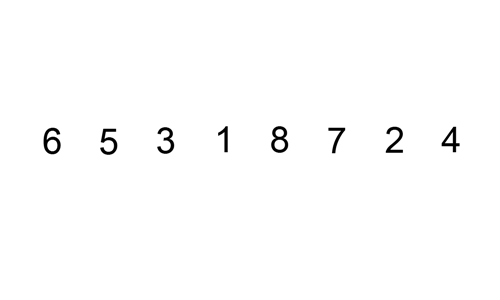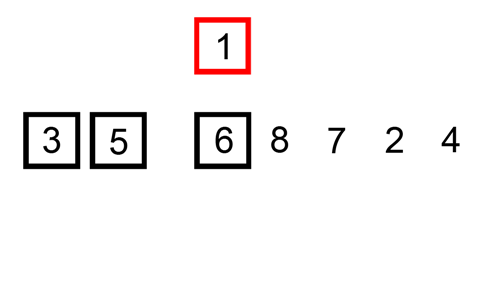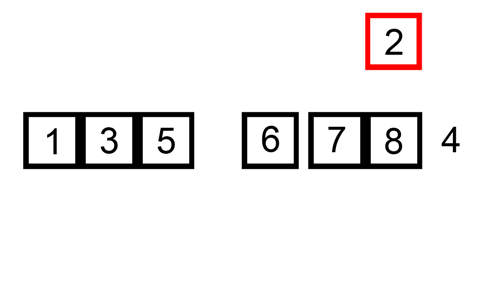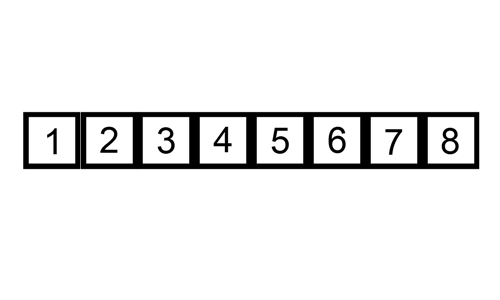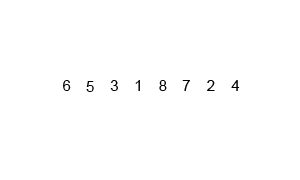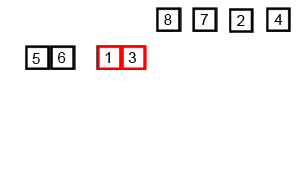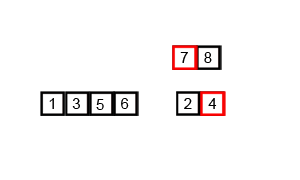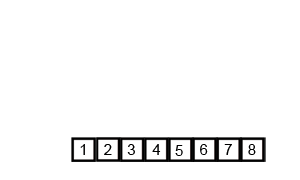In computer science, a sorting algorithm is an algorithm that puts elements of a list into an order. The most frequently used orders are numerical order and lexicographical order, and either ascending or descending.
Internal sorting means that all the data that is to be sorted is stored in memory while sorting is in progress.
External sorting means that the data is stored outside memory (like on disk) and only loaded into memory in small chunks. External sorting is usually applied in cases when data can’t fit into memory entirely, effectively allowing to sort data that does not fit in the memory.
A sorting algorithm is said to be stable if two objects with equal keys appear in the same order in the sorted output as they appear in the unsorted input.
A sorting algorithm is said to be unstable if there are two or more objects with equal keys which don’t appear in same order before and after sorting.
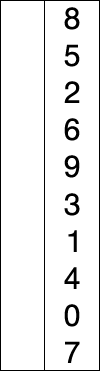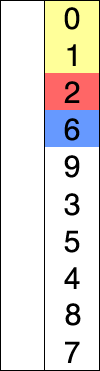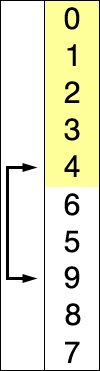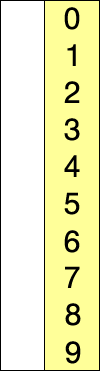
Quick Sort is an efficient divide-and-conquer algorithm. It divides a large list into two smaller sub-lists based on a pivot chosen, into smaller and larger elements. Quick Sort then recursively does this to the sub-lists finally producing a sorted list.
See more: Quicksort - Wikipedia
In insertion sort, every iteration moves an element from unsorted portion to sorted portion until all the elements are sorted in the list. An analogy of insertion sort is the sorting of a deck of cards with our hands. We select one card from the unsorted deck and put it in the right order in our hands, effectively sorting the whole deck.
See more: Insertion sort - Wikipedia
Selection sort is generally used for sorting files with very large records and small keys. It selects the smallest (or largest) element in the array and then removes it to place in a new list. Doing this multiple times would yield the sorted array.
See more: Selection sort - Wikipedia
Bubble Sort is the simplest sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in wrong order. The pass through the list is repeated until the list is sorted.
See more: Bubble sort - Wikipedia
Merge sort is a very efficient comparison-based sorting algorithm. It is a divide-and-conquer algorithm, which works by repeatedly dividing the array in small parts and merging them again in the sorted order.
See more: Merge sort - Wikipedia