The goal of this workshop is to demonstrate how to build and monitor modern applications with AWS Elastic Kubernetes Services (EKS), Amazon CloudWatch Logs and AWS X-Ray.
This workshop consists of 3 labs and will walk through the following:
- Lab 1
- Prepare your environment
- Create an AWS EKS cluster with eksctl
- Deploy eCommerce microservices demo application
- Lab 2
- Deploy a log aggregation stack
- Deploy metrics collection and visualization
- Lab 3
- Deploy AWS X-Ray and enable tracing within the sample applications
Note
This workshops is an advanced workshop (Level 300) and requires a deep understanding of AWS capabilities as well as know-how in software development, containers, and Kubernetes.
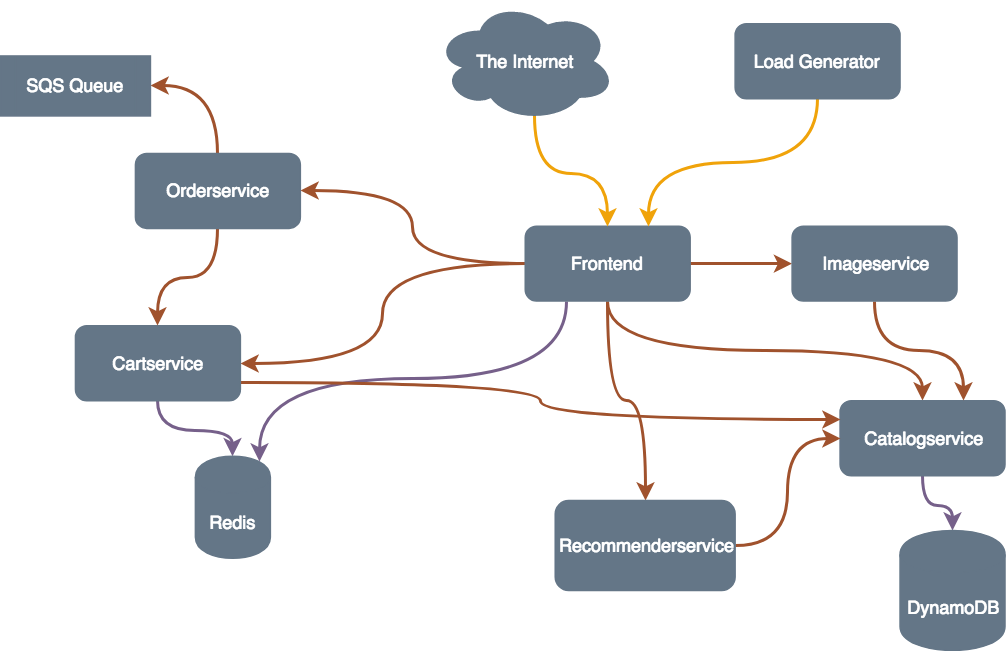
The architecture of the application we will be deploying looks like this:
The services are either build in Node.js and the Express framework or Python with the Flask framework. As data store DynamoDB is used. To store the cart and the session data a self-hosted Redis is used. The orders are put into an SQS queue, where a worker process could pick them up for order-processing.
Deploying microservices on EKS
Make sure the Cloud9 EC2 instances is running. Check that it has a public IP attached, otherwise the Browser-Component will not be able to connect.
If you can not get Cloud9 to work use a regular EC2 Linux instance to run the commands.
Make sure that you did not create the cluster with the AWS account root user. You have to use an IAM user when creating the EKS cluster.
Doublecheck that your kubectl version is at least version 1.10.0, otherwise the integration with the IAM authenticator is not yet available causing authentication to fail.
Make sure that aws-iam-authenticator is installed and executable, so kubectl can call it when authenticating against the EKS cluster.
When creating new services in Kubernetes it may take a while until the Elastic Load Balancer is created and becomes available. Also, propagation within DNS may take some additional time. If you can not access a newly created service please just wait a little while and then reload in your browser.
All load balancers are also visible in the EC2 Console -> Loadbalancers, check here for additional details.
Make sure the X-Ray daemon is running successfully. Check the log output of the daemons to see if the permissions to send traces to AWS X-Ray have been set up correctly.
Creating the EKS cluster and node group should take around 10-15 minutes. If it takes longer eksctl will run into a timeout. Delete the cluster and simply try again.
In AWS accounts that have never created a load balancer before, it’s possible that the service role for ELB might not exist yet.
We can check for the role, and create it if it’s missing.
aws iam get-role --role-name "AWSServiceRoleForElasticLoadBalancing" || aws iam create-service-linked-role --aws-service-name "elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com"When using the latest version of eksctl a StorageClass will be automatically created.
Check if a StorageClass exists for your cluster with the command
kubectl get storageclasses
If you do not have a StorageClass installed the deployment of Prometheus and Grafana will fail.
Execute the command
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
{
"kind": "StorageClass",
"apiVersion": "storage.k8s.io/v1",
"metadata": {
"name": "prometheus",
"namespace": "prometheus"
},
"provisioner": "kubernetes.io/aws-ebs",
"parameters": {
"type": "gp2"
},
"reclaimPolicy": "Retain",
"mountOptions": [
"debug"
]
}
EOFThis will create a StorageClass in your Amazon EKS cluster.
- **04/15/2020 Merge xray branch into master to ease deployment and maintainability.
This sample code is made available under a modified MIT license. See the LICENSE file.