Defining a Team API provides a shared understanding of a team's purpose, responsibilities, and ways of working. It serves as a "contract" between the team and the broader organisation, enabling seamless collaboration, reducing misunderstandings, and aligning efforts effectively.
This repository offers a framework for creating your team's Team API and guidance on embedding it into everyday operations.
A Team API is a document that acts as the "interface" for your team, similar to how a software API specifies how systems interact. It explicitly defines:
- Mission: Why the team exists and the value it brings.
- Capabilities: What the team delivers and how it contributes to organisational goals.
- Interfaces: How others can interact with the team and what they can expect.
- Expectations: Dependencies and support needed from others to operate effectively.
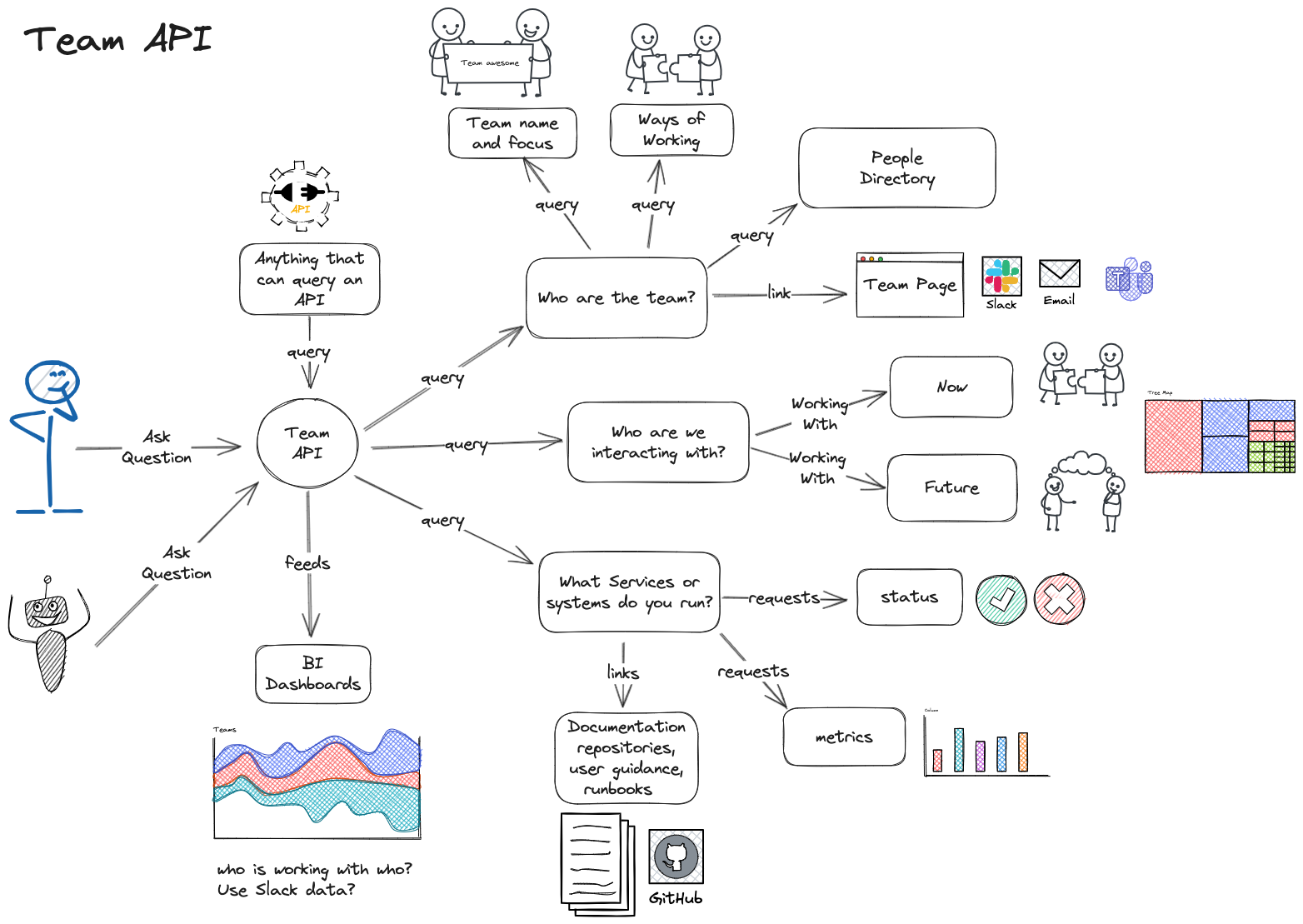
Below is a diagram illustrating the key components of a Team API:
This visual representation highlights the flow of communication, collaboration, and dependencies within a Team API. It reinforces the concept of a structured interface between the team and its stakeholders.
Check out a live example of a Team API:
👉 Team API Example Site
This site uses Swagger to present a Team API in a structured and interactive format. It is deployed as a static site, powered by GitHub Actions, making it easy to automate updates and ensure the documentation stays current.
- Interactive Format: Swagger provides a dynamic and user-friendly interface for exploring the Team API.
- Version Control: Hosted on GitHub, ensuring all changes are tracked and managed collaboratively.
- Automation: Utilises GitHub Actions to build and deploy the site automatically, ensuring minimal manual overhead.
- Swagger Specification: The Team API is defined using an OpenAPI-compliant Swagger spec.
- GitHub Actions Workflow:
- Automatically triggers builds when changes are committed to the repository.
- Deploys the static site to GitHub Pages, making it accessible to everyone in the organisation.
- Static Site Hosting: The site is hosted on GitHub Pages for fast, reliable access.
- 📢 Clear Communication: Articulates your team's role and responsibilities for internal and external audiences.
- 📏 Defined Boundaries: Prevents scope creep by outlining what the team is (and isn’t) responsible for.
- 🚀 Onboarding Made Easy: Accelerates new members’ understanding of the team's purpose and ways of working.
- 🤝 Collaboration Simplified: Reduces friction by setting clear expectations for interactions.
- 📈 Alignment & Accountability: Ensures the team’s goals align with organisational priorities.
Use the following structure to define your team’s API:
- Purpose: What does your team do, and why does it exist?
- Example: "We ensure the reliability and scalability of our customer-facing platforms to deliver exceptional user experiences."
- Outcomes: What value does the team provide to the organisation?
- Example: "Minimising downtime and optimising system performance, supporting the company’s growth objectives."
- Core Deliverables: The key services, products, or expertise your team provides.
- Example: "Automated CI/CD pipelines, platform observability tools, and system performance optimisation."
- Unique Expertise: What sets your team apart?
- Example: "Deep knowledge in distributed systems and Kubernetes scalability."
- Communication Channels: Preferred methods for interacting with the team.
- Example: "Use Slack for quick queries (#team-platform) and GitHub for feature requests."
- Collaboration Processes: How others can engage with your team.
- Example: "Submit a support request via our Jira board with detailed requirements."
- Dependencies: Teams, systems, or tools your team relies on.
- Example: "We depend on the IT Ops team for network configurations and the Product team for prioritisation guidance."
- Support Needed: Resources or inputs required to succeed.
- Example: "Timely approval of infrastructure changes and clear project specifications."
- Commitments: Any service level agreements (SLAs) or mutual expectations.
- Example: "We commit to resolving high-priority incidents within 2 hours if provided with all necessary details."
- Measuring Success: KPIs, OKRs, or other metrics.
- Example: "99.95% uptime for core systems and deployment pipeline success rates >95%."
- Feedback Mechanisms: Channels for collecting and acting on feedback.
- Example: "Quarterly stakeholder surveys and a dedicated retrospective for major collaborations."
To ensure your Team API remains a living, practical tool:
- 📖 Make it Visible: Publish your Team API in a centralised location (e.g., Confluence, GitHub, or your team wiki).
- ♻️ Regularly Update: Revisit and refine the API during quarterly reviews or after significant team changes.
- 👩💻 Use in Planning: Refer to the API during sprint planning, retrospectives, and cross-team collaborations.
- 🤝 Build Feedback Loops: Actively seek and incorporate feedback from stakeholders and team members.
- 📚 Incorporate into Onboarding: Use the API as a key resource when onboarding new team members or collaborating teams.
This framework is inspired by the Team API Template by Team Topologies. Explore their work to learn more about team dynamics and modern organisational design.
For a live example of a Swagger-based Team API site, visit 👉 https://bagg3rs.github.io/team-api/.
By defining and maintaining a robust Team API, you can transform how your team operates and collaborates across the organisation. 🚀