Analysis of commits and issues from Git Repositories using Critical Classes from ATDCodeAnalyzer.
We have been analysed four Git Repositories: Apache Cassandra, Apache ActiveMQ, Apache Kafka and Apache Hadoop. We evaluated 678 issues from Cassandra (226), ActiveMQ (132), Kafka (179) and Hadoop (141) using an inspection aided by the LLM model to classify them as either Yes or No based on their architectural impact.
We selected a representative dataset of Git repositories, encompassing significant source code repositories such as Apache Cassandra, Apache Kafka, Apache Hadoop and Apache ActiveMQ. These repositories exhibit complex software architectures, boasting many attributes, including more than 10000 commits, over 100 collaborators, over 1000 Java files, over 100000 lines of code, and at least ten-year lifetime. Consequently, these repositories are characterized by substantial commit histories, many contributors, intricate codebases, and widespread adoption within the software industry. Each repository's numerical and metric attributes will be comprehensively detailed. We applied the ATDCodeAnalyzer method to the repositories to identify critical files impacted by Architectural Technical Debt.
We examine if these issues indicate architectural problems within the software. These problems encompass: software's structure, organizational issues, quality software, issues that impact evolvability and maintainability. For example: changes to core components,performance improvements, scalability snhancements, concurrency and parallelism, resource management, data model changes, distributed system aspects, consistency and availability, extensibility and plugin frameworks, security and compliance, system modularity, data integrity and durability, etc.
Related to "architectural impact issues" found by issues in commits with critical classes in the selected software repositories:
RQ1) Do architectural impact issues affect a substantial number of LOC changes in commits?
RQ2) Do architectural impact issues affect a substantial amount of modified files in commits?
RQ3) Do architectural impact issues require more time for resolution?
Draft of Cassandra's commit and issue analysis method
-
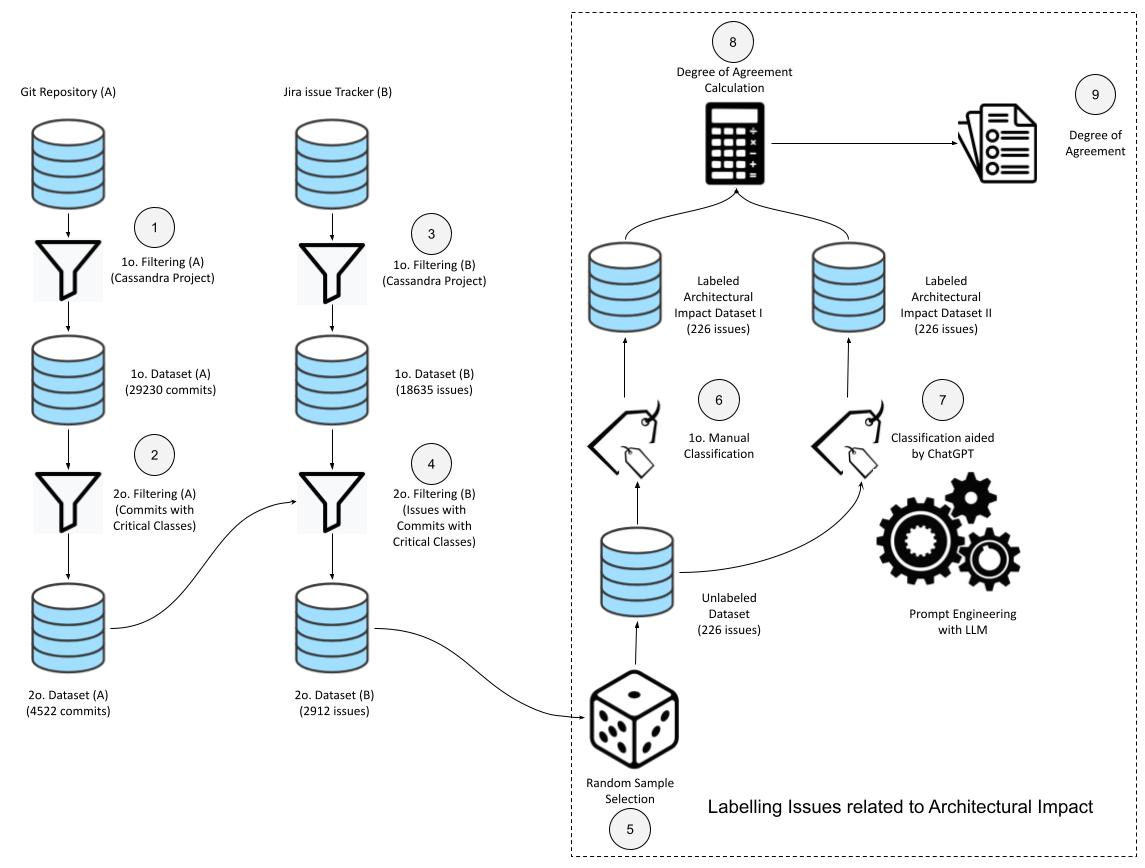
Filtering (A) - Cassandra Project: This step involves selecting and filtering data related to the Apache Cassandra project from the GitHub repository.
-
Filtering (A) - Commits with Critical Classes: After filtering the Cassandra project data, you further narrow down the focus by identifying commits that involve critical classes. Critical classes may be those that are related to architectural or high-impact changes.
-
Filtering (B) - Cassandra Project: In this step, you do a similar filtering process but on the Jira Issue Tracker, specifically looking for issues related to the Cassandra project.
-
Filtering (B) - Issues with Commits with Critical Classes: This step involves identifying Jira issues that are associated with commits containing critical classes. It's a way to link code changes with corresponding issues.
-
Random Sample Selection from 4 that results in 226 issues: Here, you randomly select a subset of the filtered issues. The reason is for further analysis. Based on a normal continuous random variable from ScyPY Based on the parameters: confidence_level = 0.95, margin_of_error = 0.05, population_proportion = 0.8 and population_size = len(issues_with_commits_with_critical_classes) sample_size = calculate_sample_size(confidence_level, margin_of_error, population_proportion, population_size) norm.ppf(): normal continuous random variable
-
Manual classification of issues to check architectural impact: You manually review and classify the selected 226 issues to assess their architectural impact. This could involve identifying whether the issue relates to architectural changes, refactoring, or other factors.
-
Semi-automatic classification aided by ChatGPT with Prompt Engineering: In this step, you use ChatGPT to assist in the classification process. You might provide prompts to ChatGPT to help automate or semi-automate some of the classification tasks. More details in https://github.com/armandossrecife/my_validation3/blob/main/inspection_process.md
-
Degree of Agreement Calculation comparing 6 and 7: This step involves calculating the degree of agreement between the manual classification and the semi-automatic classification performed with the help of ChatGPT. You need to quantify how closely the two methods align.
-
Degree Agreement using Cohen's Kappa: Cohen's Kappa is a statistical measure used to assess the agreement between two raters (in this case, the manual and ChatGPT-assisted classifications). It takes into account the possibility of agreement occurring by chance.
The calculated Cohen's Kappa score was found to be 0.752, indicating a substantial level of agreement between manual inspection and ChatGPT inspection.
In our evaluation of the model used for inspecting issues, we obtained the following key performance metrics: Precision: 0.667, Recall: 1.00, Accuracy: 0.92 and F1-Score: 0.8.
This semi-automatic inspection process (aided by ChatGPT) can help to inspect other issues from other apache projects.
More details and scripts available in https://github.com/armandossrecife/my_validation3/blob/main/my_analysis_cassandra.ipynb
ActiveMQ analysis
More details and scripts available in https://github.com/armandossrecife/my_validation3/blob/main/my_analysis_activemq.ipynb
Kafka analysis
More details and scripts available in https://github.com/armandossrecife/my_validation3/blob/main/my_analysis_kafka.ipynb
Hadoop analysis
More details and scripts available in https://github.com/armandossrecife/my_validation3/blob/main/my_analysis_hadoop.ipynb
The comparison of issues in commits with critical classes among Cassandra, ActiveMQ, Kafka and Hadoop
Conclusions Issues with architectural impact (labeled as "Yes") exhibit the following characteristics:
- They affect a substantial number of files (T1:H0A rejected).
- They involve significant code changes (T2:H0B rejected).
- They require more time for resolution (T3:H0C rejected).
Justification These conclusions are drawn from a comparative analysis of results from the Cassandra, ActiveMQ, and Kafka repositories, specifically:
- A comparison of the results related to the number of lines and files modified in issue commits with architectural impact (labeled as "Yes") and without architectural impact (labeled as "No").
- A comparison of the results concerning the average time required to resolve issues with architectural impact (also labeled as "Yes") and without architectural impact (labeled as "No").
Furthermore, the inspection of issues that appear in commits containing critical files and have an architectural impact underscores the influence of critical classes on software architecture.
Contributions
- We created an LLM model, based on prompt engineering, to help identify issues with architectural impact.
- We provided a dataset (Apache Cassandra, Apache ActiveMQ, Apache Kafka and Apache Hadoop) with detailed information of commits, and issues that have architectural impact
- We provided a dataset (Apache Cassandra, Apache ActiveMQ, Apache Kafka and Apache Hadoop) of text with details about inspections of issues with architectural impact and issues without architectural impact
- We provided a set of scripts that can be performed automatically to analyse the dataset and produce the results of analysis.
More details in
https://github.com/armandossrecife/my_validation3/blob/main/my_comparison.ipynb