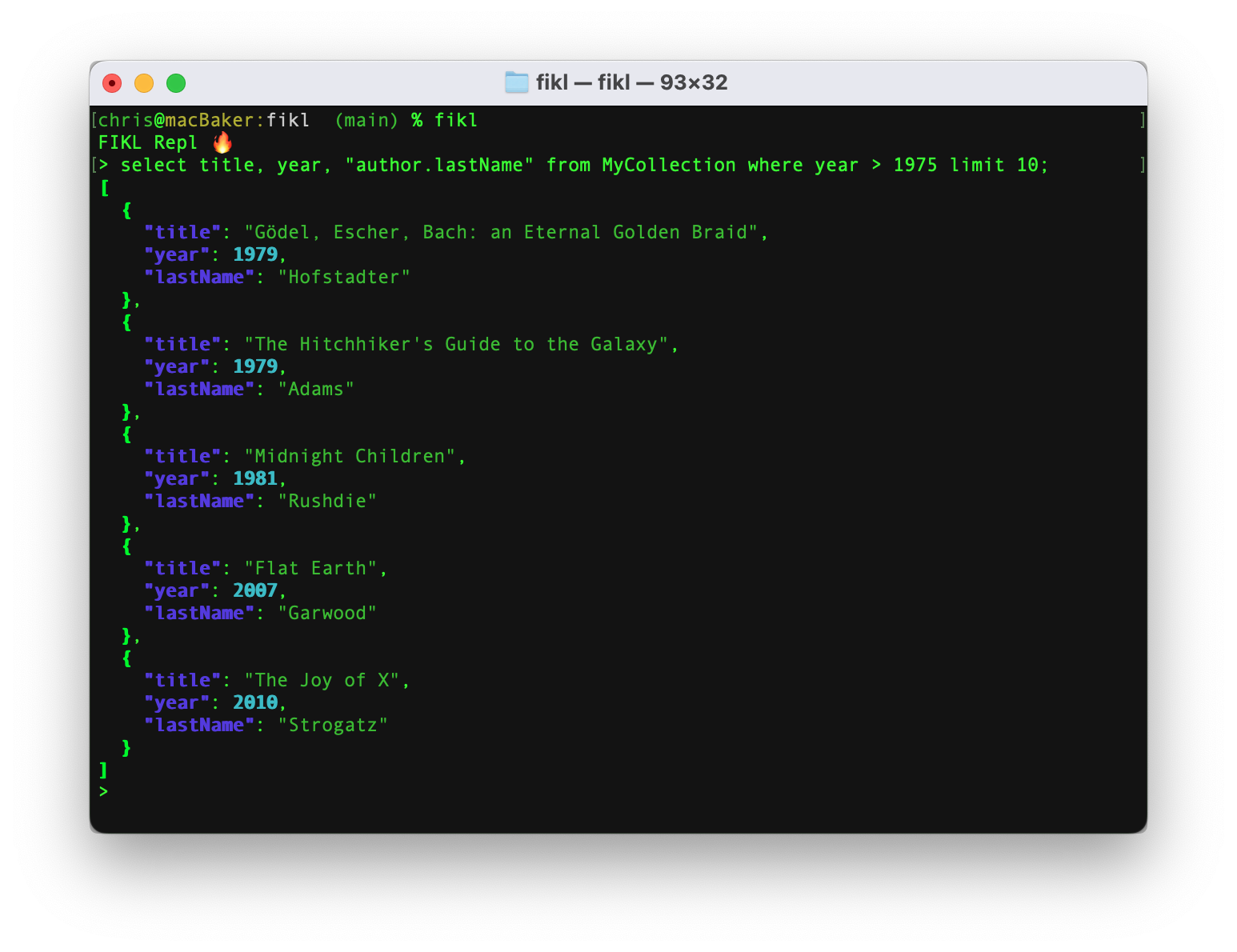
FIKL is a Firestore Query Languate CLI tool and REPL that allows users to execute SQL Like queries against a Firestore database.
- Supports
select,update,insert&deletequeries - Supports server side and local filtering and sorting
- Support for
group by,countanddistinct - Support for
likeoperator when usinglocalqueries - Query results can be output directly to a JSON file
- Full featured REPL
The FIKL CLI tool allows for SQL-like queries to be executed against a Firestore database.
- Firestore essentially has 3 different query contexts:
- Document
- Documents are fetched by specifying the path to that document. This is accomplised in FIKL by making use of the
atkeyword.
- Documents are fetched by specifying the path to that document. This is accomplised in FIKL by making use of the
- Collection
- Collections contain a number of documents and are queried by making use of the
fromkeyword.
- Collections contain a number of documents and are queried by making use of the
- Collection Group
- Collection Groups are essentially a grouping of collections that are named the same but exist within different Documents. Make use of the
withinkeyword to query within a Collection Groups.
- Collection Groups are essentially a grouping of collections that are named the same but exist within different Documents. Make use of the
- Document
- Create a new virtual environment so that you can have an isolated python environment
virtualenv venv
source venv/bin/activate- Install the required dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt- Run lint and tests
pylint lang
python -m coverage run -m unittest && coverage report && coverage html- Use
pyinstallerto create an executable. Adistdirectory will be created which will include the executable.
pyinstaller --clean -y -n fikl --add-data "fikl.lark:." ./lang/__main__.py
./dist/fikl/fiklMake sure that the GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS environment variable is set and pointing to a Google Cloud credentials json file
- To start a FIKL REPL.
fiklNote: Commands can run over multiple lines in the REPL and should be terminated with a semi-colon
- Supply a query as an argument to the fikl executable to execute a command direcly from the command prompt
fikl 'select * from MyCollection where year == 2005 limit 5'- Similary to SQL, a list of desired fields can be specified as part of a query. If all fields are required then
*can be provided. Dot-notation can be used to fetch properties from a nested object (remember to surround with double-quotes)
fikl 'select title, "author.firstName" from MyCollection where year == 2005 limit 5'- Simply run the
fiklcommand to enter the REPL. - Use the up arrow to recall previous statements
- Statements can run over multiple lines and should be terminated with a semi-colon
- Type exit to close the REPL
To fetch a single document, note that there is no need to supply a where clause when fetching a single document
Make use of the at keyword and the path to the document:
select * at "some_collection/some_document_id"Instead of specifying * in the field list, use a comma separated list of desired fields:
select title, "author.firstName" at "some_collection/some_document_id"Similar to SQL, use the set keyword followed by the fields to be updated and the respective values:
update at "some_collection/some_document_id" set title = "Some Title", "author.firstName" = "Bob"delete at "some_collection/some_document_id"Collection queries and Collection Group queries share the same features. Collection queries make use of the from keyword while Collection Group queries use within.
Make use of the from keyword to indicate that a collection is being queried, or make use of within to indicate that a collection group is being queried:
select * from some_collectionselect * from some_collection where year == 2005 and "author.lastName" == "Diamond" limit 10select * within some_collection_group limit 10select * from some_collection where year == 2005 and "author.lastName" == "Diamond" order by year desc, title limit 10Complex where clauses often require an explicit Firestore Index to be created. You can make use of local filtering and sorting by making use of ^. Place the ^ after the name of the field and that field will be evaluated locally. This avoids the need of having to create an explicit index when querying data in an ad-hoc manner. Combinations of server side and locally evaluated fields can be included in a single statement.
select * from some_collection where year == 2005 and "author.lastName"^ == "Diamond" order by year^ desc, title limit 10In the above example, the year field will be included in the where clauses as part of the Firestore query, however the author.lastName field will be filtered locally. Likewise, sorting on the year field will be performed locally due to the ^ being used in the order by statement.
When using a locally evaluated property like is a valid operator.
select * from some_collection where year == 2005 and "author.lastName"^ like "%iamond" order by year desc, title limit 10The output of a query can be grouped by a single field
select * from some_collection where year == 2005 group by "author.lastName"The distinct keyword can be used to return a unique list of documents based on the desired fields
select distinct "author.lastName", year from some_collection where year == 2005The number of records that the query returns can be output as a single number
select count * from some_collection where year == 2005A where clause is mandatory when updating documents in a collection or collection group:
update from some_collection set title = "Some Title", "author.firstName" = "Bob" where year == 2005;A where clause is mandatory when deleting documents in a collection or collection group:
delete from some_collection where year == 2005The identifier of the document that is being inserted is optional. If the "identified by" is not supplied, Firestore will automatically set a document ID
insert into some_collection set year = 2005, title = "Mutants", "author.firstName" = "Armand", "author.lastName" = "Marie Leroi" identified by "some_document_id"The results of a query can be output directly to a file at the specified location
select year, "author.firstName", "author.lastName" output "~/Desktop/books.json"Or directly to the clipboard
select year, "author.firstName", "author.lastName" from some_collection copyYou can also specify the output format of either 'csv' or 'json' (defaults to json). Unfortunately some nested objects and the results of group by clauses will results in errors or ugly CSV output.
select year, "author.firstName", "author.lastName" from some_collection format csv