This project uses image processing techniques to perform face detection and deep learning in order to replace the faces by an emoji similar to the detected facial expression.
The 10 emojis used can be found in this repository under the /emojies directory
To get the code, fork this repository or clone it using the following command:
To get the repository running, you will need the following packages: numpy, matplotlib, openCV and pyTorch
You can obtain them easily by installing the conda environment file included in the repository. To do so, run the following command from the Conda Command Window:
$ conda env create -f environment.yml
$ activate FaceEmojiNote: This step might take a few minutes
In order to perform face detection, a cascade classifier from openCV has been used. This classifier model (based on Haar transform) was pretrained on frontal face images, therefore not needing further training. More information can be found in the following website: https://docs.opencv.org/3.4/db/d28/tutorial_cascade_classifier.html
The deep learning part of the project has been developed using the PyTorch Library. The emotion detection has been preformed using a Resnet18 model (see https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf for further information about Residual networks). The model used was pretrained on the ImageNet dataset containing over 1000000 images.
In order to adapt this model to our particular task, transfer learning has been applied.
On the one hand, the convolutional part of the network, which performs feature extraction, has been kept.
On the other hand, the fully-connected part, which performs classification, has been modified. The last fully-connected layer was replaced for a new layer tailormade for our purpose.
Labeled images that map facial expressions or facial features to emoji labels are necessary to retrain the network during the transfer learning procedure. Therefore, we have created ourselves a mini-dataset containing (approximately) 200 images for each class.
The images were taken using the python scrip testTakeImages.py included in the directory /Lib/utils. After being run, this script takes an image every 500ms and saves it into a directory specified by the user as command line argument. For example, the following commands start taking images and saving them into a directory named /happy
$ python testTakeImages.py --emoji happy
$ python testTakeImages.py -e happyFor privacy issues, we do not make our dataset public, but the model state dictionaries of our trained models can be found under the directory /experiments/-/models.
The networks was retrained for 10 epochs using the ADAM optimizer and an initial learning rate of 0.001.
In just ten epochs, the loss (Binary Cross Entropy) decreases from 0.3 to just 0.05, while the accuracy increases to above 95%.
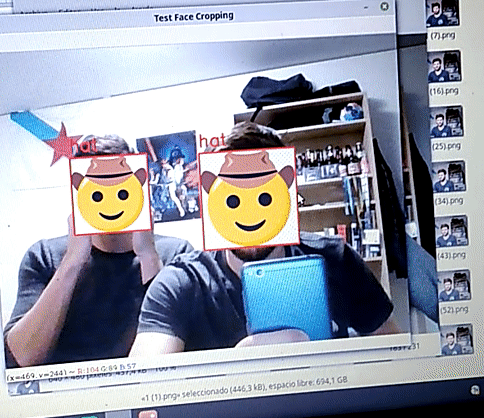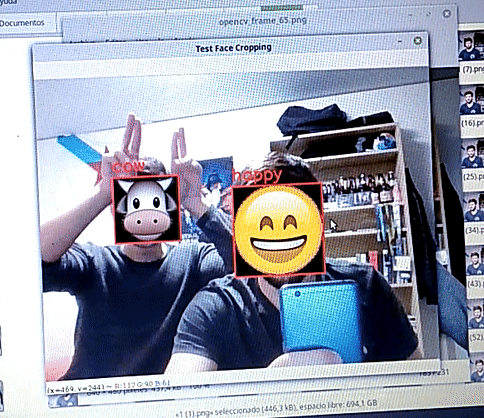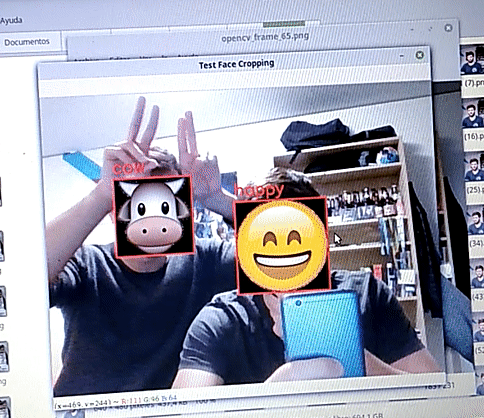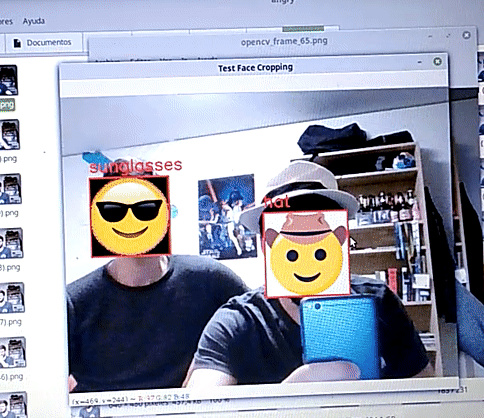
On static images, the network performs inference with a quite high accuracy. A comprehensible evaluatiion has not been carried out, but hopefully the following image is convincing: we can see how for the 6 images the network predicts the correct label.
The script test_face_cropping.py runs the algorithm in real time. Using an openCV canvas:
- Takes an image
- Crops the faces
- Uses the Deep Learning Model to predict an emoji
- Replaces the face by the emoji
The fact that the dataset used was created by us and not so large makes the network perform suboptimally. Furthermore, some emojies such as the monkey or crying are not easy to be detected as the face needs to be partially covered, thus making the performance of the face detector worse.