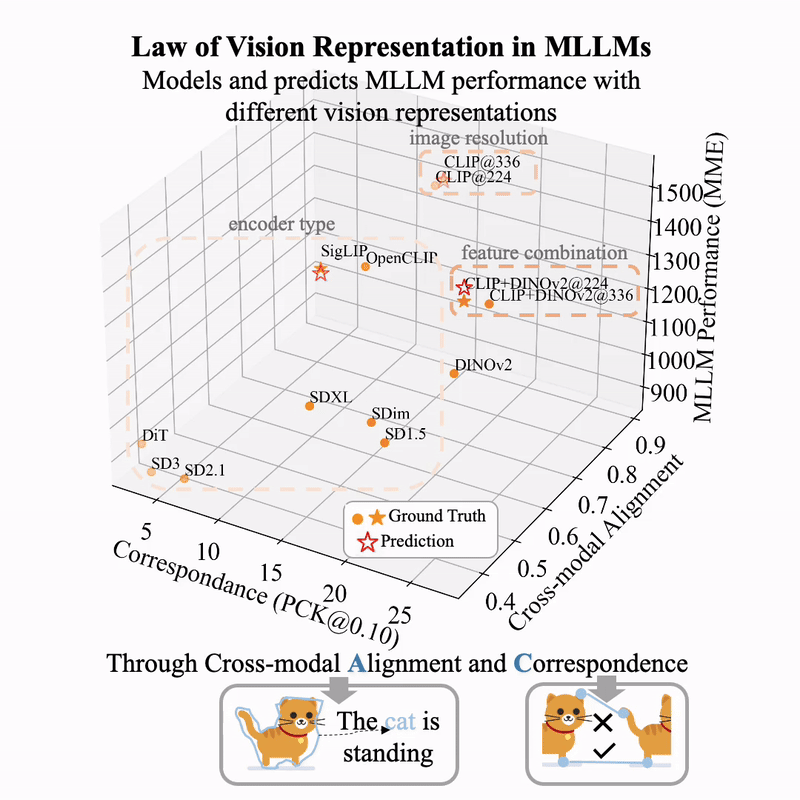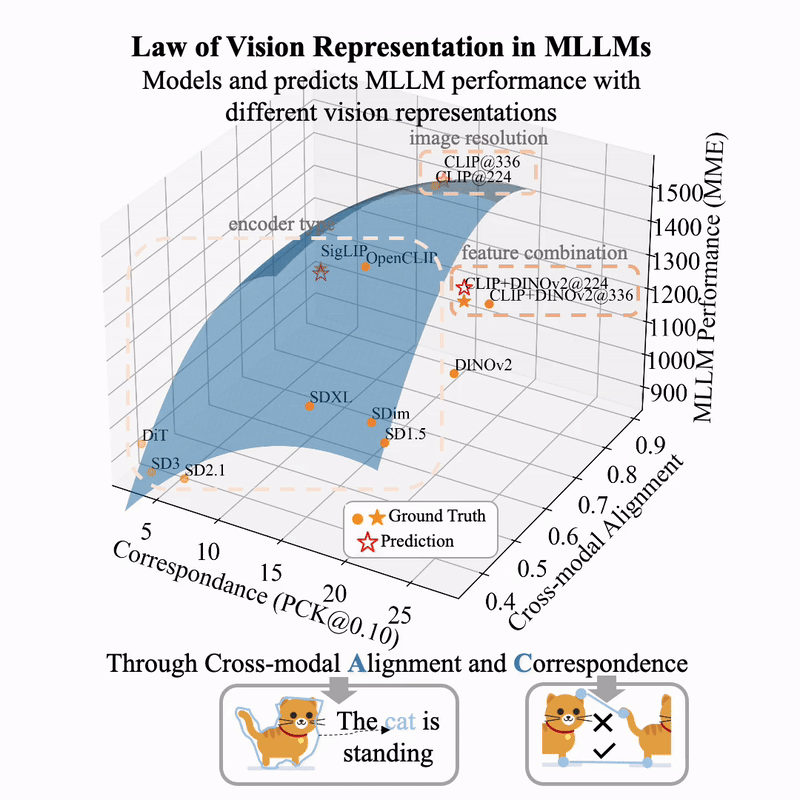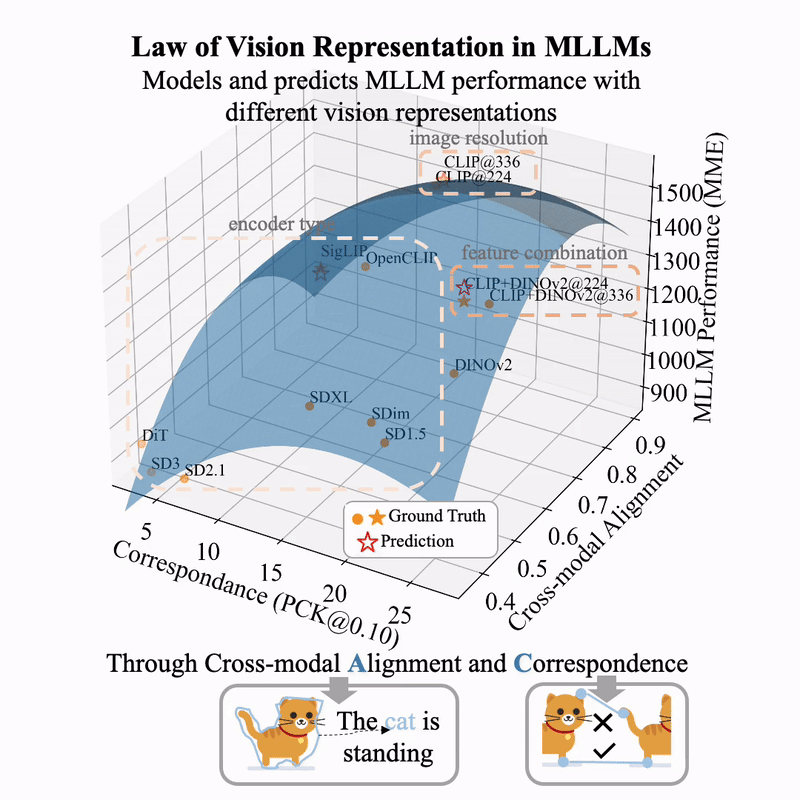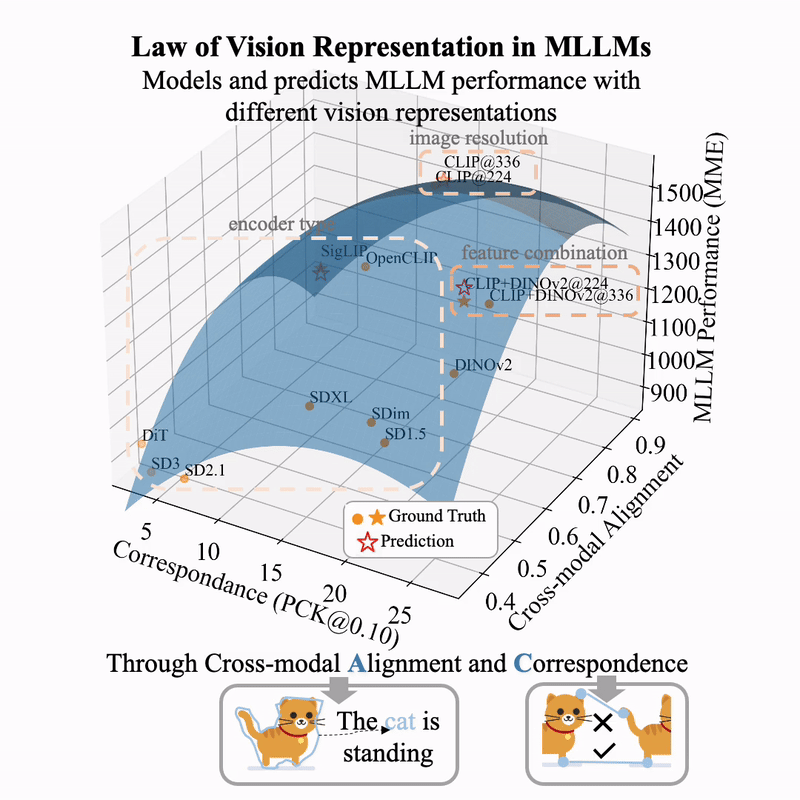
arXiv / HuggingFace / More Thoughts (Blog in English) / More Thoughts (Blog in Chinese)
- [TODO] Hard working on cleaning the code...but the messy version is here. Please stay tuned and star our repo! 😝
- [2024/09/01] We released the checkpoints of MLLMs on 13 vision representations.
- [2024/08/29] We introduce the Law of Vision Representation in MLLMs and AC Policy.
- Clone This Repository
- Train LLaVA with Custom Vision Representation
- Pretrained Weights
- Evaluations
- AC Compute
- AC Policy
- Note
- Citation
- Acknowledgement
git clone https://github.com/bronyayang/Law_of_Vision_Representation_in_MLLMs.git
cd Law_of_Vision_Representation_in_MLLMs1. Install the LLaVA Environment: Ensure that the environment is compatible with your custom vision module
conda create -n ac_llava python=3.10 -y
conda activate ac_llava
pip install --upgrade pip
bash run.shThis training environment has been tested on CUDA 12.2 and is compatible with all the encoders mentioned in the paper, except for OpenCLIP (refer to environment record for details on OpenCLIP compatibility).
To run SD3 vision representation, you'll need to install the diffusers package from the repository. Follow these steps:
cd diffusers
pip install -e .To accommodate diffusion model encoders, this environment includes the diffusers, xformers, and transformers packages. However, these packages may conflict with each other. It is strongly advised to modify pyproject.toml and install only the packages required for your custom vision encoder, rather than all 10 encoders simultaneously.
Prepare LLaVA Stage 1 Data: Follow the instructions in LLaVA's tutorial to prepare the data for Stage 1 training.
Start Training: Use the following command to start training:
bash llava/scripts/v1_5/train/pretrain.shHowever, before running the command, ensure that you modify the following parameters in the script:
--data_path--image_folder--output_dir--vision_tower
Available Vision Towers:
openai/clip-vit-large-patch14openai/clip-vit-large-patch14-336laion/CLIP-ViT-L-14-laion2B-s32B-b82Kgoogle/siglip-base-patch16-224facebook/dinov2-largerunwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1lambdalabs/sd-image-variations-diffusersstabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0facebook/DiT-XL-2-512stabilityai/stable-diffusion-3-medium-diffusers
Note: To combine features from multiple vision towers, use a dot . between the names. For example: openai/clip-vit-large-patch14.facebook/dinov2-large
Prepare LLaVA Stage 2 Data: Follow the instructions in LLaVA's tutorial to prepare the data for Stage 2 training.
Start Training: Use the following command to start training:
bash llava/scripts/v1_5/train/finetune.shHowever, before running the command, ensure that you modify the following parameters in the script:
--data_path--image_folder--output_dir--vision_tower--pretrain_mm_mlp_adapter(checkpoint from Stage 1)
If you prefer to use the same vision representations that we tested in our paper, we have released pretrained weights in Hugging Face for your convenience. This allows you to bypass the steps mentioned above and proceed directly to the next sections.
We use lmms-eval to evaluate the benchmark performance for MLLMs on various vision representations and to extract features from benchmark images for calculating the A score.
cd llava/eval/lmms-eval
pip install -e .To evaluate the model, use the following command:
accelerate launch --num_processes=8 -m lmms_eval --model llava --model_args pretrained="path-to-stage-2-checkpoint" --tasks task1 --batch_size 1 --log_samples --log_samples_suffix llava_custom_task1 --output_path ./logs/For more information, refer to the original lmms-eval repository or the README in this repository.
Our A score calculation requires visual embeddings extracted from benchmark data. This process also requires the stage 1 checkpoint to be loaded. The following method is suggested as a starting point and is not intended to encourage hardcoding:
1. Set the Random Seed: Uncomment the code in lmms-eval/lmms_eval/models /llava.py, lines 38-51
2. Enable Stage 1 Loading: Uncomment lines 105 and lines 111 in lmms-eval/lmms_eval/models/llava.py.
3. Save the Visual Embeddings: Uncomment lines 476 in llava/model/llava_arch.py.
- Saving Path Format: The path format for saving embeddings should be
/any/path/benchmark/vision_rep. For example,/Law_of_Vision_Representation_in_MLLMs/mmbench/clip336. - Shape: The shape of the saved embeddings should be
[sequence_len, hidden_dim].
4. Run the Eval Command:
Once everything is set up, run the evaluation command:
accelerate launch --num_processes=8 -m lmms_eval --model llava --model_args pretrained="path-to-stage-1-checkpoint" --tasks task1 --batch_size 1 --log_samples --log_samples_suffix llava_custom_task1 --output_path ./logs/To extract different vision representations across various benchmarks, refer to this script.
The environment setup is adapted from Telling Left from Right. If you encounter any issues, refer to the original repository and their issue tracker.
conda create -n ac_score python=3.9
conda activate ac_score
conda install pytorch=1.13.1 torchvision=0.14.1 pytorch-cuda=11.6 -c pytorch -c nvidia
conda install -c "nvidia/label/cuda-11.6.1" libcusolver-dev
cd C_score
pip install -e .Prepare Vision Embeddings: Ensure that you have the vision embeddings for CLIP@224, CLIP@336, and your target vision embeddings stored in the path /any/path/benchmark. You can find more details on how to extract these embeddings here.
Change Base Folder and Target Vision Representation Settings: Modify the base_folder variable on line 7 in A_score/compute.py to point to the folder where you saved the vision embeddings. Also, update the subfolders variable to reflect the subfolder names that correspond to the vision representations for which you want to compute the A score.
Run the A Score Computation:
cd A_score
python3 compute.pyThe A score will be printed to the console. Optionally, you can save the output to a CSV file for use in the AC policy section.
Prepare Vision Features on SPair-71k: First, download the SPair-71k dataset:
cd C_score
bash data/prepare_spair.shNext, modify the input_path and output_path variables starting at line 16 in C_score/extract_feature.py.
input_path: Set this to the location where you downloaded the SPair-71k dataset, typically./data/SPair-71k/JPEGImages.output_path: Set this to./data/SPair-71k/features, aspck_train.pyexpects features to be in a fixed path.
Additionally, modify the feature variable at line 23 to specify the vision representation you want to extract.
Run the following command to extract the features:
python extract_feature.pyRun the C Score Computation: Once the features are extracted, you can compute the C score with the following command:
python pck_train.py --config configs/eval_zero_shot_spair.yamlThe results will be logged.
If you wish to run feature combination, use the pck_train_two.py script and the configs/eval_zero_shot_spair_two.yaml configuration file, which concatenates features along the channel dimension.
Under Reconstruction...
I aim to provide and maintain this repository in an easy-to-use form for everyone. However, please note that I am the sole maintainer of this codebase and have limited bandwidth. Before the process of cleaning up the code, I lost access to compute clusters and GPUs, which means some parts of the tutorial, such as environment setup and feature extraction, may be hardcoded or less than ideal, and the overall structure could be improved.
Make sure to reproduce the AC score in Appendix before you compute your own, and reflect any issue in GitHub. I would greatly appreciate any pull requests (PRs) to help enhance this repository. Your contributions are highly valued! Many thanks!
If you find this project useful, please cite our work:
@article{yang2024law,
title={Law of Vision Representation in MLLMs},
author={Yang, Shijia and Zhai, Bohan and You, Quanzeng and Yuan, Jianbo and Yang, Hongxia and Xu, Chenfeng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.16357},
year={2024}
}
- LLaVA is the codebase we built upon, allowing us to easily add custom vision representations.
- lmms-eval is an easy-to-use evaluation tool that enabled us to evaluate numerous benchmarks and extract features efficiently.
- Telling Left from Right provides the correspondence computation on the SPair-71k dataset.