/ˈəːvr(ə)/
Pronounced as: uh·vruh | noun: oeuvre; plural noun: oeuvres
Meaning: The body of work of a painter, composer, or author. A work of art, music, or literature.
This project is in design and analysis phase. Please feel free to go through the code and documentation and if you have any Questions or Suggestions, you can use the Issues tab.
The Documentation is in progress. The author is working in write-now-and-edit-later mode, therefore please expect grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and typos. In case of any factual errors, please report them using the Issues section.
Programmers who can contribute to the project.
TOC is Incomplete - Plesase scroll down for more topics
3. Stratergy and Technology Must Go Hand-In-Hand
5. A Need for a Project Like Oeuvre
6. How Real World Evolution Works
7. Lessons Worth Learning From Real World Evolution
8. How To Make Principles Of Evolution Work for Architecture
10. Dangers of Overuse of Concepts
11. Reasons for Selection of Domain Driven Design Architecture
12. The Hexagonal Architecture
Oeuvre is not a demonstration, it is Software Evolution in motion.
Oeuvre is a social article publishing portal that enables users to write and publish and share their articles. At some level Oeuvre is an Experimental Test-Bed for Evolutionary Architecture. This project will show how quickly and efficiently DDD aligns to the changes in business.
The technology stack used is .Net, but the concept can be applied to all the programming language that supports OOPS.
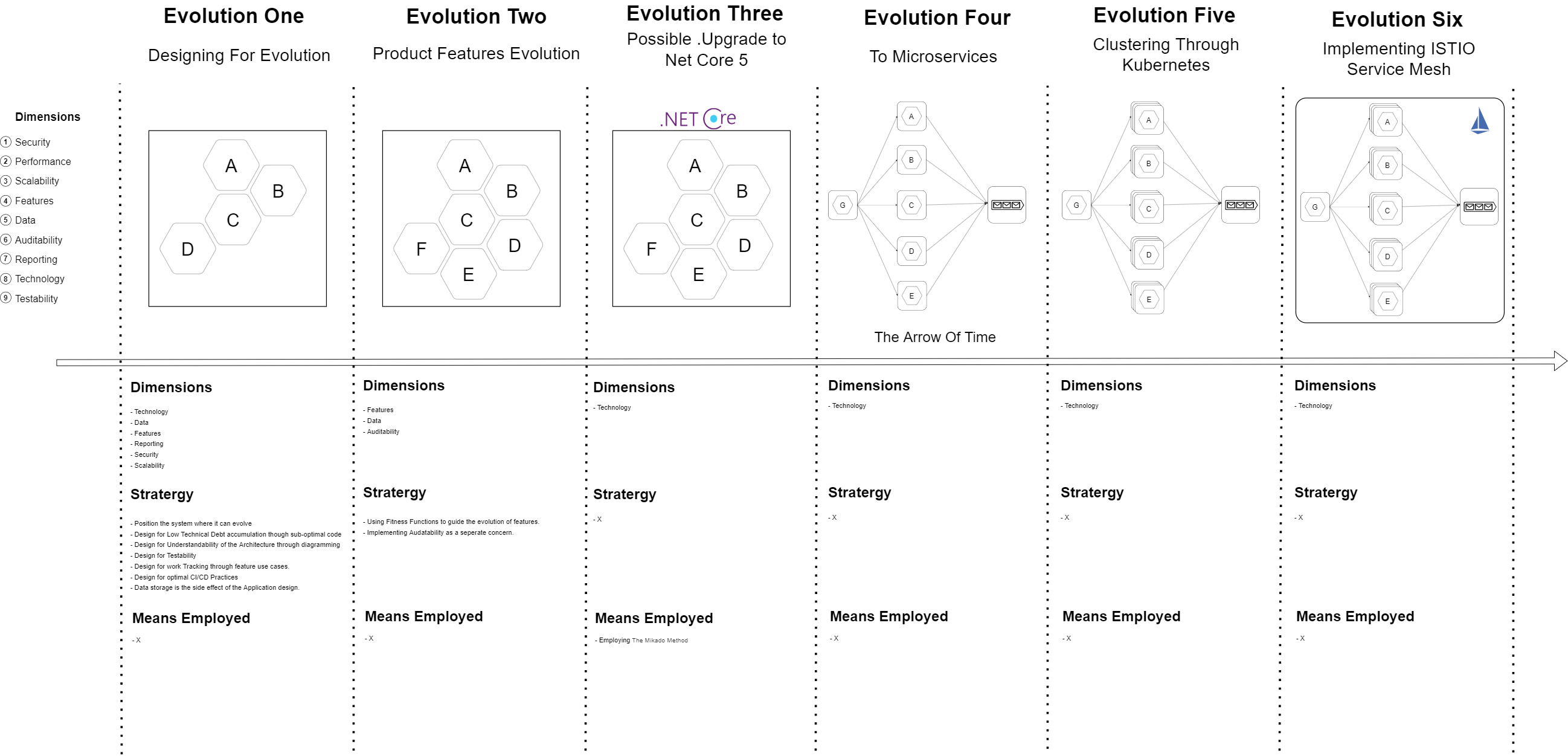
1. Dividing the application into most conducive Architectural Quanta
The Architectural Quantas that we will be employing are discussed the section Evolution In Action.
2. Restricting the Business Logic at the Core
We will be employing design philosophies like Hexagonal - Prots and Adapters in combination with Domain Driven Design to make Business Logic the core of the Architecture from where everything else originates.
3. Modularity through Application Boundaries
The application will be designed using the modular monolith approach and each module will be isolated from each other and allowed to exchange information through integration services and in-memory messaging. This approach will help the application to evolve later to Microservices.
4. Modularity at the Database Level
Even though the application will use the same database, the tables of each modules will be isolated. This will help the application to scale to the microservices level.
5. Diagramming the Application
The section No Silver Bullet explains why diagrams give a sense of orientation to the design and is needed for software because is abstract and does not by nature have a geometry.
Oeuvre will be guided by duagrams from the very begining and evolutionary stratergies will be deviced first at the digrammatic level.
The process flow of the application will be discovered and guided by Event Storming
6. Well defined use cases as the Unit of Feature Evolution
The feature evoltion of Oeuvre will be guided by BDD and the use cases defined by gherkin will reflect in the tests at various levels.
7. Evolution will be guided by Fitness Function
The section How To Make Principles Of Evolution Work for Architecture explains the usefulness of Fitness functions for guiding through incremental evolution. The Guided Evolution describes the stratergy for applying fitness functions at right places in the architecture.
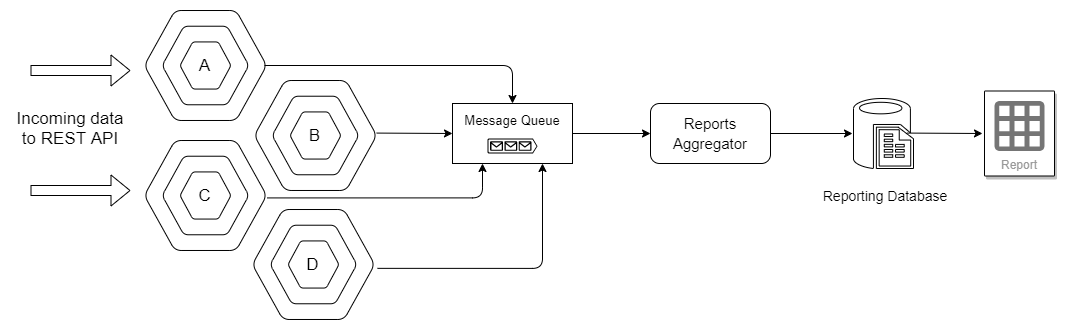
8. Communication through Messaging
The The Reactive Manifesto encourages the systems to communicate through messaging. Even though our modules are in close promixity to each other, we wouldbe using messaging to pass messages and receive messages between them. Messages will also be used to create reports and audit trail.
Using messages will make it easier to later separate these modules when the application evolves to microservices. The in-memory message bus will be replaced my a message queue.
9. Continuous Monitoring
According to The 12 Factor Apps the logs generated by the App can be routed to a file, and also streamed to an analysis system so that it provides the following benifits:
- Introspecting an app’s behavior over time.
- Finding specific events in the past.
- Large-scale graphing of trends (such as requests per minute).
- Active alerting according to user-defined heuristics (such as an alert when the quantity of errors per minute exceeds a certain threshold).
Each module will log errors to its own file. Which analysis engine to be used will be decided later. (Probably - ELK in combination with Spark)
Software does not exist in isolation. It is built to solve a acclerate proccessess or solve problem in the market. Business Stratergy must gives direction to technology. If technology is the muscle, stratergy is the mind.
Business itself exists in the market to server a purpose. It has has its stratergies for growth, and many times does its course corrections. The IT stratergy must align itself to the Business stratergy to provide the business its maneuverability. In the end the Technology must be aligned what the business needs and grow with it hand in hand. If they are not tuned to each other then an imbalance is likely to occur.
There is no exact science to drive the technology with the Business Stratergy. It mostly depends on the current position of the business and the Architects knowledge and skill. For instance, an extablished company just wanting to digitize their services might need a different stratergy than a stratup launching a product. A manufacturing company wanting to upgrade their legacy system to cloud might need a different stratergy than a a company wanting their products to be opened to a different market with different laws.
Technology can be the core of the business but it must be driven by Business.
Business Stratergy for Oeuvre
For Oeuvre we assume that it's being launched by a startup which is optimistic about its growth, and at the same time wants to experiment with its product in the market and needs the application to adjut to changes in short amount of time. At the same time the company wants to keep upgrading to latest technologies as better technologies come to the market.
When the load increases on the application down the line, the company wants the product to evolve without the need for re-enginering.
SetUp instructions for this project can be found here.
It is a well known fact, often inconvenient, that in the long run the many of the projects become unmaintainable. New requirements come in, new capabilities are demanded due to changes in the market, the technology landscape becomes better, and the softwares is expected to accommodate these things without software rewrites.
Oeuvre is a quest to find answers to whether the software can be constructed in such a way that it evolves with new requirements over time.
There is no intentional design in the real world evolution. Organized compexities are built out of primeval simplicity. Structure and the functions of system emerge bit by bit without resort to a goal of any kind. The process is mindless.
In this playground of evolution, the force that induces the design is our environment. The species design themselves through random mutations to increase their chances for survival. Random mutations that favor the survival of species in that environment get propogated to the next generation, continuouing the same process again.
Environmental changes also affect.
The change happens at a single level, that is the genetic level and then manifests itself into the physical features of the species. The Genetic Code determines the external features of the species.
It is through these trial and errors, eligant designs emerge.
“A complex system that works is invariably found to have evolved from a simple system that worked. The inverse proposition also appears to be true: A complex system designed from scratch never works and cannot be made to work. You have to start over, beginning with a working simple system.” ~Galls Law
1. Iteration cannot be avoided to arrive at the design
It's difficult to to arrive at a optimal design without indulging in a bit or trial on error. It's cheaper to do trial and errors on the drawing board first before inplementing them. Afer implementing, some more iterations might be required.
2. Business logic is the genetic code and should be at the core
The business logic must influence the design. It must be at a single place so that it can be comprehended as a whole and in a logical manner. The change must happen at one fundemental level and then transform the outer layers. There needs to be a Unit of Evolution and the business logic is a good Unit.
3. Requirements are the environment that influences the design
Design depends on and is guided by the environment, hence there is a very close link between the design and the requirement. The business logic must change to meet the requirements. Environmental changes influnce design.
4. Persistance Design is Not the Unit of Application Design
Real world entities do not have a persistance database. In the real world the Entity itself is information, hence database design should be a side effect of the application design.
Software entities require a persistance mechanism because there is a need for them to be reconstuted at system reboot. Real world entities cannot be rebooted or switched off. They themselves are persistence.
5. Single Responsibility is the Universal Rule
Evolution has created system with system within systems, with one fundemental property - each system or the unit of the system does one thing and one thing perfectly. This allows the parts of the system evolve independently.
6. Evolution has a trejectory
The next stages of design will depend upon the current stage of the design.
7. Paradoxical nature of designs cannot be avoided
There will always be times when you get one part of the design right, the other part somehow does not fit. Sometimes compromises have to be made till the designs are perfected over time.
8. Framework and Application structure must allow for experimentation
As menitoned, design is an iterative process, a rigid application structure will not allow for rearranging and experementation. This will hurt the evolution of the Architecture.
9. Incremental Design is the way
Successful designs evolve from designs that were already successfully working. It becomes an imperative that you must get the design right before the next step of the evolution.
10. Designs tend towards perfection but can still not be perfect
Design is something that is always happening, therefore the attitude of perfectionism must be avoided, at the same time the process of evolution must continue.
11. The relation between the environment and the species is causal
Environment influences the species and sometimes the Species incluences the environment it lives in.
"Even in the world of make-believe there have to be rules. The parts have to be consistent and belong together." ~ Daniel Keyes, Flowers for Algernon
"Don’t build architecture for the sake of architecture—you are trying to solve a problem." ~ Building Evolutionary Architectures, Neal Ford, Rebecca Parsons, Patrick Kua
Design should be guided by the requirement. Key to a good architecture is getting requirements right. Requirement is where everything starts from. Requirement is the unit of change of architecture.
Requirements will influence all dimentions of the architecture. Requirements are the environment in which the Architecture should thrive. When the requirement changes, the Architecture must evolve to catchup with the change.
Architect's ability for creating a design depends on his ability to analyze the business requirement and understanding the business domain. Architects have to balance the business and the technical concerns.
If the requirement instead of religning the architecture is seen as changing a few lines of code in the layers, then probably the architecture is built around technical concerns and layers.
Software must be modelled around business and domain knowledge, and not technology or layers.
To have a better Evolutionary maneuverability of the architecture its important that each subsystem be designed in such a way that it performs only one function and performs it pretty well. This applies for both Architectural as well as Business Component.
In my article All You Might Really Need is a Monolith Disguised as Microservices I have talked in detail why boundaries help the Architectue Evolve.
Take a huge stone (Aka a Monolith) and drop it from the top of a building on a hard surface on the ground. Repeat the same with a loosely packed bag of pebbles (Aka Microservices). Which is more likely to survive the fall without breaking? Software systems are constantly under stress of Changing Market Behavior, Changing Customer Behavior, Weather (read AWS region outages), Business Course Corrections, Leadership Changes, Technology Changes ect…..
We must design systems to survive stress, otherwise they become extinct.
It just takes a single Black Swan event to completely dissamate the poorly designed monolith, whereas a system designed with proper boundaries has better resistance to Black Swans.
In his groundbreaking book “Antifragile”, Nassim Nicholas Taleb describes Antifragile systems as systems that become stronger when subjected to stress. For systems to grow under stress, some amount of instability is required. Boundaries provide that right amount of instability. We tend to make systems more and more stable and that backfires. To put it interestingly, we must design a system like a Swiss government — Modular, bottom-up, with some amount of instability. Here is how Nassim Nicholas Taleb describes the swiss government.
“Things break on a small scale all the time, in order to avoid large-scale generalized catastrophes.” ~ Nassim Nicholas Taleb, Antifragile
Nature loves small errors. They are the basis of evolution. Errors help the system evolve without causing the errors to affect the other boundaries. A part of the system might not work for some time, but the system as a whole will keep functioning. When the error is identified and fixed, the system becomes stronger than before. Boundaries give room for trial and error. It is through some amount of chaos, strong systems are born. Small Means Focused
I must confess that even after developing software for so many years, when I look at a system as one big thing, I get intimidated. Boundaries allow you to focus on parts without worrying about the whole, hence improving quality of work.
“It is not the strongest of the species that survive, but rather, that which is most adaptable to change.” — A quote often attributed to Darwin’s Ideas.
I cannot stress this enough — Architecting is a continuous activity. Software design is something that develops over time. Nature also draws boundaries in systems to help them evolve as a whole. Boundaries help components take separate evolutionary trajectories without stepping on each other and at the same time efficiently collaborate with each other.
"The fitness function drives architectural decision making, guiding the architecture while allowing the changes needed to support changing business and technology environments."
~ Building Evolutionary Architectures, Neal Ford, Rebecca Parsons, Patrick Kua
Fitness function is a term borowed from Genetic Algorithm Design. In a Genetic Algorithm small incremental changes are done to the algorithm and after every generational change the output is assessed to see how close it is to the exact solution. This assessment is done by a function called the fitness function. The fithess function forces or guides the code to become better over time. Fitness function selects the varants of algorithm that provide solutions closer to exact solution.
The architecture should ge guided by fitness functions. Fitness Functions are the environment inside which the architecture should evolve. When a requirement changes, first the fitness function changes and indicates to the Architecture that it must evolve to the next stage. All the fitness functions collectively evaluste of the evolution was successful.
Technology gets better over time and it can have the following effects of the Architecture. Fitness Function helps the architecture to evolve to accomodiate these changes because the Architecture is working to satisfy those Fithess Function.
-
The Requirement remains the same, but the Architecture must adopt the new technology.
-
Requirement changes to take advantage of the new technology. Technology can also influence the requirements.
Earlier the Fitness Functions are identified, the better they will help the Arcitecture to evolve.
Like evolution, Architecture is a game of tradeoffs. Fitness Functions will help the architect to take informed decissions on what to trade for what in the architecture, till an optimal solution is found later.
Fitness functions need to be constantly reviewed to ensure the integrity of the whole architecture and to access if the Architecture is following the optimal evolutionary trejectory. They provide a check for Architectural degradation.
"Quantum size determines the lower bound of the incremental change possible within an architecture." ~ Building Evolutionary Architectures, Neal Ford, Rebecca Parsons, Patrick Kua
In the physical word the Quantam is defined as a measure of the smallest amount of something — usually energy — that something can possess. Or, it can also be a smallest amount of action that can cause significant change.
In bilolgy the evolutionary changes begin at the genetic level. The origin point is the genetic suquence in the DNA. Small change in the sequence can lead to drastic changes in the species.
The sign of good design of a good Quanta is, the change must begin at one place and ripple through the other layers forcing them to re-align. Can also be called as the origin point of change.
Designing the architecture around quanta can give Architects immense evolutionary power over the their acrhitecture. Lesser the quantam size of the architecture, easier it is for the developers to make evolutionary changes. Single responsibility principle plays an important part over here.
Designing well-defined integration points play an important role here because the quantas can evolve independently and the change can be communicated to other Quantas via signals through integration points.
Designing optimal Architectral Quanta and Integration Points enables faster evolution cycles.
"It fell to the floor, an exquisite thing, a small thing that could upset balances and knock down a line of small dominoes and then big dominoes and then gigantic dominoes, all down the years across Time. Eckels' mind whirled. It couldn't change things. Killing one butterfly couldn't be that important! Could it?" ~ Ray Bradbury, A Sound of Thunder
In Ray Bradbury's Short Story, A Sound of Thunder A hunter named Eckels travels 66 million years back in time and steps on and crushes a Butterfly which apparently caused a rift in the evolutionary timeline. Upon returning to 2055, Eckels notices subtle changes: English words are now spelled and spoken strangely, people behave differently, and Eckels discovers that Deutscher has won the election instead of Keith. The mere incident of just stepping on a butterfly alters the history.
In chaos theory, This phenemenon is also knwn as the Butterly Effect - The sensitive dependence on initial conditions in which a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state.
So, how do we get the Evolutionary Trejectory right? There are no right answers to that. It depends on the Architects knowledge, vision and some capabilities of predection. Architects just need to trust themselves and focus on the present and avoid an attitude of perfectionism, but at the same time if the need arises, in the light of new information or insights, they should be wiling to go back and re-design, re-model or re-arrange things.
Untill now, we have only talked about one dimension of evolution, that is Business Requirements. For obvious resons, this is the most important dimension because the software exists for business.
Our software has to live in a technology landscape that is ever changing. The OS gets better each year, the virtuilization technology improves, better secure protocols are introduced, frameworks get version improvememts, libraries have changed implementations, more appealing web and mobile UI technologies appear, and more technologies battle it out in the market and some emerge as clear winners.
This puts pressure on your software to implement them, otherwise your software is left behind and becomes legacy.
In the book Building Evolutionary Architectures: Support Constant Change the authors have identified dimensions like - Auditability, Data, Security, Performance, Legality, and Scalability.
Each Application might have its own dimensions of evolution, like Oeuvre might want following extra dimensions
- Reportability - Ease of creating reports.
- Monitoribility - Ease of monitoring the faults in the system.
Well defined Fitness functions will guide the application to evolve in multiple dimensions.
"We prefer the word evolutionary over adaptable because we are interested in architectures that undergo fundamental evolutionary change, not ones that have been patched and adapted into increasingly incomprehensible accidental complexity." ~ Building Evolutionary Architectures, Neal Ford, Rebecca Parsons, Patrick Kua
Human bodies are home to number of micro-organisms, some of which might have been harmful to us at some point in our evolution. We have evolved to tolerate them or to live with them symbyotically. There are many micro-organisms that are harmful to us, so we have created Anti-biotics for them. Administering anti-biotics is a form of adaptation and it has its limits. Sooner or later the mrico-organisms will develop tolerance to it.
Evolutionary change is permanent and from within, on the other hand Adaptatation is force fitting a solution to a problem. There can be limits to adaptation. There might come come a time when the system is just not able to adapt to change, whereas the evolution changes the system from inside out.
Finding solutions that make the system Evolve rather that Adapt is benificial in the long run.
Without guidance, evolutionary architecture becomes simply a reactionary architecture. Thus, a crucial early architectural decision for any system is to define important dimensions such as scalability, performance, security, data schemas, and so on. Conceptually, this allows architects to weigh the importance of a fitness function based on its importance to the system’s overall behavior. ~Building Evolutionary Architectures, Neal Ford, Rebecca Parsons, Patrick Kua
Real world evolution is a random process and it depends largely on ariving on the right design through trial and error, therefore it is an exteremely long process. The good news here is that when an Architect plays the hand of evolution the process can be controlled, but you cannot ruleout indulging in some trial and error. Architects will have to take the responsibility of controlling as many unknown factors as possible to guide the architecture, through incremental changes, across multiple dimensions to arrive at an optimal design.
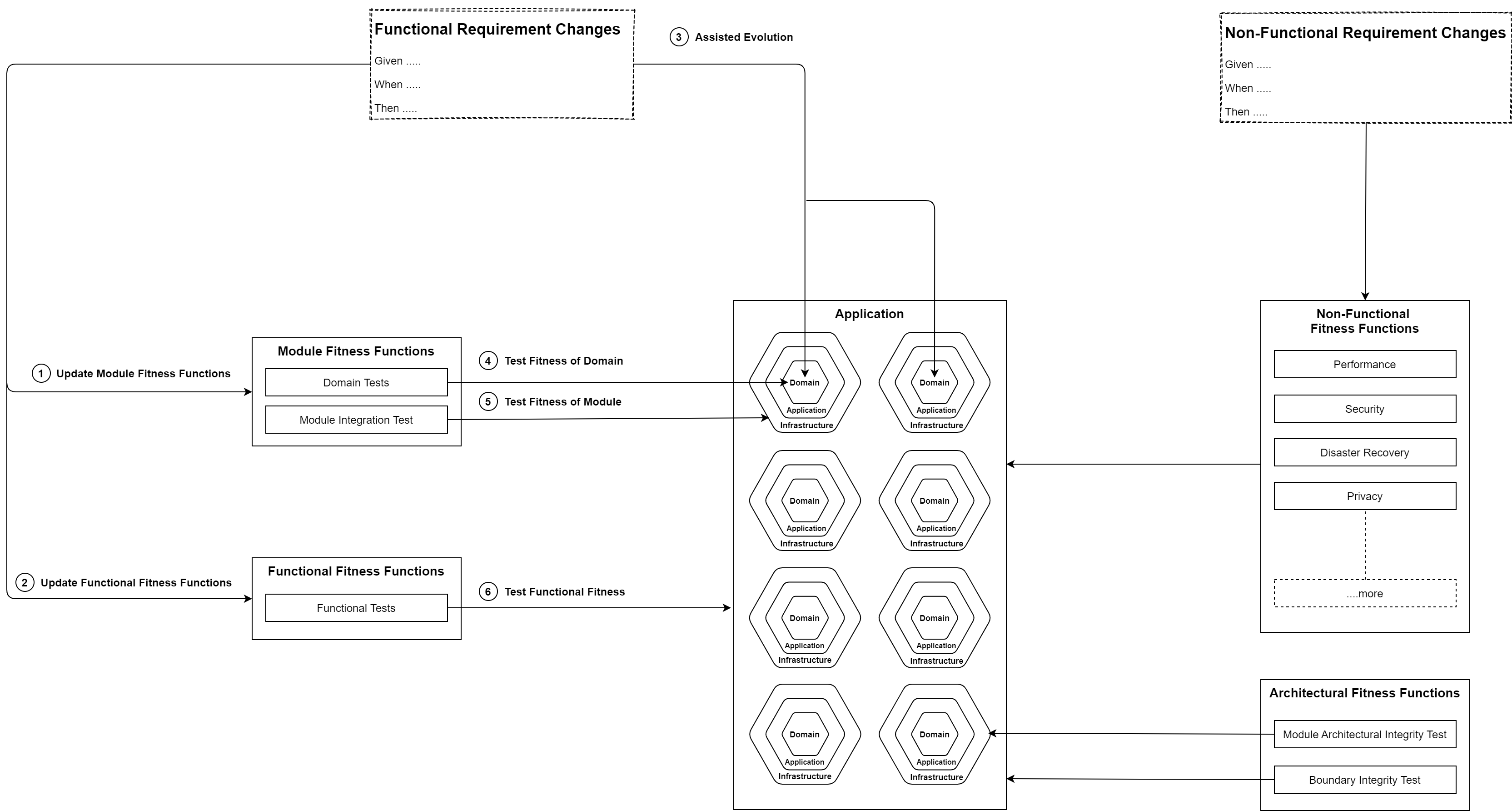
Whenever a fitness finction changes, our architectute is guided to evolve to a level where it passes the fitness function. For better evolvability, as discussed earlier, when the fitness function changes, the change in the architecture must begin at one place, which I call the origin point, and the changes should ripple outward. The origin point is the domain that contains the business logic.
These are the Fitness Functions your Application will have to satisfy to evolve to serve the Business Requirements:
When the business requirement changes, the domain takes the first hit. Now the domain must evolve to satisfy the new Domain fitnes test.
When the Domain test passes, the functionality of the feature belonging to that module can be tested as a whole, which includes:
-
Whether the Module is receiving the right input.
-
Whether the data is persisting in the Database.
-
Whether the Events are being transmitted to the other Modules.
-
Wether the Module is sending data correctly outside the application, my means of E-Mails, Webhooks, or GRPC.
-
Wether the Module is receiving correct data from outside the Application.
-
Wether the Module gives correct output.
These tests are at the edge of the application and will test the following:
-
API input and output communication.
-
Wether the modules are coordinating together to satisfy the feature of the application.
Non-Functional functions will help the Applcation to evolve in multiple dimentions like:
- Performance
- Security
- Disaster Recovery
- Privacy
ect...
The list will have pretty significant items as the application grows
This mostly one time activity. Once the rules of the game are set, it generally stays the same. These fitness functions will make sure that the structural integrity of the applications are maintained. It will check if for the wrong references between projects. It will most inportantly check if the modules of the application are correctly isolated. This is exteremely important if the architecture wants to make the next leap into microservices.
"I remember seeing an elaborate and complicated automatic washing machine for automobiles that did a beautiful job of washing them. But it could do only that, and everything else that got into its clutches was treated as if it were an automobile to be washed. I suppose it is tempting, if the only tool you have is a hammer, to treat everything as if it were a nail." ~Abraham Maslow, The Psychology of Science
Once we like a concept we tend to use it for every situation, while ignoring the other useful concepts that would fit better in a particular situation. While evolving the application you will use well established techniques, and you will also device few of your own. But, before using a concept it is always wiser to stop and question yourself whether or not the technique is sutable by comparing it with other techniques available. Sometimes playing the blind game cannot be avioded, but taking an informed decision will help.
Concepts should fit together in an optimal manner, or to put in a different way, the design should aim for conceptual integrity.
"As defined in physics, the quantum is the minimum amount of any physical entity involved in an interaction. An architectural quantum is an independently deployable component with high functional cohesion, which includes all the structural elements required for the system to function properly. In a monolithic architecture, the quantum is the entire application; everything is highly coupled and therefore developers must deploy it en mass." ~Building Evolutionary Architectures, Neal Ford, Rebecca Parsons, Patrick Kua
1. The Origin of Design is the Database
As discussed earlier, there is something un-natural about designing the behaviour of the application through its persistance. Database design should be the side-effect of application design and not vice versa.
When the application design is started with database design, it's difficult to envision the modularity at the database level. Therefore, the concepts from tables belonging to other domains/modules leak into Tables that are unrelated. For example, take this example, it might be a bit extereme but demonstrates the problem.
2. Reading from Database is not Really Business Logic
Most of the time during read, the Business Layer simply relays the message of the DataLayer to the UI Layer. Having a Business Layer becomes a mere techonological formality during reads and serves no purpose and creates extra efforts for the develpers because the read operations in the Application exceed write operations.
3. ORMs are Viewed as Extensions Of Database
Without modilarity, the ORM entity structure becomes complex and that leads to performance issues because it loads data that are most of the times not required. Moreover, for the read operations developers use LINQ queries that can become complex. LINQ ultimately gets converted to Native SQL, and the Conversion from LINQ to SQL sometimes does not happen optimally, hence database reads have performance issues.
4. Architecture is Built Around Technology and not Business Requirement
The terms "Data Layer", "Business Layer" and "UI Layer", themselves have no mention of the functionality of the application. A 3-Tier architecture is just an architecture built to satisfy the need for seperation without any concern for modularization and evolution.
5. Modularity is at the Layer Level
Each layer is an Archeterical quanta, so huge that they becomes too stubbotn to evolve.
6. Cross-Component Communication is Dificult to Control
There is nothing that stops any component from the Business Layer to call any component of Data Layer, or any component of Data Layer to access any table from the Database and so on. It becomes a Big Ball Of Mud at a layered level.
1. Things are Designed at a Linguistic Level
“The limits of my language mean the limits of my world.” — Ludwig Wittgenstein
Language plays an important role in how we percieve the world. We define systems in terms of languages. More importantly, we define the software requirements in the unit of language. Software exists to solve real world problems, therefore there is a strong link between the code and the outside reality. But, our computer languages do not have strigent rules around designing the systems that reflect the outside entities and processess, therefore a programmer generally omits this facts and things in terms of programming concepts.
All business software are simulations of real world processes. If the business reality is not aligned with the inner reality of the code, it creates an impedance — a resistance for change. Until and unless you devise a way to make your code a replica of the outside business, it will resist changes, because it does not understand the language of the outside world.
The challenges here are not technical but structural and, more importantly, lingual.
DDD has a concept called Ubiquitous Language which unifies the vocabulary of the Project across all the stages of development. This is a language that is used by the Business Analysts, Stakeholders, Testers, and Developers. More more importantly, this is the language in which the core of DDD will be designed, hence the code reflects the requirements of the application.
2. Business requirement changes hit the Domain first and forces the things to change from inside out
Whenever there is a change in the Requirements at a Business Level, the first that gets affected by the changes is the Domain. This is the origin point of the change because the Business Logic resides in the Domain. Once the domain is changed to accomodiate the business requirement, the underlying database can be adjusted and the outer layers, the Application and Infracture realign to support those changes.
This mimics the behaviour of the cell where the changes begins at the DNA level.
DDD is designed to evoles from within, rather than adapt.
7. Database creation is the side effect of the design
"DDD is not about structuring data in a normalized fashion. It is about modelling the Ubiquitous Language in a consistent Bounded Context" ~ Vaughn Vernon, IDDD
The domain controls the behaviour of the application, because the business logic resides in the domain. When the behaviour of the application is expected to change due to requirement change, the changes are done in the Domain. According to changes in the domain, the pesristance disign is created. Application design is not Database Design Driven.
This sets you free from thinking about Application Design from a Database perspective.
4. Encourages Modularity
Domain Driven Design has a concept of Bounded Context, which are the boundaries between which an application is divided. Each bounded context handles a particular concept within an application. The bounded contexts are loosely couples and pass information to each other using messages and receive messages using the API.
[Bounded Context Diagram]
5. Optimal Architectural Quanta
Since the Domain Model is the heart of DDD and contains the business logic, the unit of change of the business logic is the Domain. All the changes to business logic start from the domain, making the Architectural Quanta centered, small and managable.
6. Business Logic can be tested without dependencies
Unit Tests can be target at the Domain to test the integrity of the business logic even before other layers are written around it. This gives a sense that the application is moving in the right direction.
It's understood that Domain Driven Design requires programmers to climb a steep learning curve, and after that, a lot of practice to truly understand the concepts. A middle path can be taken, where the concepts of classical 3-tier and modular monoliths can be combined. The Business Layer along with Data Layer can be considered as a domain. There is no garuantee that cross communication between components avoided, but they will be contained within the module.
"One of the great bugaboos of software applications over the years has been infiltration of business logic into the user interface code." ~Alistair Cockburn
Alistair Cockburn, in his seminal paper Hexagonal Architecture talks about how in software development there has been a problem of business logic infiltrating into the UI layer. These causes the following problems:
- It becomes difficult to test the system with automated tests because the part of the business logic that needs to be tested is in the UI, for instance, a button click event.
- Other systems cannot utilize the functionality of the system because UI is becomes the only gateway to the system.
So, the application needs to be designed in such a way that it provides it provides the business functionality through an API that becomes the gateway to the application. This will enable us to
- Automate testing the application without the UI.
- Other applications can utilize the functionality of the application.
- Business logic can be kept out of the UI layer.
What are Port and Adapters?
Ports
The Ports acts as a gateway through which communication takes place as an inbound or outbound port. An Inbound port is something like a service interface that exposes the core logic to the outside world. Ports are at the application boundary.
Adapters
The adapters act as an implementation of a port that handles user input and translate it into the language-specific call. It basically encapsulates the logic to interact with outer systems such as message queues, databases, etc. It also transforms the communication between external objects and core. Adapters implement a concrete protocol by which some external system or device can communicate with the application. An adapter translates between a specific technology and a technology free port. An adapter allows a technology to interact with a port of the hexagon.
In most of cases, REST controller act as a our primary adapter, providing endpoints accessing domain through port.
The adapters can be classified into 2 types:
Inbound Adapters: They drive the application using the inbound port of an application. Examples of primary adapters could be WebViews or Rest Controllers.
Outpound Adapters: They are the implementation of an outbound port that is driven by the application. Connection with messaging queues, databases, and external API calls are some of the examples of Secondary adapters.
There can be more than one adapter for a single port. For instance if a port offering a business logic has to be accessed by a web application through REST and at the same is accessed by some other application through GRPC, then two adapters REST and GRPC van be created for a port.
If another device wants to communicate with the application through other means, another adapter can be created. For example, an adapter can be created for listening to messages thrown by that application into the message queue.
Database – “the other side”
On the other side the application communicates with the database. The application needs to be designed in such a way that ff the database type is changed, the conversation across the API should not change. Then we have the following advantages:
- Persistence can be replaced with any kind of data store. Even flat files.
- APIs can be tested without the database using mocks.
An outbound port is something like a repository interface that facilitates communication from application to persistence system. Here the application has an outbound port and adapter to access the data or to store the data. The application can employ multiple adapters for communication with different databases of persistence mechanisms. From the testing point of view it can have an adapter to mock the database.
Application itself can communicating with the port of another application using an adapter provided by that application.
The sole motive of all this is to keep the Use Cases confined to the Application, which is the core of the Hexagonal Architecture. It also helps in testing the behaviour of the Application without any dependencies.
DDD and Hexagonal Architecture
In DDD the Application of HA can be viewed as a combination of Domain and Application, while the infrastructure provides the ports to persistence and API provides the ports to UI. Each bounded context can be a separate hexagon. That is, the application can be divided into multiple hexagons that communicate with each other to complete one use case. This application can be a modular monolith or a microservice.
Advantages
- Since the application is divided into multiple hexagons, changes in one area of an application has no effect on the other areas of the application. The complexities are contained.
- Technical decisions for adding features can be visualized easily and implemented.
- Debugging is easy as the developers can concentrate on the small area of the application at a time.
- Automated integration and unit tests become easy and controllable.
- Mocks can be easily integrated by creating mock Adapters
- Maintenance is easy because the application has well define inputs and outputs and is modular in nature with well defined separation of concern, and the business logic lies at the core. Adding feature to one Hexagon has minimum effect on the other.
- The things like UI and database become replaceable by creating specialized adapters.
- Accumulates low technical debt.
Creating reports using complex SQL Join queries is not the best way to create reports. The queries become slow over time and require constant DB tuning. Using LINQ queries for reporting is an overkill. Never do it!
Reports need to be created when the data enters the system. The listeners must listen to the data and construct the reports.
In his paper No Silver Bullet – Essence and Accident in Software Engineering, Fred Brooks argues that
There is no single development, in either technology or management technique, which by itself promises even one order-of-magnitude improvement within a decade in productivity, in reliability, in simplicity.
Developing a software in indeed a very complex task. There is alwats some new framework or management methodology that promises to make the job easier, but they have not had any dramatic impact on the speed and improvement of software development.
The paragraph that immediately caught caught my attention was this. I want to present it as it is, because nobody could have expressed it better than the author himself.
Software is invisible and unvisualizable. Geometric abstractions are powerful tools. The floor plan of a building helps both architect and client evaluate spaces, traffic flows, and views. Contradictions become obvious, omissions can be caught. Scale drawings of mechanical parts and stick-figure models of molecules, although abstractions, serve the same purpose. A geometric reality is captured in a geometric abstraction.
The reality of software is not inherently embedded in space. Hence it has no ready geometric representation in the way that land has maps, silicon chips have diagrams, computers have connectivity schematics. As soon as we attempt to diagram software structure, we find it to constitute not one, but several, general directed graphs, superimposed one upon another. The several graphs may represent the flow of control, the flow of data, patterns of dependency, time sequence, name-space relationships. These are usually not even planar, much less hierarchical. Indeed, one of the ways of establishing conceptual control over such structure is to enforce link cutting until one or more of the graphs becomes hierarchical.
In spite of progress in restricting and simplifying the structures of software, they remain inherently unvisualizable, thus depriving the mind of some of its most powerful conceptual tools. This lack not only impedes the process of design within one mind, it severely hinders communication among minds.
A good softwares is designed when a strong spatial sence is applied. Code needs to be seen as a geometric distribution. Diagrams can be powerful tools for desigining software. They give a sense of orientation to things that are ingerently invisible.
Requirement gathering is also a complex task in Software development as the Author rightly points out
I would go a step further and assert that it is really impossible for clients, even those working with software engineers, to specify completely, precisely, and correctly the exact requirements of a modern software product before having built and tried some versions of the product they are specifying.
Much of present-day software acquisition procedures rests upon the assumption that one can specify a satisfactory system in advance, get bids for its construction, have it built, and install it. I think this assumption is fundamentally wrong, and that many software acquisition problems spring from that fallacy. Hence they cannot be fixed without fundamental revision, one that provides for iterative development and specification of prototypes and products.
The requirement gathering also becomes a contunuous process involving the client. The logical integrity of the requirement gets continuously while the product is built.
The Author then suggests that to deal with this problem, the software should be grown by incremental development. This is also the phisosophy Galls Law echos.
Growing software organically, adding more and more function to systems as they are run, used, and tested.
Our Purpose
-
Our purpose while developing Oeuvre is not to invent a Silver Bullet, because it is assured that there never will be a silver bullet.
-
We will be growing the system in all the evolutionary directions incrementally.
-
We will use the spatial dimention to develop and grow this software, because it will prove to be a powerful tool.
Software development is also a very decision driven craft. Suboptimal decisions sometimes give rise to unwanted outcomes or steer the project into an unknown direction. We always take architectural or technology decisions within a context and sometimes the team forgets the context as the time passes, or others do not see the context in which the decision was taken and it often gets mis-understood.
Logging your Architecture Decisions works at two levels:
- By logging them you are taking a conscious present decision.
- It sets a context in which the decision was taken and can act as a reference for taking better decisions.
Michael Nygard’s Architecture Decision Template is the popular template through which you can record your architectural decisions.
Michael Nygard's template will be used to record Architectural Decisions. The logs can be found in this folder.
A relational database is structured for write, but not read. When the volumes of data increase, the reads become very slow. Mostly only 20% of the time the application writes to the database, but 80% of the request to the database are read requests. Therefore, it does not make any sense to use a database that is meant writing, to read from it.
Unit of communication of a task Internal or External nternal tasks enter into the Domain through Commands.
Unit of Retrieving Information.
Unit of Communication within the domain
Unit of communication between Bounded Contexts / Modules
Unit of getting information from other bounded contexts
Automic Unit of Business Logic / The change of business requirement
Unit of Deployment
-
Design the Domain Structure in accordance with the Feature in the feaure files.
-
Write Domain Unit Tests in accordance with the Feature in the feaure files.
-
Write the behaviour of the Domain so that the Domain Unit Tests pass.
-
Modify the Database Scripts as per the changes in the Domain Above.
-
Write Module Integration Tests in accordance with the Feature in the feaure files.
-
Write the behaviour of the application so that the Unit Tests pass.
- Should be scalable to microservices.
- OS Independent.
- Self Healing - able to bounce back from crashes on its own.
Registrant : One who has just registred to Oeuvre Portal through registration page,
but will not qualify as a user unless they verify their EMail through
the link sent in his EMail.
User : One who has registered and verified his EMail.
EMail Verification :
Profile :
Settings :
#<FeatureNameCode>
Feature: <Feature Name>
<Feature Description>
#<FeatureNameCode>-<SceneraoNumber>
Scenario: <Feature Scenerao>
Given <#BusinessRule-1>
And <#BusinessRule-2>
When <#Command> -- No ANDs for this expected
Then <#DominEvent-1> <#Policy-1> <#InternalCommand-1>
And <#DominEvents-2> <#Policy-2> <#InternalCommand-2>
#FREG
Feature: Registration
#FREG-S1
Scenario: New Registrant registers using an EMail Id that does not belong to any Oeuvre user
Given I have not registered at Oeuvre
And there is no other User registered with my EMailId "[email protected]"
And I have Accepted the Terms and Conditions
When I register using the following valid details
|TenantId |FirstName |LastName |EMail |Password |MobileNoCountryCode |MobileNumber |
|47d60457-5a80-4c83-96b6-890a5e5e4d22 |Mary |Carpenter |Mary@TheCarpenters.com |topoftheworld |+1 |4387790052 |
Then I should be a Registrant on Oeuvre
And I should receive a registration EMail containing an email verification link account
And my User confirmation should be pending
#FREG-S2
Scenario: Registrant registers more than once with Unique EMail Id / while his email is pending verification
Given I have already registered at Oeuvre
And there is no other User registered with my EMailId "[email protected]"
And I have Accepted the Terms and Conditions
When I register using the following valid details
|TenantId |FirstName |LastName |EMail |Password |MobileNoCountryCode |MobileNumber |
|47d60457-5a80-4c83-96b6-890a5e5e4d22 |Mary |Carpenter |Mary@TheCarpenters.com |topoftheworld |+1 |4387790052 |
Then I should be a Registrant on Oeuvre
And I should again receive a registration EMail containing an email verification link account
And my User confirmation should be pending
#FREG-S3
Scenario: Registrant registers after his EMail Verification Link Expires
Given I had registered at Oeuvre
And I did not confirm my Registration
And I have Accepted the Terms and Conditions
And there is no other User registered with my EMailId "[email protected]"
When I register using the following valid details
|TenantId |FirstName |LastName |EMail |Password |MobileNoCountryCode |MobileNumber |
|47d60457-5a80-4c83-96b6-890a5e5e4d22 |Mary |Carpenter |Mary@TheCarpenters.com |topoftheworld |+1 |4387790052 |
Then I should be a Registrant on Oeuvre
And I should receive a registration EMail containing an email verification link account
And my User confirmation should be pending
#FREG-S4
Scenario: Registrant registers with already existing User's EMail Id
Given That I register at Oeuvre
And a User with my EMail Id "[email protected]" already exists
And I have Accepted the Terms and Conditions
When I register with the following details
| TenantId | FirstName |LastName |EMail |Password |MobileNoCountryCode |MobileNumber |
| 47d60457-5a80-4c83-96b6-890a5e5e4d22 | Mary |Carpenter |Mary@TheCarpenters.com |topoftheworld |+1 |4387790052 |
Then I should not be able to register
And I should not receive a registration mail containing the email verification link
#FREG-S5
Scenario: New Registrant registers without accepting the Terms and Conditions
Given I have not registered at Oeuvre
And there is no other User registered with my EMailId "[email protected]"
And I have NOT Accepted the Terms and Conditions
When I register using the following valid details
|TenantId |FirstName |LastName |EMail |Password |MobileNoCountryCode |MobileNumber |
|47d60457-5a80-4c83-96b6-890a5e5e4d22 |Mary |Carpenter |Mary@TheCarpenters.com |topoftheworld |+1 |4387790052 |
Then I should be a Registrant on Oeuvre
And I should receive a registration EMail containing an email verification link account
And my User confirmation should be pending
#-----Not Complete - Working On Them-----
#FREGSOCIAL
Feature: Social Media Registration
#FREGSOCIAL-F1
Scenario: New Member register using Facebook
Given I am not a User of Oeuvre
When I choose to register through my Facebook account
Then a new account will be created for me 2
#FREGSOCIAL-F2
Scenario: New Member register using Google
Given I am not a User of Oeuvre
When I choose to register through my Google account
Then a new account will be created for me
#FRC
Feature: Registration Confirmation
#FRC-S1
Scenario: Registrant Clicks on EMail Verification Link
Given I have registered on Oeuvre portal
And I have received an EMail verification link in my EMail
And There is no other user having my EMail Id on Oeuvre
When I click on the EMail verification link
Then I should become a User of Oeuvre Portal
#FRC-S2
Scenario: Registrant clicks on verification EMail more than once
Given I have registered on Oeuvre portal
And I have received an EMail verification link in my EMail
And I have Already clicked the EMail verification link
When I click on the EMail verification link again
Then Nothing should happen
#FRC-S3
Scenario: Registrant clicks on verification EMail after the Expiration Period
Given I have registered on Oeuvre portal
And I have received an EMail verification link in my EMail
And My Email Verification link has Expired
When I click on the EMail verification link
Then I should not become the user of Oeuvre
#FAUTH
Feature: Authentication
#FAUTH-S1
Scenario: Logging-In with valid credentials
Given I am logged out
And I am a User of Oeuvre Portal
And I am an Active User
When I try to authenticate using valid
|email | password |
|email@gmail.com | Passw0rd123 |
Then I should be authenticated
#FAUTH-S2
Scenario: Logging-In with in-valid credentials
Given I am logged out
And I am a User of Oeuvre Portal
And I am an Active User
When I try to authenticate using in-valid
|email | password |
|email@gmail.com | Passw0rd123 |
Then I should not be authenticated
#FAUTH-S3
Scenario: Logging-In with valid credentials when User is NOT Active
Given I am logged out
And I am a User of Oeuvre Portal
And I am NOT an Active User
When I try to authenticate using valid
|email | password |
|email@gmail.com | Passw0rd123 |
Then I should not be authenticated
#FAUTH-S4
Scenario: Logging-In with valid credentials when the Registrant has not verified his EMail Id
Given I am logged out
And I have Registered on the Oeuvre Portal
And I have Not verified my EMail Id
When I try to authenticate using valid
|email | password |
|email@gmail.com | Passw0rd123 |
Then I should not be authenticated
#FUD
Feature: DeActivate A User
#FUD-S1
Scenario: Admin can DeActivate a User
Given I an Admin of Oeuvre Portal
When I DeActivate a User
Then that user should not be allowed to login
#FUD-S2
Scenario: Admin can DeActivate a User while the user is Logged-In
Given I an Admin of Oeuvre Portal
When I DeActivate a User who is already Logged-In
Then the user should be logged-out
And that user should not be allowed to login again
#FUA
Feature: Admin can Activate A DeActivated User
#FUA-S1
Scenario: Admin can Activate a User who is DeActivated
Given I am the Admin of Oeuvre Portal
And a User is DeActivated
When I Activate that User
Then that user should be allowed to login
@TODO: Refactor this into tables to transform this to SpecFolw Tests
#FFPR
Feature: ForgotPasswordRequest
As a Member who has forgotten his Oeuvre password
In order to login again
I want to be able to reset my password
#FFPR-S1
Scenario: Password reset requested by an Active User with Correct EMail Id
Given I am a regestered User #BusinessRule-1
And I am an Active User #BusinessRule-2
When For reseting my password I enter EMail-Id I had given at the time of registration #Command
Then I should get the Email with Password Reset Link #DomainEvent #Policy #Command
#FFPR-S2
Scenario: Password reset requested by an InActive User with Correct EMail Id
Given I am a regestered User
And I am an InActive User
When For reseting my password I enter EMail-Id I had given at the time of registration
Then I should NOT get the Email with Password Reset Link
#FFPR-S3
Scenario: Password reset requested by an Active User with Wrong EMail Id
Given I am a regestered User
And I am an Active User
When For reseting my password I enter EMail-Id I had given at the time of registration
Then I should NOT get the Email with Password Reset Link
#FFPR-S4
Scenario: Password reset requested by an InActive User with Wrong EMail Id
Given I am a regestered User
And I am an InActive User
When For reseting my password I enter EMail-Id I had given at the time of registration
Then I should NOT get the Email with Password Reset Link
#FRP
Feature: ResetPassword
#FRP-S1
Scenario: Reseting the password after forgot password request
Given that I have received the reset password EMail with the reset link
And the password reset link is not expired
And I click on the link
When supply the new password along with comfirm password
Then my password should be reset to the new password
#FRP-S2
Scenario: Reseting the password when the link in the EMail has Expired
Given that I have received the reset password EMail with the reset link
And the password reset link is expired
When I click on the link which is Expired
Then I should not be allowed to reset the password
#FRP-S3
Scenario: Reseting the password again using the same EMail Link
Given that I have received the reset password EMail with the reset link
And the password reset link is not expired
And I have already used that link to reset my password
When I click on the link to reset my password
Then I should not be allowed to reset the password
#FUP
Feature: UserProfile
#FUP-S1
Scenario: Member can Update the User Profile
Given I am a Registered User
When I try to update my User Profile
Then My user Profile should be Updated
#FUS
Feature: UserSettings
#FUS-S1
Scenario: Member can update his Settings
Given I am a Registered User
When I try to update my Settings
Then My user Settings should be updated
| Feature | URL | Method | Request JSON | Response JSON | Success Code | Failure Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Register | http://localhost:5000/identityaccess/register | POST | {TenantId" : "47d60457-5a80-4c83-96b6-890a5e5e4d22", "FirstName" : "Mary", "LastName" : "Carpenter", "Password" : "topoftheworld", "MobileNoCountryCode" : "+1", "MobileNumber" : "4387790052", "EMail" : "[email protected]" } | 200 | 400 | |
| Confirm Registration |
Test Driven Design will be followed
Arch Unit Tests
Write Domain Unit Tests
Write Module Integration Unit Tests
Write Application Integration Test
Write ArchUnit to check if boundaries dont cross over each other.
Write Non Functional Tests
| User Story | Feature | View | Command | Rules | Aggregate | Event | Policy | Command | Aggregate | Event |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registration | Feature File | Registration Form | Register | 1. EMail Id must be unique | Registration | User Registered | Email with confirm URL must be sent | Send Registration Email | Registration | User Verification Email Sent |
| Components | Registration.feature | RegisterNewUserCommandHandler.cs | Registration.cs, UserEmailIdLoginMustBeUniqueRule.cs | Registration.cs | Registration.cs, NewUserRegisteredEnqueueEmailConfirmationHandler.cs, SendUserRegistrationConfirmationEmailCommandHandler.cs | SendUserRegistrationConfirmationEmailCommandHandler.cs | Registration.cs | Not Implemented - Not Required | ||
| Tests |
All Integration Tests are done on a separate database "oeuvre_integration_testing". All the tables and seed data are added before the test and removed after the tests. Instructions for running tests and code coverage can be found here.
- Talks
- Evolutionary Architecture with Patrick Kua
- Manchester Geek Nights - Principles and Techniques of Evolutionary Architecture with Dr. Rebecca Parsons
- Principles of Evolutionary Architecture - Rebecca Parsons
- Microservices & Evolutionary Architecture - Rebecca Parsons
- The Evolution of Evolutionary Architecture - Rebecca Parsons
- Voxxed Days Vienna - Evolutionary Software Architectures - Neal Ford
- SATURN2016 - Evolutionary Architecture with Patrick Kua
- SDDConf 2016 - Keynote on Evolutionary Architectures
- Implementing Domain-Driven Design
- Patterns, Principles, and Practices of Domain-Driven Design
- Domain-Driven Design: Tackling Complexity in the Heart of Software
- Hands-On Domain-Driven Design with .NET Core
- Ready for changes with Hexagonal Architecture - Netflix Technology Blog
- Hexagonal architecture
- Hexagonal Architecture with Java and Spring
- Hexagonal Architecture in Java
- Hexagonal Architecture: Introduction Part I
- Simple Domain Events with EFCore and MediatR
- Avoid In-Memory Databases for Tests
- DeactivateUser
- Avoid Soft Deletes
- Julie Lerman talks about DDD and EF Core 3
- Julie LERMAN: Mapping DDD Domain Models with EF Core 2.1 @ Update Conference Prague 2018
Issues encountered diring development of this application and their workarounds can be found here.