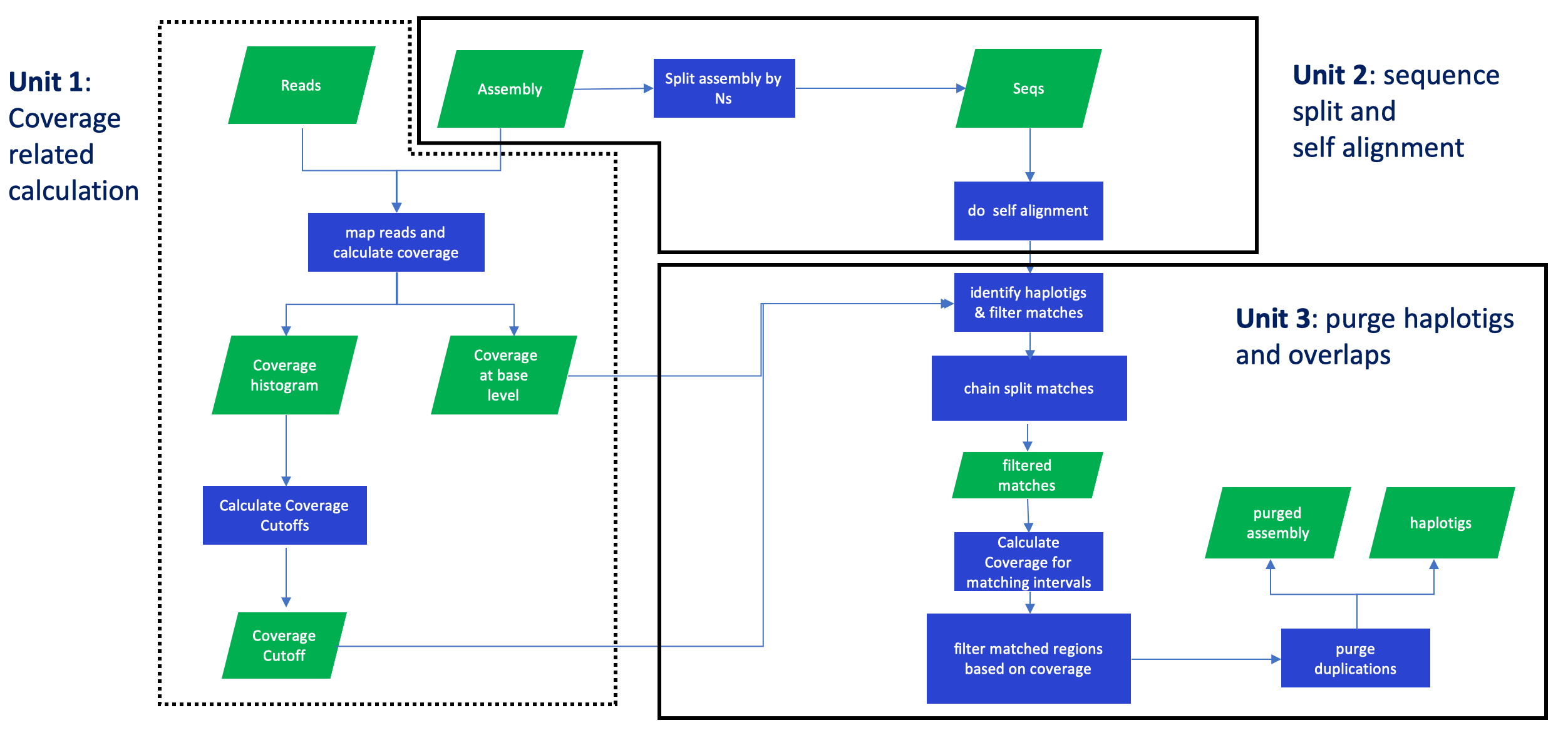
purge haplotigs and overlaps in an assembly based on read depth
- scripts/pd_config.py: script to generate a configuration file used by run_purge_dups.py.
- scripts/run_purge_dups.py: script to run the purge_dups pipeline.
- scripts/run_busco: script to run busco, dependency: busco.
- scripts/run_kcm: script to make k-mer comparison plot.
- scripts/sub.sh: shell script to submit a farm job.
- src: purge_dups source files.
- src/split_fa: split fasta file by 'N's.
- src/pbcstat: create read depth histogram and base-level read depth for an assembly based on pacbio data.
- src/ngstat: create read depth histogram and base-level read detph for an assembly based on illumina data.
- src/calcuts: calculate coverage cutoffs.
- src/purge_dups: purge haplotigs and overlaps for an assembly.
- src/get_seqs: obtain seqeuences after purging.
- bin/* : all purge_dups excutables.
purge_dups is designed to remove haplotigs and contig overlaps in a de novo assembly based on read depth.
You can follow the Usage part and use our pipeline to purge your assembly or go to the Pipeline Guide to build your own pipeline.
- zlib
- minimap2
- runner (optional)
- python3 (optional)
Run the following commands to intall purge_dups (required):
git clone https://github.com/dfguan/purge_dups.git
cd purge_dups/src && make
Run the following commands to install runner (optional), this is only needed when you want to run scripts/run_purge_dups.py:
git clone https://github.com/dfguan/runner.git
cd runner && python3 setup.py install --user
If you also want to try k-mer comparision plot, run the following commands to install the tool (optional).
git clone https://github.com/dfguan/KMC.git
cd KMC && make -j 16
usage: pd_config.py [-h] [-s SRF] [-l LOCD] [-n FN] [--version] ref pbfofn
generate a configuration file in json format
positional arguments:
ref reference file in fasta/fasta.gz format
pbfofn list of pacbio file in fastq/fasta/fastq.gz/fasta.gz format (one absolute file path per line)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-s SRF, --srfofn SRF list of short reads files in fastq/fastq.gz format (one record per line, the
record is a tab splitted line of abosulte file path
plus trimmed bases, refer to
https://github.com/dfguan/KMC) [NONE]
-l LOCD, --localdir LOCD
local directory to keep the reference and lists of the
pacbio, short reads files [.]
-n FN, --name FN output config file name [config.json]
--version show program's version number and exit
Example:
./scripts/pd_config.py -l iHelSar1.pri -s 10x.fofn -n config.iHelSar1.PB.asm1.json ~/vgp/release/insects/iHelSar1/iHlSar1.PB.asm1/iHelSar1.PB.asm1.fa.gz pb.fofn
configuration file is in json format, it has all the information required by run_purge_dups.py. Here is an example of a configuration file.
{
"cc": {
"fofn": "iHelSar1.pri/pb.fofn",
"isdip": 1,
"core": 12,
"mem": 20000,
"queue": "normal",
"bwa_opt":"",
"mnmp_opt":"",
"ispb": 1,
"skip": 0
},
"sa": {
"core": 12,
"mem": 10000,
"queue": "normal"
},
"busco": {
"core": 12,
"mem": 20000,
"queue": "long",
"skip": 0,
"lineage": "insecta",
"prefix": "iHelSar1.PB.asm1_purged",
"tmpdir": "busco_tmp"
},
"pd": {
"mem": 20000,
"queue": "normal"
},
"gs": {
"mem": 10000,
"oe": 1
},
"kcp": {
"core": 12,
"mem": 30000,
"fofn": "iHelSar1.pri/10x.fofn",
"prefix": "iHelSar1.PB.asm1_purged_kcm",
"tmpdir": "kcp_tmp",
"skip": 0
},
"ref": "/lustre/scratch116/vr/projects/vgp/user/dg30/dg30/projects/vgp/purge_dups/190508.primary/purge_dups/iHelSar1.pri/iHelSar1.PB.asm1.fa",
"out_dir": "iHelSar1.PB.asm1"
}
This file use several key words to define resource allocation, input files or output files, they are listed as follows.
- core: CPU number
- skip: Bool value set to skip this job
- prefix: Output file prefix
- fofn: Sequencing files list
- mem: Maximum amount of RAM in MB
- tmpdir: Temporary directory
- lineage: Busco database
- queue: job queue
- ref: Assembly file path
- out_dir: Working directory
- ispb: Bool value set for pacbio data, 0 for Illumina data
- oe: only remove the haplotypic duplications occuring at the ends of the contigs
Notice: isdip is deprecated.
The dictionary "kcp" keeps paramaters for run_kcm script.
The dictionary "gs" sets parameters for get_seqs (purge_dups executable file), designed to produce primary contigs and haplotigs.
The dictionary "pd" sets parameters for purge_dups (purge_dups executable file), designed to purge haplotigs and overlaps in an assembly.
The dictionary "cc" sets parameters for minimap2/bwa.
The dictionary "sa" sets parameters for minimap2.
The dictionary "busco" sets parameters for run_busco.
usage: run_purge_dups.py [-h] [-p PLTFM] [-w WAIT] [-r RETRIES] [--version]
config bin_dir spid
purge_dups wrapper
positional arguments:
config configuration file
bin_dir directory of purge_dups executable files
spid species identifier
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p PLTFM, --platform PLTFM
workload management platform, input bash if you want to run locally
-w WAIT, --wait WAIT <int> seconds sleep intervals
-r RETRIES, --retries RETRIES
maximum number of retries
--version show program's version number and exit
Example:
python scripts/run_purge_dups.py config.iHelSar1.json src iHelSar1
After the pipeline is finished, there will be four new directories in the working directory (set in the configuration file).
- coverage: coverage cutoffs, coverage histogram and base-level coverage files
- split_aln: segmented assembly file and a self-alignment paf file.
- purge_dups: duplicate sequence list.
- seqs: purged primary contigs ending with .purge.fa and haplotigs ending with .red.fa, also K-mer comparison plot and busco results are also in this directory.
If the busco and k-mer comparison plot scripts are working, please modify them with the following instructions.
- run_busco: set the PATH variables in run_busco script to your own related path.
- run_kcm: set kcm_dir variable in run_kcm script to your own KMC directory path.
Given a primary assembly pri_asm and an alternative assembly hap_asm (optional, if you have one), follow the steps shown below to build your own purge_dups pipeline, steps with same number can be run simultaneously. Among all the steps, although step 4 is optional, we highly recommend our users to do so, because assemblers may produce overrepresented seqeuences. In such a case, The final step 4 can be applied to remove those seqeuences.
Step 1. Run minimap2 to align pacbio data and generate paf files, then calculate read depth histogram and base-level read depth. Commands are as follows:
For PacBio CLR reads
for i in $pb_list
do
minimap2 -xmap-pb $pri_asm $i | gzip -c - > $i.paf.gz
done
bin/pbcstat *.paf.gz (produces PB.base.cov and PB.stat files)
bin/calcuts PB.stat > cutoffs 2>calcults.log
For PacBio CCS reads
for i in $pb_list
do
minimap2 -xasm20 $pri_asm $i | gzip -c - > $i.paf.gz
done
bin/pbcstat *.paf.gz (produces PB.base.cov and PB.stat files)
bin/calcuts PB.stat > cutoffs 2>calcults.log
Notice If you have a large genome, please set minimap2 -I option to ensure the genome can be indexed once, otherwise read depth can be wrong.
bin/split_fa $pri_asm > $pri_asm.split
minimap2 -xasm5 -DP $pri_asm.split $pri_asm.split | gzip -c - > $pri_asm.split.self.paf.gz
bin/purge_dups -2 -T cutoffs -c PB.base.cov $pri_asm.split.self.paf.gz > dups.bed 2> purge_dups.log
bin/get_seqs -e dups.bed $pri_asm
Notice this command will only remove haplotypic duplications at the ends of the contigs. If you also want to remove the duplications in the middle, please remove -e option at your own risk, it may delete false positive duplications. For more options, please refer to get_seqs -h.
- Read depth cutoffs calculation: the coverage cutoffs can be larger for a low heterozygosity species, which causes the purged assembly size smaller than expected. In such a case, please use script/hist_plot.py to make the histogram plot and set coverage cutoffs manually.
- Repeats: purge_dups has a limited ability to process repeats.
Q1 Can I use purge_dups with short reads?
Yes, purge_dups does have a program to process Illumina reads, it's called ngscstat under the bin directory. But I have not got time to test it. If you want to play with it, please follow this workflow:
bwa mem $pri_asm $sr_1.fq $sr_2.fq | samtools view -b -o - > $sr.bam
ngscstat $sr.bam... # The program will generate two/three outputs, TX.stat and TX.base.cov which functions the same way as PB.stat and PB.base.cov respectively.
After you get the TX.stat and TX.base.cov file, you can following the normal purge_dups routine to clean your assembly.
Q2 Can I validate the cutoffs used by purge_dups?
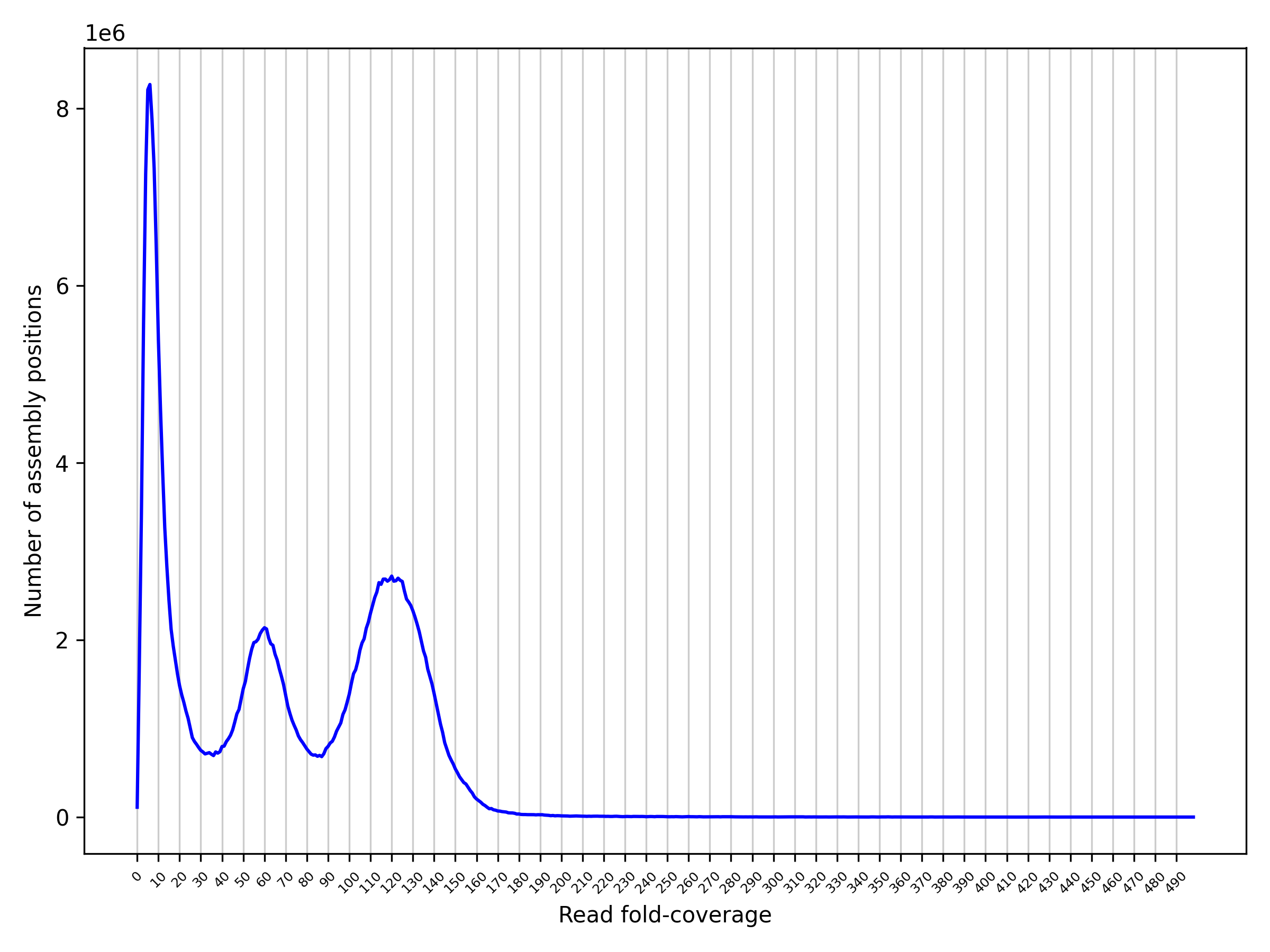
Yes, we highly recommend this step. A script "hist_plot.py" is available, you can use it to produce a coverage histogram:
pip install matplotlib
python3 scripts/hist_plot.py -c cutoff_file PB.stat PB.cov.pngQ2' How do I then set my own cutoffs?
From the coverage histogram, you need to set low, mid and high coverages:
- Contigs with average coverage below the low coverage threshold are set to 'JUNK' in
purge_dups' BED output. - mid coverage represents the transition between haploid and diploid coverages. Contigs with average coverage below mid coverage are tested for haplotypic duplications.
- Contigs with average coverage above high coverage are used for classifying contigs as
'REPEAT' in
purge_dups' BED output.
As an example, from the coverage histogram below:
you could use 5, 85 and 190 for low, mid and high respectively.
calcuts -l 5 -m 85 -u 200 PB.stat > cutoffs_manual
bin/purge_dups -2 -T cutoffs_manual -c PB.base.cov $pri_asm.split.self.paf.gz > dups.bed 2> purge_dups.logQ3 How can I validate the purged assembly? Is it clean enough or overpurged?
There are many ways to validate the purged assembly. One way is to make a coverage plot for it which can also be hist_plot.py, the 2nd way is to run BUSCO and another way is to make a KAT plot with KAT (https://github.com/TGAC/KAT) or KMC (https://github.com/dfguan/KMC, use this if you only have a small memory machine) if short reads or some accurate reads are available.
Q4 Why do I get much fewer haplotypic duplications than expected?
First check the original contig names, they should not contain any colons. Then check the cutoffs, if purge_dups automatically use a fairly low read depth for haplotypic duplications, it may remove nothing. In this case, you need to set the cutoffs manually.
Q5 why does purge_dups remove middle sequence in a contig?
Some of them are real, while others may not. We are currently investigating them. Please use -e for get_seqs command if you only want to remove the duplications at the ends of the contigs.
Wellcome to use, you can use github webpage to report an issue or email me [email protected] with any advice.