Generate equivolumetric surfaces: creates equivolumetric surfaces based on the ratio of areas of the mesh surfaces, without the trouble of dealing with volumetric operations.
Takes WMC datatype as input and generates n equally spaced equivolumetric surfaces, that can then be viewed in Freesurfer. (i.e. n_surfs = 5 will generate the pial and white matter surfaces as well as 3 equally spaced intermediate surfaces)
The smoothing or "diffusion smoothing" value (fwhm, Full Width at Half Maximum of the Gaussian, in mm, default 0) determines the extent to which the surfaces are smoothed (e.g. sharp jumps in neighboring data points on the surfaces will be smoothed out, generally increasing the signal-to-noise ratio)
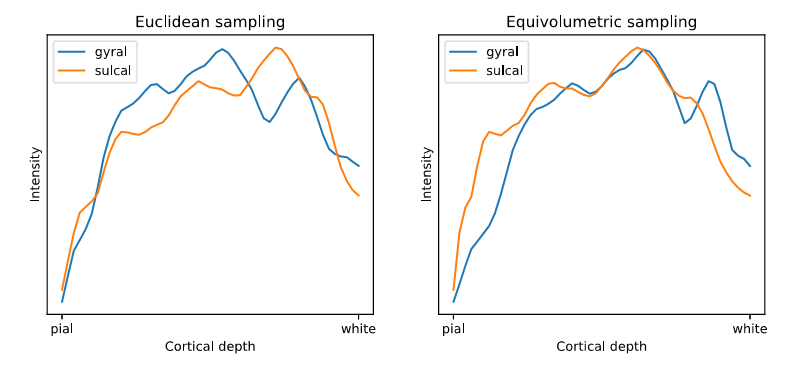
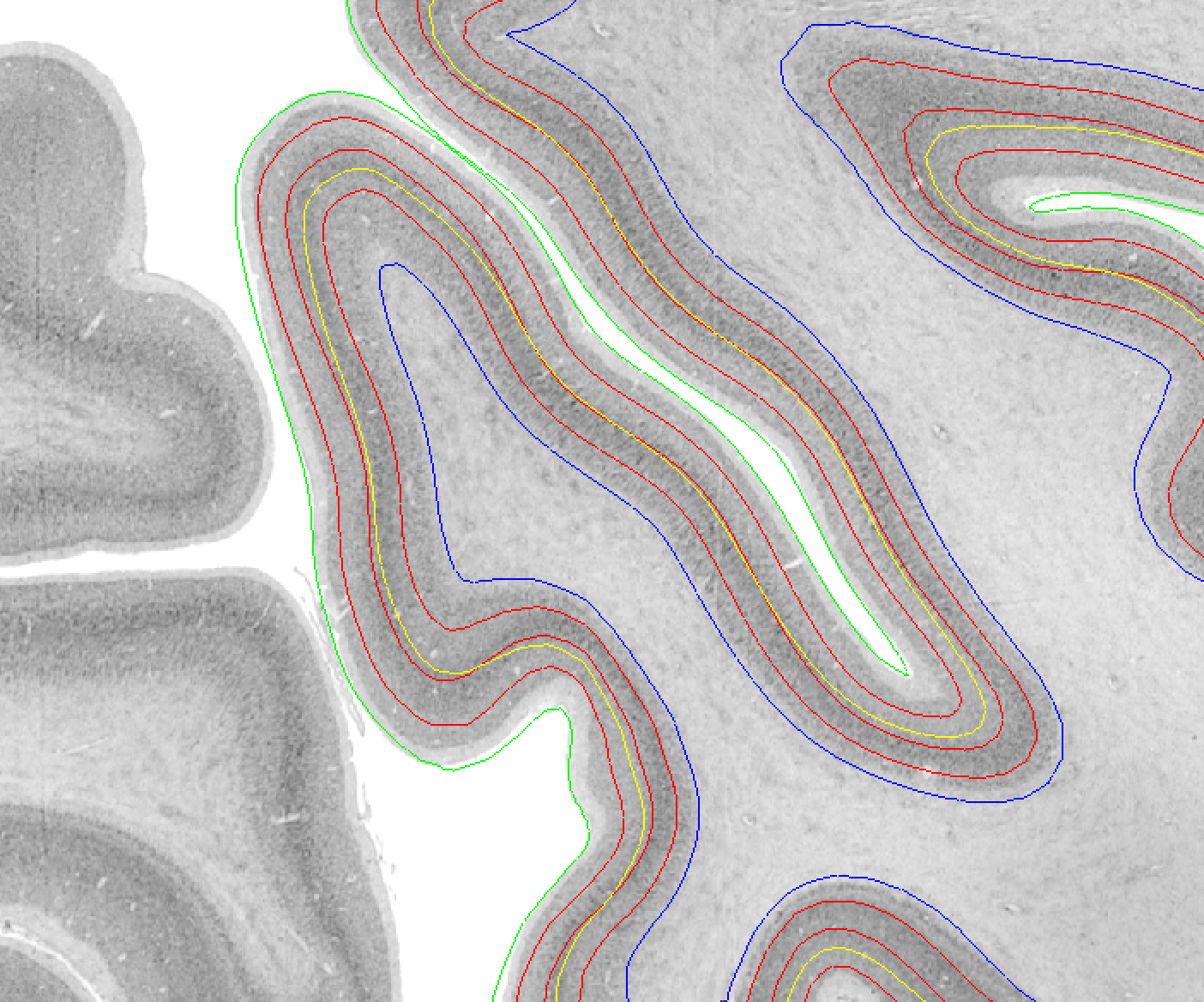 Equivolumetric surfaces (red) at 0.25, 0.5 and 0.75 cortical depth on the BigBrain. Euclidean surface (yellow) at mid depth. The euclidean surface samples different layers in gyri and sulci, while equivolumetric surfaces sample the gyri and sulci more consistently.
Equivolumetric surfaces (red) at 0.25, 0.5 and 0.75 cortical depth on the BigBrain. Euclidean surface (yellow) at mid depth. The euclidean surface samples different layers in gyri and sulci, while equivolumetric surfaces sample the gyri and sulci more consistently.
The code requires FreeSurfer to be installed.
This code has so far been tested on:
- python 2.7 and 3.6, freesurfer v.6 and on linux (Ubuntu 16.04) and macOS (10.12.6)
- Konrad Wagstyl ([email protected])
- David Hunt ([email protected])
- Franco Pestilli ([email protected])
Written by Konrad Wagstyl and Alexander Huth at a Brain Hack, a version is also available in Pyrocortex. Casey Paquola and Richard Bethlehem were involved in piloting these scripts on CIVET and FreeSurfer respectively.
The io_mesh code was copied and adapted from https://github.com/juhuntenburg/laminar_python, another great tool for doing volume-based equivolumetric laminar processing.
The equations for generating equivolumetric surfaces come from Waehnert et al 2014: "Anatomically motivated modeling of cortical laminae" https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.03.078
Code is demo-ed here on the BigBrain (Amunts et al., 2013), freely available histological atlas of the human brain https://bigbrain.loris.ca/
brainlife.io is publicly funded and for the sustainability of the project it is helpful to Acknowledge the use of the platform. We kindly ask that you acknowledge the funding below in your publications and code reusing this code.
We kindly ask that you cite the following articles when publishing papers and code using this code.
- Avesani, P., McPherson, B., Hayashi, S. et al. The open diffusion data derivatives, brain data upcycling via integrated publishing of derivatives and reproducible open cloud services. Sci Data 6, 69 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0073-y
You can submit this App online at https://doi.org/10.25663/brainlife.app.126 via the "Execute" tab.
- git clone this repo.
- Inside the cloned directory, create
config.jsonwith something like the following content with paths to your input files.
{
"n_surfs": 5,
"output": "./input/freesurfer/output",
"smoothing": 5
}
3. Launch the App by executing `main`
```bash
./mainIf you don't have your own input file, you can download sample datasets from Brainlife.io, or you can use Brainlife CLI.
npm install -g brainlife
bl login
mkdir input
bl dataset download 5a0662225ab38300be518f53 && mv 5a0662225ab38300be518f53 input/freesurfer
All output files will be generated under the current working directory (pwd). The main output of this App is a directory called output_surfaces. This file contains the 2n (rh and lh) generated equivolumetric surfaces (*.pial).
This App only requires singularity to run. If you don't have singularity, you will need to install following dependencies.






