OADP is OpenShift Application Data Protection operator. This operator sets up and installs Velero on the OpenShift platform.
- Docker/Podman
- OpenShift CLI
- Access to OpenShift cluster
You can install the OADP Operator from the Openshift's OperatorHub. You can search for the operator using keywords like oadp or velero
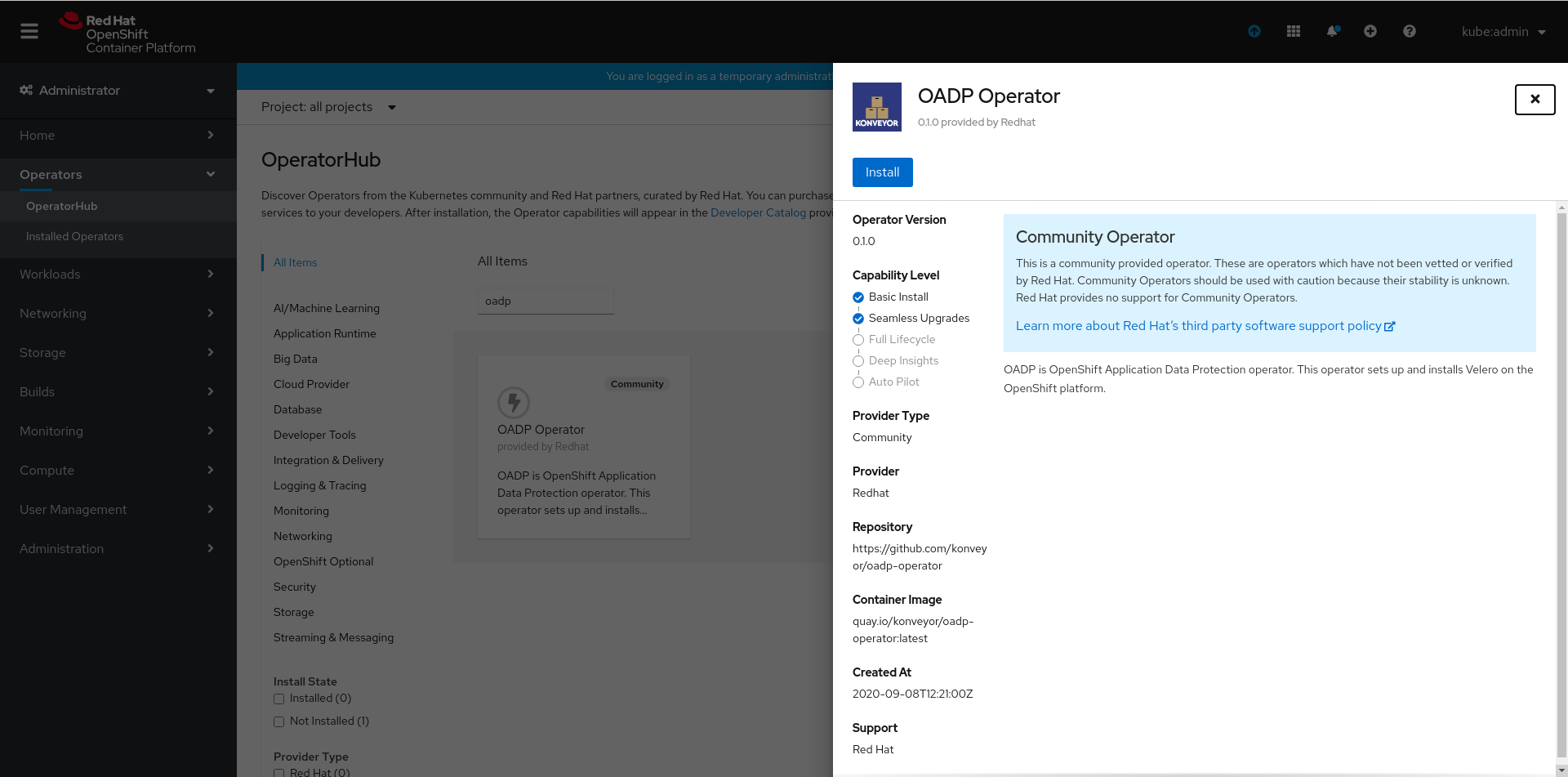
Now click on Install
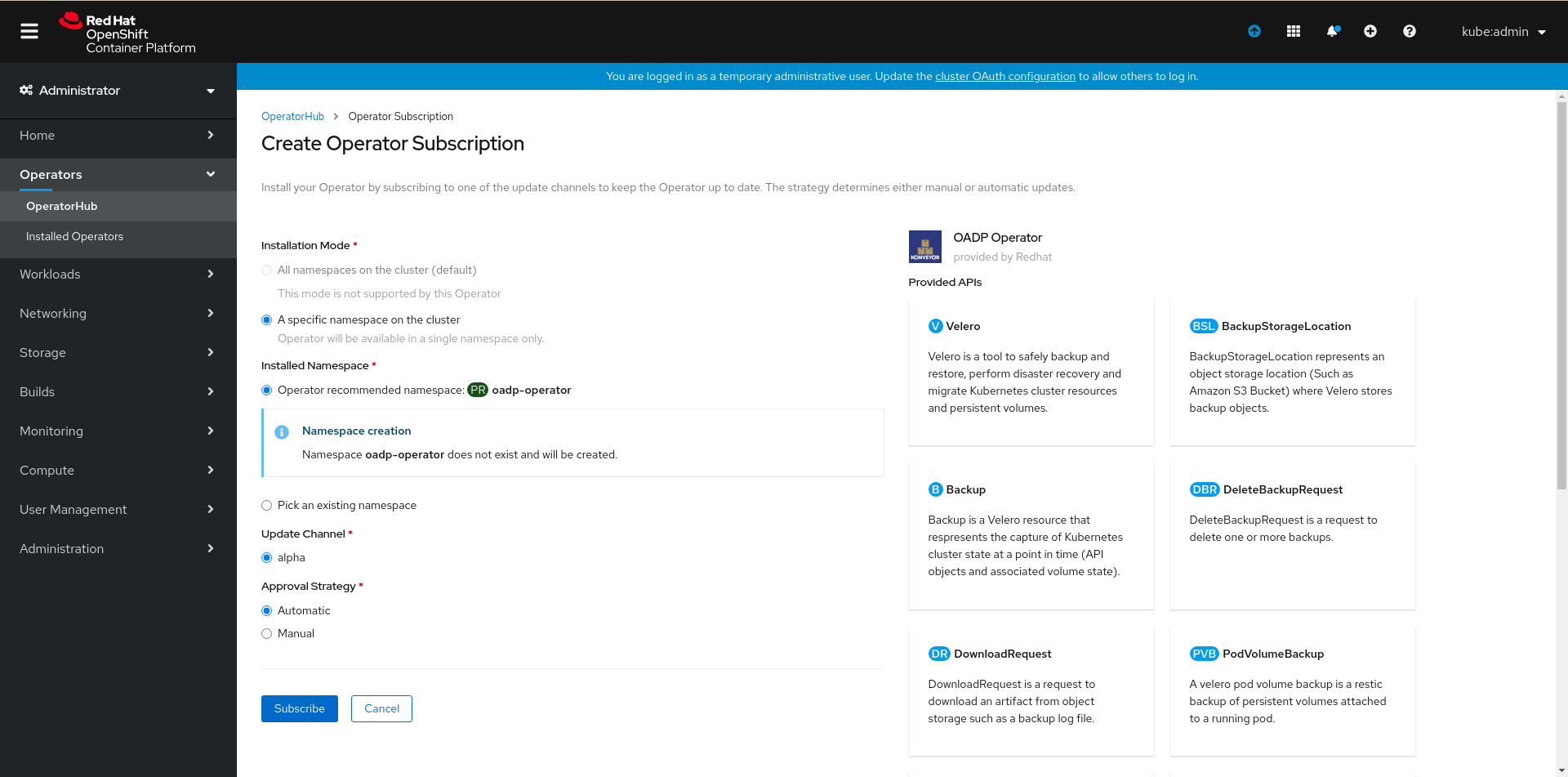
Finally, click on subscribe, this will create a namespace named oadp-operator if it does not exist and install the OADP operator in it.
Create secret for the cloud provider credentials to be used. Also, the credentials file present at CREDENTIALS_FILE_PATH shoud be in proper format, for instance if the provider is AWS it should follow this AWS credentials template
oc create secret generic <SECRET_NAME> --namespace oadp-operator --from-file cloud=<CREDENTIALS_FILE_PATH>
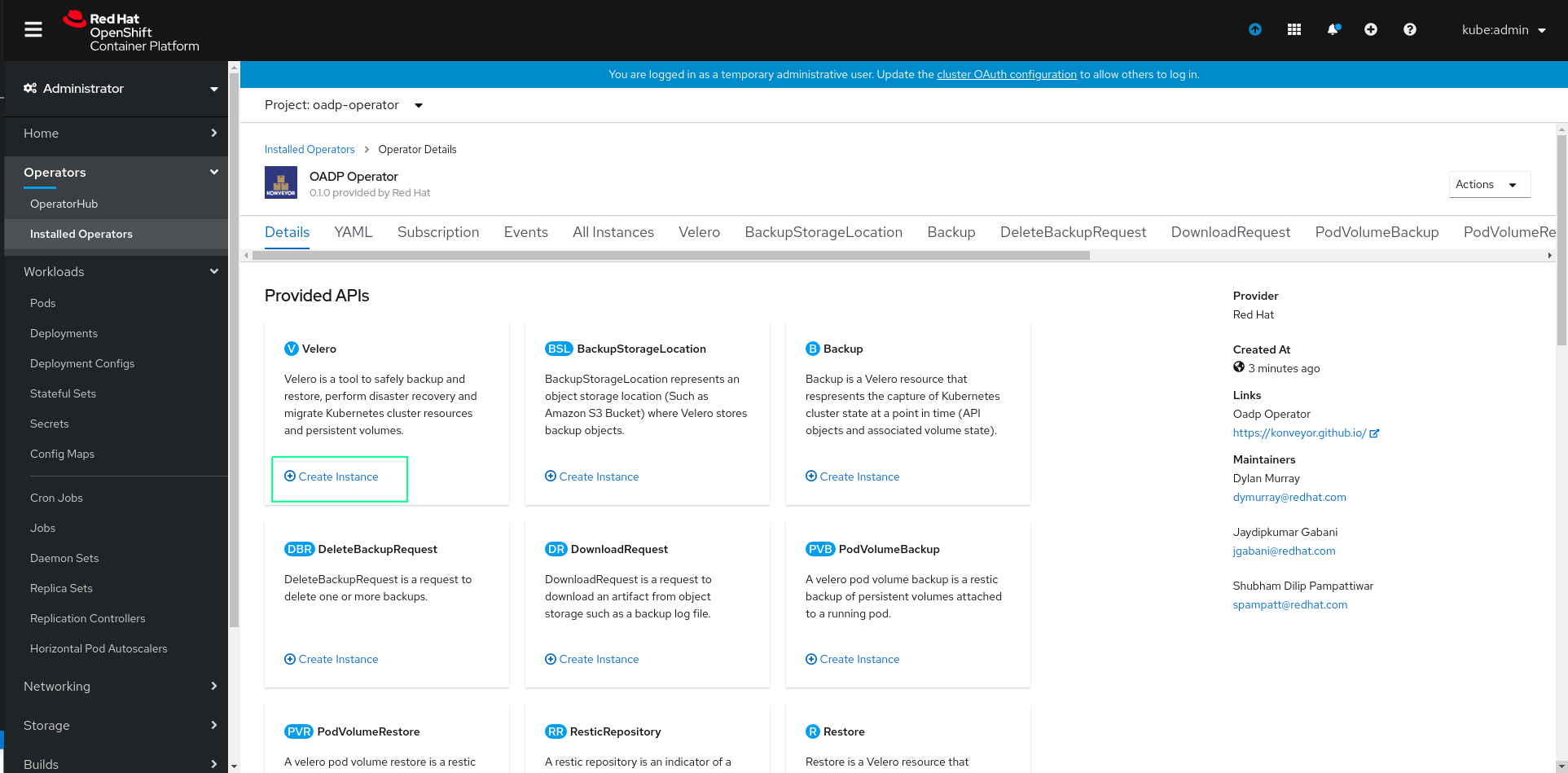
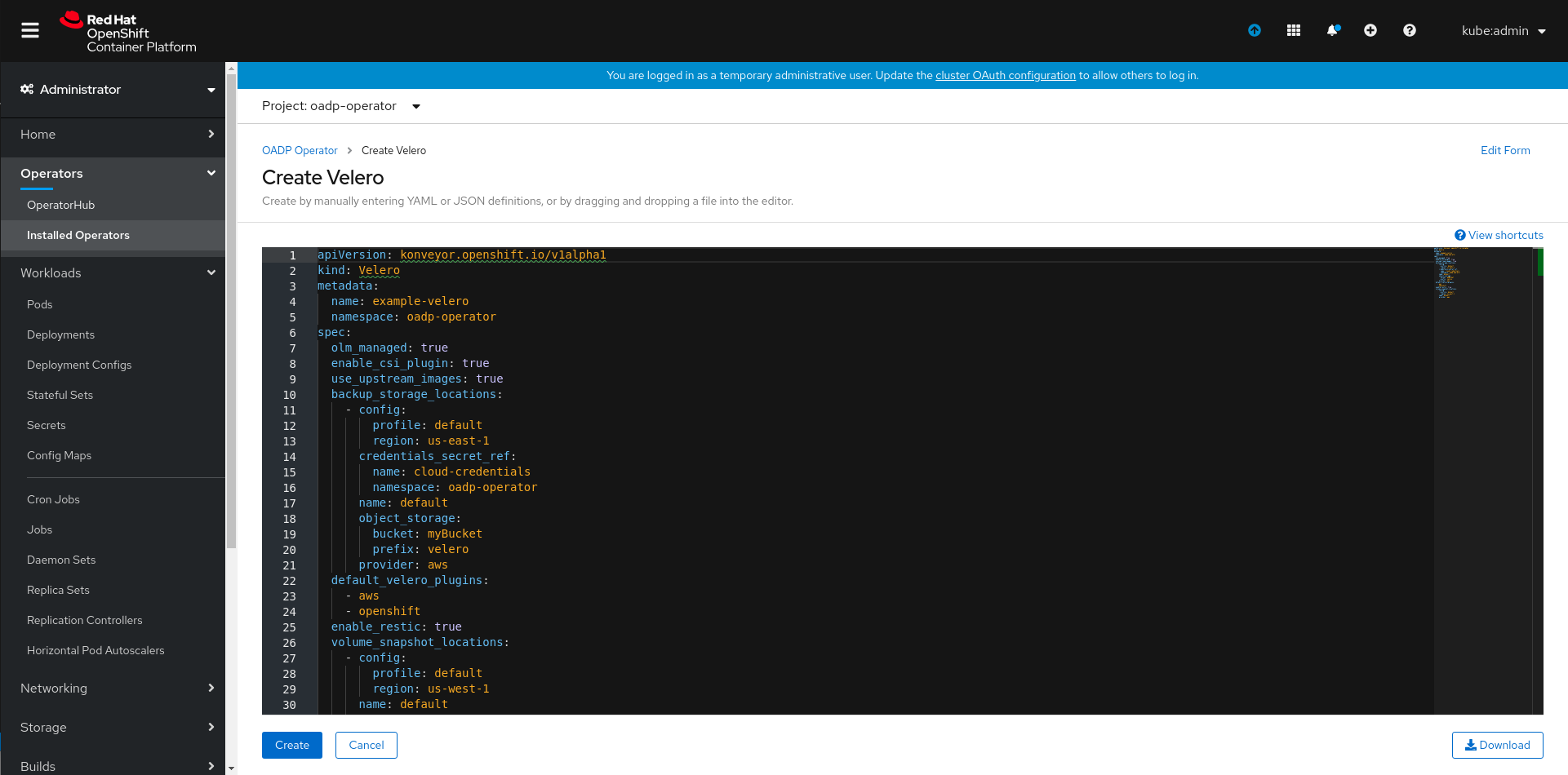
Now create an instance of Velero CR by clicking on Create Instance as highlighted below:
Finally, set the CR spec values appropriately and click on create.
Checkout this OADP Operator repository:
git clone [email protected]:konveyor/oadp-operator.git
cd oadp-operator
Build the OADP operator image and push it to a public registry (quay.io or dockerhub)
There are two ways to build the operator image:
- Using operator-sdk
operator-sdk build oadp-operator - Using Podman/Docker
podman build -f build/Dockerfile . -t oadp-operator:latest
After successfully building the operator image, push it to a public registry.
In order to use a locally built image of the operator, please update the operator.yaml file. Update the image of the oadp-operator container with the image registry URL. You can edit the file manually or use the following command( <REGISTRY_URL> is the placeholder for your own registry url in the command):
sed -i 's|quay.io/konveyor/oadp-operator:latest|<REGISTRY_URL>|g' deploy/operator.yaml
For OSX, use the following command:
sed -i "" 's|quay.io/konveyor/oadp-operator:latest|<REGISTRY_URL>|g' deploy/operator.yaml
Before proceeding further make sure the image is updated in the operator.yaml file as discussed above.
To install OADP operator and the essential Velero components follow the steps given below:
- Create a new namespace named
oadp-operatoroc create namespace oadp-operator - Switch to the
oadp-operatornamespaceoc project oadp-operator - Create secret for the cloud provider credentials to be used. Also, the credentials file present at
CREDENTIALS_FILE_PATHshoud be in proper format, for instance if the provider is AWS it should follow this AWS credentials templateoc create secret generic <SECRET_NAME> --namespace oadp-operator --from-file cloud=<CREDENTIALS_FILE_PATH> - Now to create the deployment, role, role binding, cluster role, cluster rolebinding, and service account, use the following command:
oc create -f deploy/non-olm - Deploy the Velero custom resource definition:
oc create -f deploy/crds/konveyor.openshift.io_veleros_crd.yaml - Finally, deploy the Velero CR:
oc create -f deploy/crds/konveyor.openshift.io_v1alpha1_velero_cr.yaml
Post completion of all the above steps (Non-OLM or OLM), you can check if the operator was successfully installed or not, the expected result for the command oc get all -n oadp-operator is as follows:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/oadp-operator-7749f885f6-9nm9w 1/1 Running 0 6m6s
pod/restic-48s5r 1/1 Running 0 2m16s
pod/restic-5sr4c 1/1 Running 0 2m16s
pod/restic-bs5p2 1/1 Running 0 2m16s
pod/velero-76546b65c8-tm9vv 1/1 Running 0 2m16s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/oadp-operator-metrics ClusterIP 172.30.21.118 <none> 8383/TCP,8686/TCP 5m51s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
daemonset.apps/restic 3 3 3 3 3 <none> 2m17s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/oadp-operator 1/1 1 1 6m7s
deployment.apps/velero 1/1 1 1 2m17s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/oadp-operator-7749f885f6 1 1 1 6m7s
replicaset.apps/velero-76546b65c8 1 1 1 2m17s
Note: For using the velero CLI directly configured for the oadp-operator namespace, you may want to use the following command:
velero client config set namespace=oadp-operator
There are mainly two categories of velero plugins that can be specified while installing Velero:
default-velero-plugins:
Five types of default velero plugins can be installed - AWS, GCP, Azure, OpenShift, and CSI. For installation, you need to specify them in thekonveyor.openshift.io_v1alpha1_velero_cr.yamlfile during deployment.The above specification will install Velero with all five default plugins.apiVersion: konveyor.openshift.io/v1alpha1 kind: Velero metadata: name: example-velero spec: default_velero_plugins: - azure - gcp - aws - openshift - csi
Note:
- For usage of the
csiplugin with Velero you will need to additionally set--features=EnableCSI, please refer the section titled Usage of Velero--featuresoption for more details. This repository has more information about the CSI plugin. - Similarly, for installation of
vsphereplugin, please refer the section titled Usage of Velero--featuresoption for more details. This repository has more information about the vSphere plugin.
-
custom-velero-plugin:
For installation of custom velero plugins, you need to specify the pluginimageand pluginnamein thekonveyor.openshift.io_v1alpha1_velero_cr.yamlfile during deployment.For instance,
apiVersion: konveyor.openshift.io/v1alpha1 kind: Velero metadata: name: example-velero spec: default_velero_plugins: - azure - gcp custom_velero_plugins: - name: custom-plugin-example image: quay.io/example-repo/custom-velero-pluginThe above specification will install Velero with 3 plugins (azure, gcp and custom-plugin-example).
Velero supports backup storage locations and volume snapshot locations from a number of cloud providers (AWS, Azure and GCP). Please refer the section configure Backup Storage Locations and Volume Snapshot Locations.
In order to use the upstream images for Velero deployment as well as its plugins, you need to set a flag use_upstream_images as true in the konveyor.openshift.io_v1alpha1_velero_cr.yaml during installation of the operator.
Note: If the flag use_upstream_images is set, the registry will be switched from quay.io to docker.io and v1.4.0 (current upstream version) image tag will be used for Velero and latest image tag will be used for the plugins.
By default, the Velero deployment requests 500m CPU, 128Mi memory and sets a limit of 1000m CPU, 256Mi. Customization of these resource requests and limits may be performed using steps specified in the Resource requests and limits customization section.
If you intend to use Velero with a storage provider that is secured by a self-signed certificate, you may need to instruct Velero to trust that certificate. See Use self-sigend certificate section for details.
Some of the new features in Velero are released as beta features behind feature flags which are not enabled by default during the Velero installation. In order to provide --features flag values, you need to use the specify the flags under velero_feature_flags: in the konveyor.openshift.io_v1alpha1_velero_cr.yaml file during deployment.
Some of the usage instances of the --features flag are as follows:
- Enabling Velero plugin for CSI: To enable CSI plugin you need to add two things in the
konveyor.openshift.io_v1alpha1_velero_cr.yamlfile during deployment.- First, add
csiunder thedefault_velero_plugins - Second, add
EnableCSIunder thevelero_feature_flags
- First, add
default_velero_plugins:
- csi
velero_feature_flags: EnableCSI
- Enabling Velero plugin for vSphere: To enable vSphere plugin you need to do the following things in the
konveyor.openshift.io_v1alpha1_velero_cr.yamlfile during deployment.- First, add
vsphereunder thedefault_velero_plugins - Second, add
EnableLocalModeunder thevelero_feature_flags - Lastly, add the flag
use_upstream_imagesand set it astrue.
- First, add
default_velero_plugins:
- vsphere
velero_feature_flags: EnableLocalMode
use_upstream_images: true
Note: The above is an example of installing the Velero plugin for vSphere in LocalMode . Setting EnableLocalMode features flag is not always necessary for the usage of vSphere plugin but the pre-requisites must be satisfied and appropriate configuration must be applied, please refer Velero plugin for vSphere for more details. Also, if you plan on using multiple feature flags at once, pass them to velero_feature_flags as comma seperated values, for instance, velero_feature_flags: EnableLocalMode,EnableCSI
For installing/uninstalling the OADP operator directly from OperatorHub, follow this document OLM Integration for details.
Install OADP Operator and use NooBaa as a BackupStorageLocation
Cleanup OADP Operator with NooBaa
For cleaning up the deployed resources, use the following commands:
oc delete -f deploy/crds/konveyor.openshift.io_v1alpha1_velero_cr.yaml
oc delete -f deploy/crds/konveyor.openshift.io_veleros_crd.yaml
oc delete -f deploy/non-olm/
oc delete namespace oadp-operator
oc delete crd $(oc get crds | grep velero.io | awk -F ' ' '{print $1}')
Following are some of the examples where OADP Operator is used:
-
OADP Capstone: This repository showcases steps describing the overall workflow of using the OADP Operator, these steps provide detailed instructions right from installing the operator, to using it in order to perform backup and restore operations for complex applications like Cassandra and Postgres.
-
Velero Examples: This repository consists of a collection of examples with Velero custom resource to show backup and restore workflows.
By default, OADP will install the forked versions of Velero that exist under the konveyor organization. These images have minor tweaks to support the OpenShift specific use cases of using Velero with OCP. The konveyor images tend to lag behind Velero upstream releases as we are more cautious about supporting older versions. Here is the default mapping of versions:
| OADP Version | Velero Version |
|---|---|
| v0.1.1 | v1.4.1 |
| v0.1.2 | v1.4.2 |
| v0.1.3 | v1.4.2 |
| v0.1.4 | v1.4.2 |
| v0.2.0 | v1.5.2 |
Optionally, you can set use_upstream_images: true to force OADP to install the upstream Velero images (which defaults to v1.5.2) but note that this is not technically supported by OADP with the default plugins installed as it does not get tested.