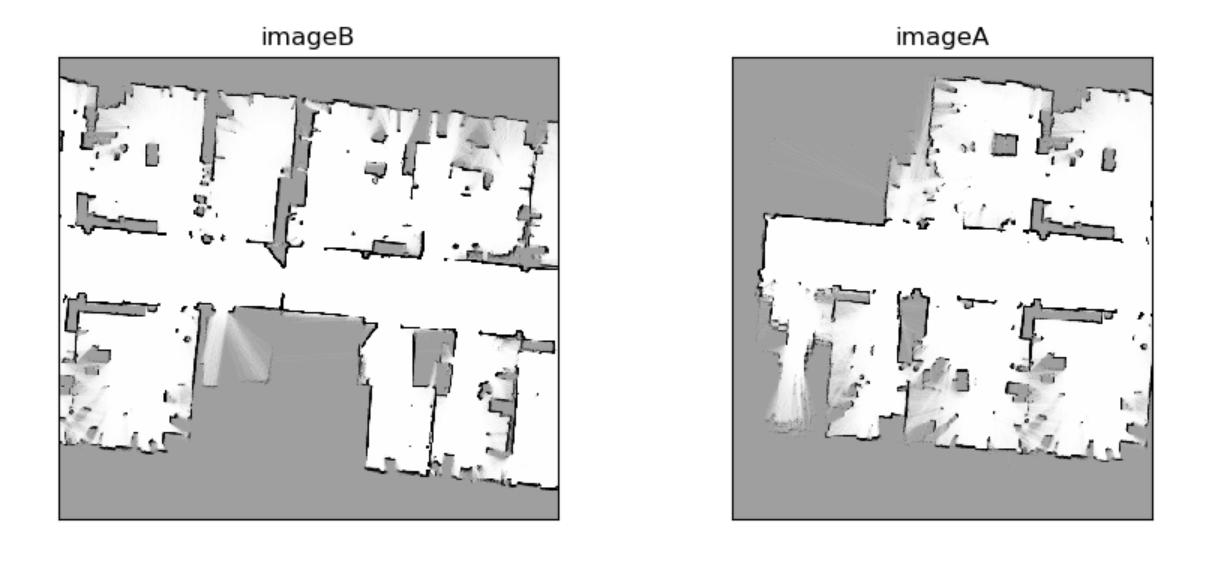
自动控制创新实践要求合并多机器人的slam地图,既合并有重叠部分的两张或多张图片, 比如说下面两张图片
使用SIFT算法进行特征检测,得到特征图
得到匹配结果
- 由于无法提前知道两张图片的位置关系,对于透视变换,可能图片会映射到整个选取区域的左边,这样的话,无法正常显示图片,因此,要对透视变换后的图片进行面积检查,如果比原来的图片面积小太多,就用另一张图片来进行透视变换
"""
计算两张图的透视关系
"""
matchCount = len(matches)
M = getHomography(kpsA, kpsB, matches, reprojThresh=4)
if M is None:
print("Error!")
(matches, H, status) = M
"""
将图片A进行透视变换并检查图片位置
"""
result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageA, H, ((imageA.shape[1] + imageB.shape[1])*2, (imageA.shape[0] + imageB.shape[0]) * 2))
resultAfterCut = cutBlack(result)
# 检查图片位置
if np.size(resultAfterCut) < np.size(imageA) * 0.95:
print("图片位置不对,将自动调换")
# 调换图片
kpsA,kpsB = swap(kpsA, kpsB)
imageA, imageB = swap(imageA, imageB)
if feature_matching == 'bf':
matches = matchKeyPointsBF(featuresB, featuresA, method=feature_extractor)
elif feature_matching == 'knn':
matches = matchKeyPointsKNN(featuresB, featuresA, ratio=0.75, method=feature_extractor)
if len(matches) < 10:
return None
matchCount = len(matches)
M = getHomography(kpsA, kpsB, matches, reprojThresh=4)
if M is None:
print("Error!")
(matches, H, status) = M
得到结果图,合并效果很完美
很简单,反复调用合并两张图片就行,但是有些细节问题,无法提前得知多张图片的位置,先合并哪个?
既然我们有特征匹配环节,优先合并匹配特征数多的就行。
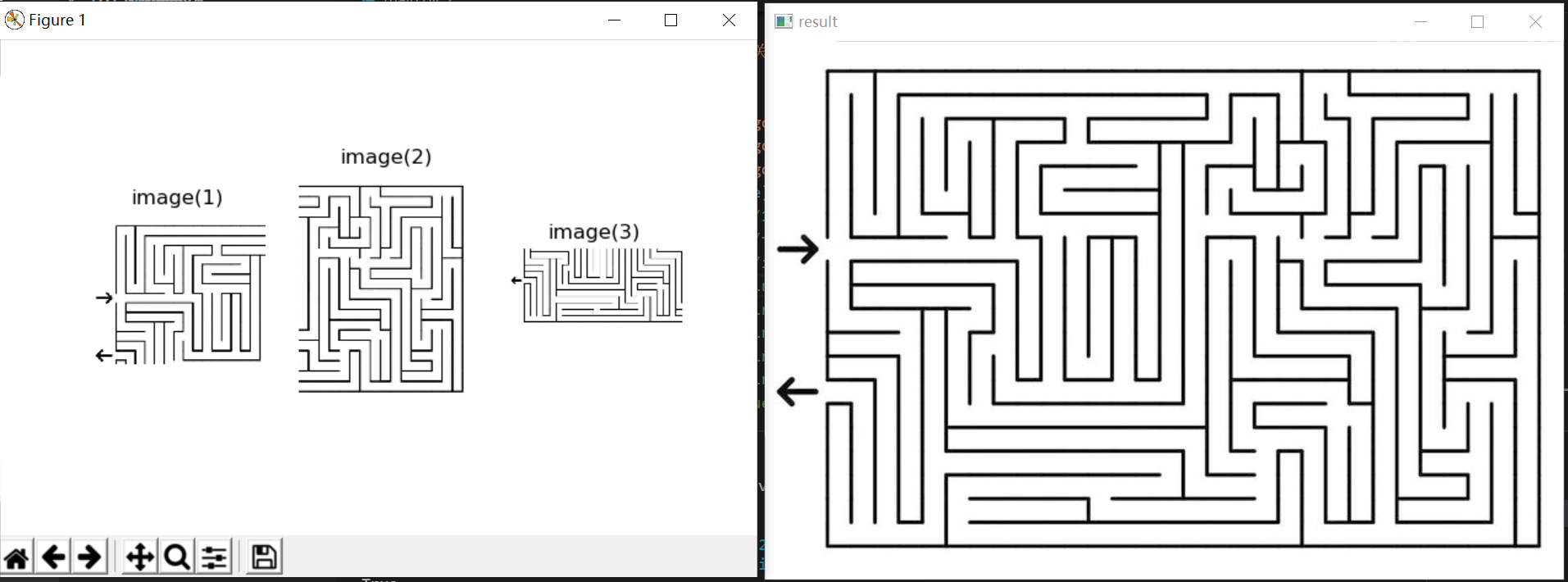
第一个迷宫图
第二个slam地图
效果还行。
注释很详细,不用怕看不懂
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
from numpy.core.defchararray import array
# ================================================================== #
# 选择特征提取器函数
# ================================================================== #
def detectAndDescribe(image, method=None):
assert method is not None, "You need to define a feature detection method. Values are: 'sift', 'surf'"
if method == 'sift':
descriptor = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
elif method == 'surf':
descriptor = cv2.xfeatures2d.SURF_create()
elif method == 'brisk':
descriptor = cv2.BRISK_create()
elif method == 'orb':
descriptor = cv2.ORB_create()
(kps, features) = descriptor.detectAndCompute(image, None)
return (kps, features)
# ================================================================== #
# 暴力检测函数
# ================================================================== #
def matchKeyPointsBF(featuresA, featuresB, method):
bf = createMatcher(method, crossCheck=True)
best_matches = bf.match(featuresA,featuresB)
rawMatches = sorted(best_matches, key = lambda x:x.distance)
print("Raw matches (Brute force):", len(rawMatches))
return rawMatches
# ================================================================== #
# 使用knn检测函数
# ================================================================== #
def matchKeyPointsKNN(featuresA, featuresB, ratio, method):
bf = createMatcher(method, crossCheck=False)
rawMatches = bf.knnMatch(featuresA, featuresB, 2)
# print("Raw matches (knn):", len(rawMatches))
matches = []
for m,n in rawMatches:
if m.distance < n.distance * ratio:
matches.append(m)
# print(f"knn匹配的特征点数量:{len(matches)}")
return matches
# ================================================================== #
#
# ================================================================== #
def createMatcher(method,crossCheck):
"Create and return a Matcher Object"
if method == 'sift' or method == 'surf':
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_L2, crossCheck=crossCheck)
elif method == 'orb' or method == 'brisk':
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=crossCheck)
return bf
# ================================================================== #
# 计算关键点的透视关系
# ================================================================== #
def getHomography(kpsA, kpsB, matches, reprojThresh):
# convert the keypoints to numpy arrays
kpsA = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kpsA])
kpsB = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kpsB])
if len(matches) > 4:
# construct the two sets of points
ptsA = np.float32([kpsA[m.queryIdx] for m in matches])
ptsB = np.float32([kpsB[m.trainIdx] for m in matches])
# estimate the homography between the sets of points
(H, status) = cv2.findHomography(ptsA, ptsB, cv2.RANSAC,
reprojThresh)
return (matches, H, status)
else:
return None
# ================================================================== #
# 去除图像黑边
# ================================================================== #
def cutBlack(pic):
rows, cols = np.where(pic[:,:,0] !=0)
min_row, max_row = min(rows), max(rows) +1
min_col, max_col = min(cols), max(cols) +1
return pic[min_row:max_row,min_col:max_col,:]
# ================================================================== #
# 调换
# ================================================================== #
def swap(a, b):
return b,a
# ================================================================== #
# 主要的函数
# 合并两张图(合并多张图基于此函数)
# ================================================================== #
def handle(path1, path2, isShow = False):
"""
定义超参数
"""
feature_extractor = 'sift'
feature_matching = 'knn'
"""
读取原始图像
"""
if isinstance(path2,str):
imageA = cv2.imread(path2)
imageA = cv2.cvtColor(imageA,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
else:
imageA = path2
imageA_gray = cv2.cvtColor(imageA, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
if isinstance(path1,str):
imageB = cv2.imread(path1)
imageB = cv2.cvtColor(imageB,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
else:
imageB = path1
t = np.size(imageB)
imageB_gray = cv2.cvtColor(imageB, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
"""
显示输入的两张图片
"""
if isShow:
f = plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
f.add_subplot(1,2,1)
plt.title("imageB")
plt.imshow(imageB)
plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
f.add_subplot(1,2,2)
plt.title("imageA")
plt.imshow(imageA)
plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
"""
提取两证图片的特征
"""
kpsA, featuresA = detectAndDescribe(imageA_gray, method=feature_extractor)
kpsB, featuresB = detectAndDescribe(imageB_gray, method=feature_extractor)
"""
显示关键点
"""
if isShow:
fig, (ax1,ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(10,4), constrained_layout=False)
ax1.imshow(cv2.drawKeypoints(imageA_gray,kpsA,None,color=(0,255,0)))
ax1.set_xlabel("(a)key point", fontsize=14)
ax2.imshow(cv2.drawKeypoints(imageB_gray,kpsB,None,color=(0,255,0)))
ax2.set_xlabel("(b)key point", fontsize=14)
"""
进行特征匹配
"""
if feature_matching == 'bf':
matches = matchKeyPointsBF(featuresA, featuresB, method=feature_extractor)
img3 = cv2.drawMatches(imageA,kpsA,imageB,kpsB,matches[:100],
None,flags=cv2.DrawMatchesFlags_NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS)
elif feature_matching == 'knn':
matches = matchKeyPointsKNN(featuresA, featuresB, ratio=0.75, method=feature_extractor)
if len(matches) < 10:
return None
img3 = cv2.drawMatches(imageA,kpsA,imageB,kpsB,np.random.choice(matches,100),
None,flags=cv2.DrawMatchesFlags_NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS)
"""
匹配的特征展示
"""
if isShow:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
plt.imshow(img3)
plt.title("feature match")
plt.axis('off')
"""
计算两张图的透视关系
"""
matchCount = len(matches)
M = getHomography(kpsA, kpsB, matches, reprojThresh=4)
if M is None:
print("Error!")
(matches, H, status) = M
"""
将图片A进行透视变换并检查图片位置
"""
result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageA, H, ((imageA.shape[1] + imageB.shape[1])*2, (imageA.shape[0] + imageB.shape[0]) * 2))
resultAfterCut = cutBlack(result)
# 检查图片位置
if np.size(resultAfterCut) < np.size(imageA) * 0.95:
print("图片位置不对,将自动调换")
# 调换图片
kpsA,kpsB = swap(kpsA, kpsB)
imageA, imageB = swap(imageA, imageB)
if feature_matching == 'bf':
matches = matchKeyPointsBF(featuresB, featuresA, method=feature_extractor)
elif feature_matching == 'knn':
matches = matchKeyPointsKNN(featuresB, featuresA, ratio=0.75, method=feature_extractor)
if len(matches) < 10:
return None
matchCount = len(matches)
M = getHomography(kpsA, kpsB, matches, reprojThresh=4)
if M is None:
print("Error!")
(matches, H, status) = M
result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageA, H, ((imageA.shape[1] + imageB.shape[1])*2, (imageA.shape[0] + imageB.shape[0]) * 2))
"""
合并图片
"""
# cv2.imshow("Perspective transformation", result)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
result[0:imageB.shape[0], 0:imageB.shape[1]] = np.maximum(imageB, result[0:imageB.shape[0], 0:imageB.shape[1]])
result = cutBlack(result)
return result, matchCount
# ================================================================== #
# 合并多张图
# ================================================================== #
def handleMulti(*args, isShow = False):
print(isShow)
l = len(args)
if isShow:
row = math.ceil(l / 3)
f = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))
for i in range(l):
f.add_subplot(row, 3, i + 1)
plt.title(f"image({i+1})")
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(args[i]), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
assert(l > 1)
isHandle = [0 for i in range(l - 1)]
nowPic = args[0]
args = args[1:]
for j in range(l - 1):
isHas = False # 在一轮中是否找到
matchCountList = []
resultList = []
indexList = []
for i in range(l - 1):
if (isHandle[i] == 1):
continue
result, matchCount = handle(nowPic, args[i])
if not result is None:
matchCountList.append(matchCount)
resultList.append(result)
indexList.append(i)
isHas = True
if not isHas: # 一轮找完都没有可以合并的
return None
else:
index = matchCountList.index(max(matchCountList))
nowPic = resultList[index]
isHandle[indexList[index]] = 1
print(f"合并第{indexList[index] + 2}个")
# cv2.imshow("temp", nowPic)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
return nowPic
# ================================================================== #
# 主函数
# ================================================================== #
if __name__ == "__main__":
"""
处理两张图,可以打印特征点与对应关系
"""
result, _ = handle("./input/222.png", "./input/111.png", isShow=True)
if not result is None:
cv2.imshow("result", result[:, :, [2, 1, 0]])
plt.show()
cv2.waitKey(0)
else:
print("没有找到对应特征点,无法合并")
exit()
"""
处理多张图,不可以打印特征点与对应关系
"""
# result = handleMulti(
# "./input/migong (1).png",
# "./input/migong (2).png",
# "./input/migong (3).png",
# isShow=True)
# result = handleMulti("./input/111.png", "./input/222.png","./input/333.png", isShow=True)
# result = handleMulti("./input/foto7A.jpg", "./input/foto7B.jpg") #合并的不好的图
result = handleMulti("./input/intel_lab (1).png",
"./input/intel_lab (2).png",
"./input/intel_lab (3).png",
"./input/intel_lab (4).png",
"./input/intel_lab (5).png",
"./input/intel_lab (6).png",
isShow=True)
if not result is None:
cv2.imshow("result", result[:, :, [2, 1, 0]])
plt.show()
cv2.waitKey(0)
else:
print("没有找到对应特征点,无法合并")