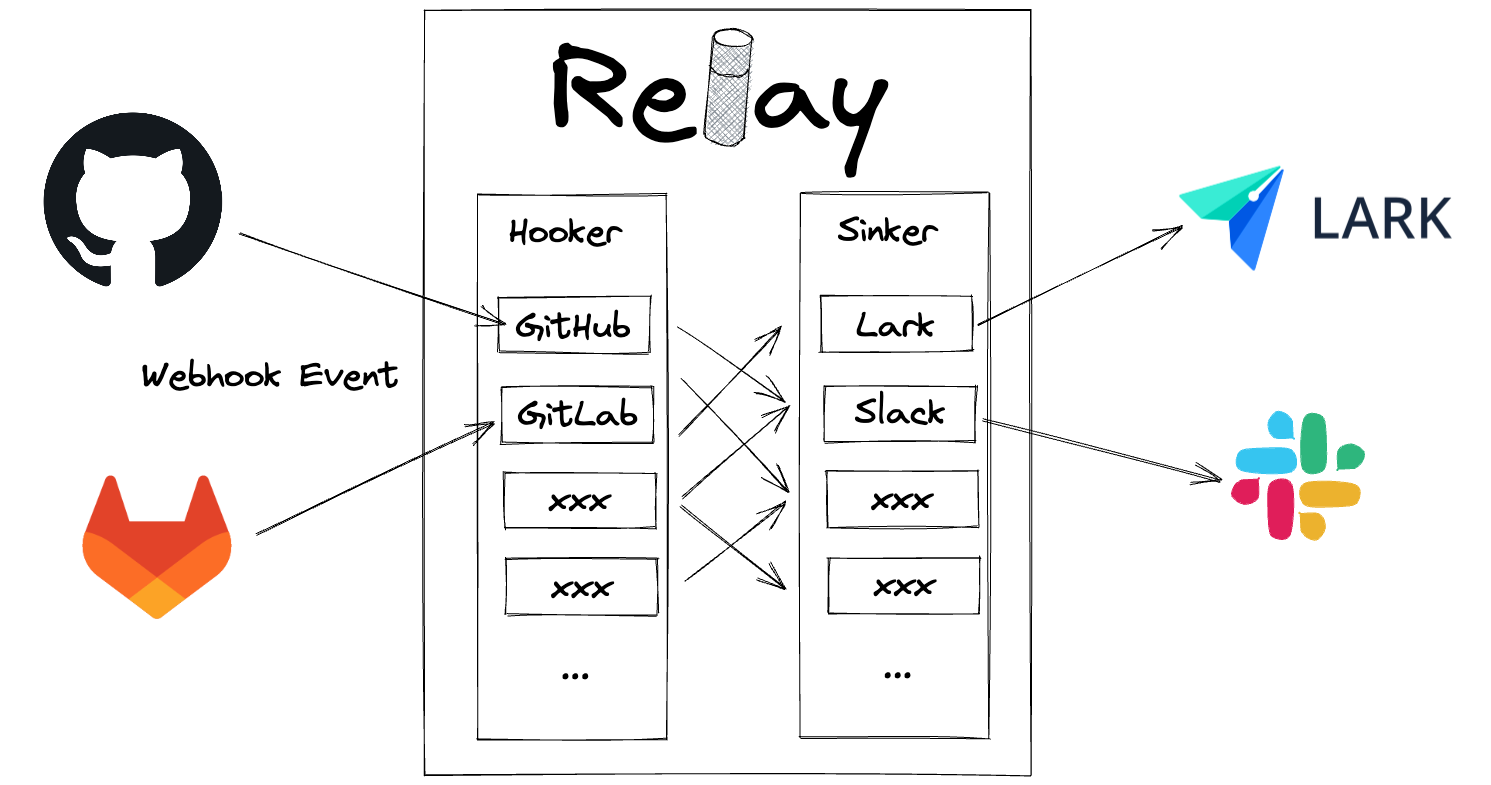
Relay is a web server for forwarding events from service A to service B. While forwarding the event, it allows injecting arbitrary logic for processing the event such as filtering and augmenting.
You may think Relay as a very very simplified version of self hosted Zapier.
Relay Contains 2 components, Hooker and Sinker.
Hooker - Receive the webhook event from upstream services such as GitHub, GitLab, do some processing, and pass the processed payload to Sinker.
Sinker - Receive the payload from Hooker, do some processing, and send the event to downstream services such as Slack, Lark.
To relay an event from Service A to Service B, you would
- Implement a Hooker to receive event from service A.
- Implement a Sinker to process payload from that Hooker and send the processed message to Service B.
- Register the Hooker to listen to event from service A and register the Sinker with the Hooker.
The address where Relay runs. Default localhost:5678.
When configuring GitHub Webhook, make sure to set the webhook content type as application/json.
The prefix for the GitHub ref. GitHub Webhook iteself doesn't allow to specify a particular branch or branch filter. You can use --github-ref-prefix to only observe the events from the interested branch(es).
Currently we only support monitor one branch in one repository.
Target repository. Will ignore the webhook message if the repository mismatched.
Target branch in the repository. Will ignore the webhook message if the branch mismatched.
The Gerrit service URL. We need to call the Gerrit service to list files in the change, and get the file content in the change.
The Gerrit account name.
The Gerrit account password.
A comma-separated list of Lark message group webhook URLs.
The Bytebase sinker will receive messages from the Gerrit hook, then create the issue for the SQL change.
The Bytebase service URL. You can use the external URL in production. Check the docs about external URL: https://www.bytebase.com/docs/get-started/install/external-url
The Bytebase service account. Used to call the Bytebase OpenAPI.
The Bytebase service key. Used to call the Bytebase OpenAPI.
$ go run main.go --github-ref-prefix="refs/heads/release/" --lark-urls="https://open.feishu.cn/open-apis/bot/v2/hook/foo" --gerrit-account="<gerrit-account>" --gerrit-password="<gerrit-password>" --gerrit-repository="<gerrit-repository>" --gerrit-branch="<gerrit-branch>" --bytebase-url="https://bytebase.example.com" --bytebase-service-account="<bytebase-service-account>" --bytebase-service-key="<bytebase-service-key>"
# --lark-url can also be a comma separated list
$ go run main.go --github-ref-prefix="refs/heads/release/" --lark-urls="https://open.feishu.cn/open-apis/bot/v2/hook/foo,https://open.feishu.cn/open-apis/bot/v2/hook/bar" --gerrit-account="<gerrit-account>" --gerrit-password="<gerrit-password>" --gerrit-repository="<gerrit-repository>" --gerrit-branch="<gerrit-branch>" --bytebase-url="https://bytebase.example.com" --bytebase-service-account="<bytebase-service-account>" --bytebase-service-key="<bytebase-service-key>"
# Runs on localhost:8080
$ go run main.go --address=localhost:8080 --github-ref-prefix="refs/heads/release/" --lark-urls="https://open.feishu.cn/open-apis/bot/v2/hook/foo" --gerrit-account="<gerrit-account>" --gerrit-password="<gerrit-password>" --gerrit-repository="<gerrit-repository>" --gerrit-branch="<gerrit-branch>" --bytebase-url="https://bytebase.example.com" --bytebase-service-account="<bytebase-service-account>" --bytebase-service-key="<bytebase-service-key>"