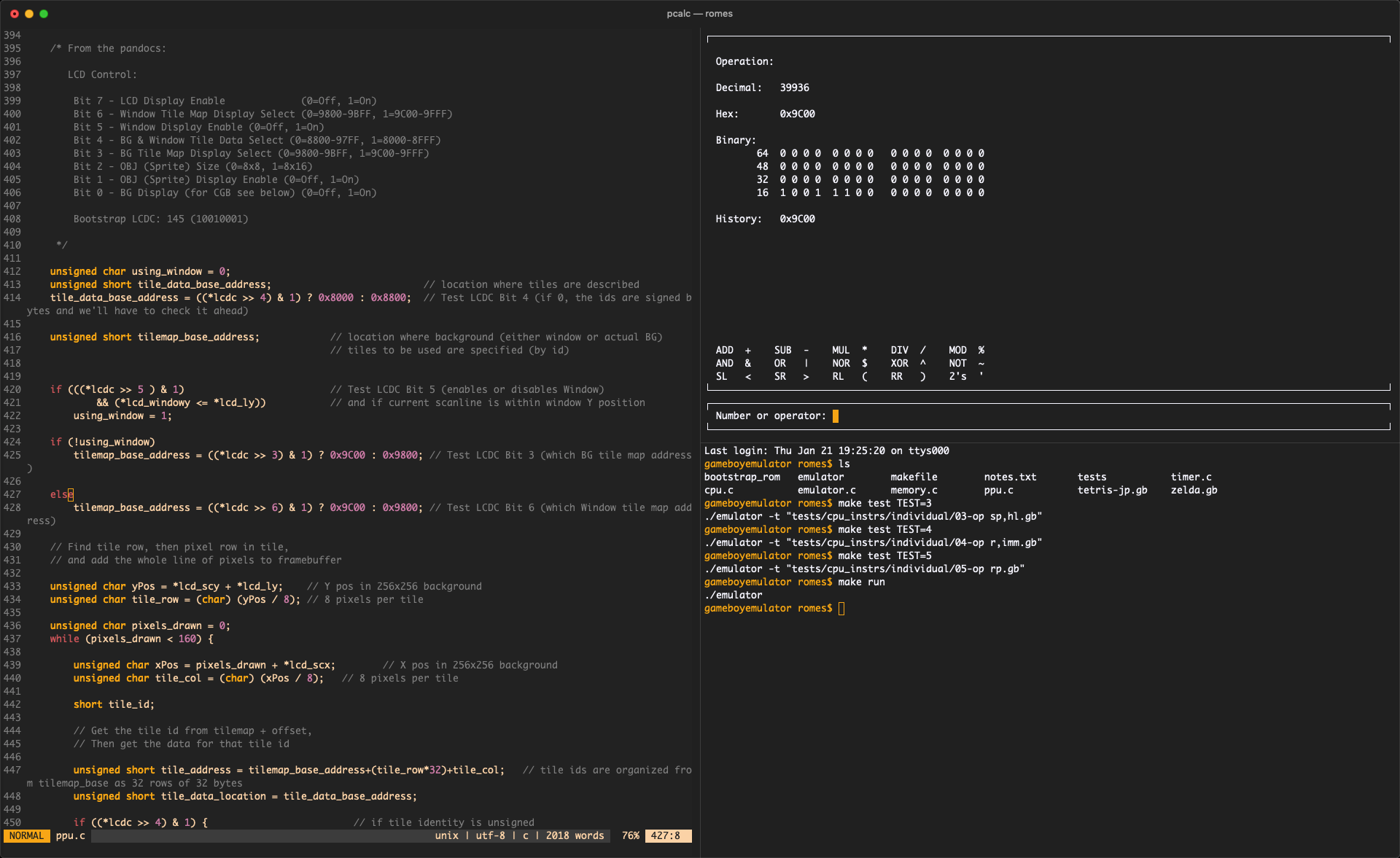
The programmer calculator is a simple terminal tool designed to give maximum efficiency and flexibility to the programmer working with:
- binary, hexadecimal and decimal representations at the same time
- bitwise operations
- various operand sizes (16bits, 32bits, 8bits, etc)
and who likes:
- a clear, simple and customizable interface
- open source software
- terminal/cli tools
The idea was born while developing a Nintendo Gameboy Emulator. Romes - the pitcher - found that the tools given online were clunky and did not allow for "nice multitasking"
With the constant need to visualize and manipulate bits, it became evident that a better solution had to come to life
First, create a new tap
$ brew tap alt-romes/pcalc
Then, install the program
$ brew install pcalc
Install from AUR
$ yay -S programmer-calculator
To build from source you need gcc, ncurses, and the source files. If you don't have ncurses, please install it (i.e. with your system's package manager) first.
First, clone the repository
$ git clone https://github.com/alt-romes/programmer-calculator
Then, compile the code into an executable file
$ make
Finally, move the executable to a directory reachable by $PATH
$ mv -i output/pcalc /usr/local/bin
Either re-build from source, or, using brew do
$ brew update
followed by
$ brew upgrade pcalc
Just run the programmer calculator program
$ pcalc
There are various ways to insert values/operators, see the example 2 + 2 below:
- 2, followed by +, followed by 2
- 2, followed by +2
- 2+, followed by 2
- 2+2 (or 2 + 2+ 2, 2 +2, 2+ 2, ...)
You can also do inline math, but without priorities.
This means 2 + 3 * 2 is valid, but it's equal to 10, not 8, because expressions are evaluated from left to right
That said, any inline math is valid i.e.: 0x13 + 135 - 0b101 < 2 * 3 ~
All three number representations are available at the same time, you can insert 0xff + 0b101101 - 5 directly onto the calculator
By default, 64 bits are used for arithmetic, however, when working with bits, quite often we want to work with less. With this calculator you can change the amount of bits used. the number displayed will be unsigned
To use 16 bits instead, type 16cb (cb for "change bits")
To use 8 bits, type 8cb
To use 0 < n <= 64 bits, type ncb
While running the calculator, you can type what you see for it to appear/disappear:
history to toggle the history
decimal to toggle the decimal representation
binary to toggle the binary representation
hex to toggle the hexadecimal representation
operation to toggle the operation display
To set a default interface, define an alias for the program with the desired hidden options
$ alias pcalc='pcalc -hbxdos'
h: history, b: binary, x: hex, d: decimal, o: operation, s: symbols
ADD + SUB - MUL * DIV / MOD %
AND & OR | NOR $ XOR ^ NOT ~
SL < SR > RL ( RR ) 2's '
- ADD: a + b arithmetic addition
- SUB: a - b arithmetic subtraction
- MUL: a * b arithmetic multiplication
- DIV: a / b arithmetic integer division
- MOD: a % b modulus from the division
- AND: a & b bit-wise AND (&) operation
- OR : a | b bit-wise OR (|) operation
- NOR: a $ b bit-wise NOR ($) operation : opposite of OR
- XOR: a ^ b bit-wise XOR (^) operation : exclusive OR
- NOT: a~ bit-wise NOT (~) operation : change all bits of a, 0's into 1's and 1's into 0's
- SL : a < b bit-wise SHIFT-LEFT (<) operation : shift a left b number of times
- SR : a > b bit-wise SHIFT-RIGHT (>) operation : shift a right b number of times
- RL : a ( b bit-wise ROTATE-LEFT (() operation : rotate a left b number of times
- RR : a ) b bit-wise ROTATE-LEFT ()) operation : rotate a right b number of times
- 2's: a' 2's complement (') operation : 2's complement of a
- Compare two numbers?
- Up arrow scrolls history (like a terminal)