eShopOnSteroids is a well-architected, distributed, event-driven, domain-driven, server-side e-commerce application powered by the following building blocks of microservices:
- API Gateway (Spring Cloud Gateway)
- Service Discovery (Netflix Eureka)
- Distributed Tracing (Sleuth, Zipkin)
- Circuit Breaker (Resilience4j)
- Message Bus (RabbitMQ)
- Database per Microservice (PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Redis)
- Centralized Monitoring (Prometheus, Grafana)
- Control Loop (Kubernetes, Terraform)
This code follows best practices such as:
- Unit Testing (JUnit 5, Mockito)
- Integration Testing (Testcontainers)
- Design Patterns (Builder, Singleton, PubSub, ...)
microservices, event-driven, distributed systems, e-commerce, domain-driven-design, spring cloud, spring boot, spring cloud gateway, spring cloud config, spring cloud sleuth, zipkin, resilience4j, postgresql, mongodb, redis, cache, kubernetes, k8s, prometheus, grafana, rabbitmq, terraform
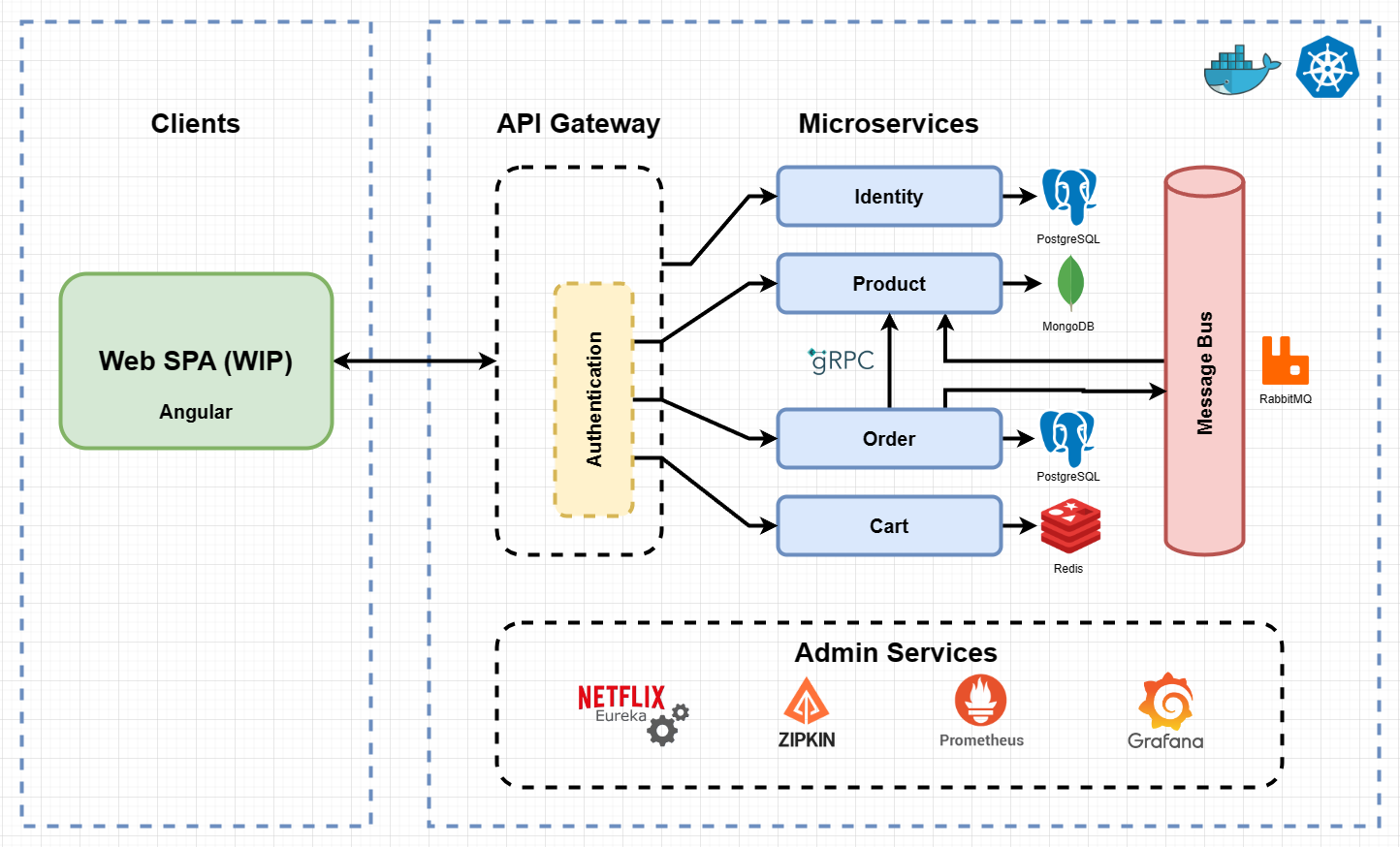
The architecture proposes a microservices oriented implementation where each microservice is responsible for a single business capability. The microservices are deployed in a containerized environment (Docker) and managed by a control loop (Kubernetes) which compares the state of each microservice to the desired state, and takes necessary actions to constantly achieve the desired state.
Each microservice stores its data in its own database tailored to its requirements, such as an In-Memory Database for a shopping cart whose persistence is short-lived, a Document Database for a product catalog for its flexibility, or a Relational Database for an order management system for its ACID properties.
Microservices communicate externally via REST through a secured API Gateway, and internally via
- gRPC for synchronous communication which excels for its performance
- a message bus for asynchronous communication in which the receiving microservice is free to handle the message whenever it has the capacity
Below is a visual representation:
- All microservices are inside a private network and not accessible except through the API Gateway.
- The API Gateway routes requests to the appropriate microservice, and validates the authorization of requests to all microservices except the Identity Microservice.
- The Identity Microservice acts as an Identity Issuer and is responsible for storing users and their roles, and for issuing authorization credentials.
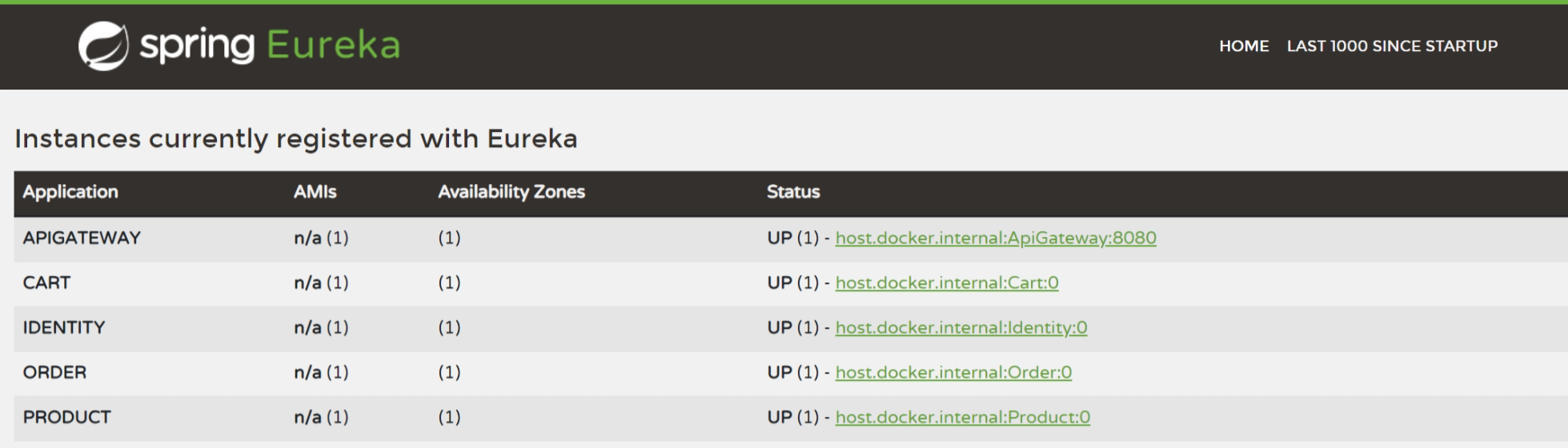
- All microservices send periodic heartbeats to the Discovery Server which helps them locate each other as they may have multiple instances and IP addresses.
- The Cart Microservice manages the shopping cart of each user. It uses a cache (Redis) as the storage.
- The Product Microservice stores the product catalog and stock. It's subscribed to the Message Bus to receive notifications of new orders and update the stock accordingly.
- The Order Microservice manages order processing and fulfillment. It performs a gRPC call to the Product Microservice to check the availability of the products in the order pre-checkout, and publishes a message to the Message Bus when an order is placed successfully.
- The gRPC communication between the microservices is fault-tolerant and resilient to transient failures thanks to Resilience4j Circuit Breaker.
Admin services include:
- Eureka dashboard to monitor the availability of microservices
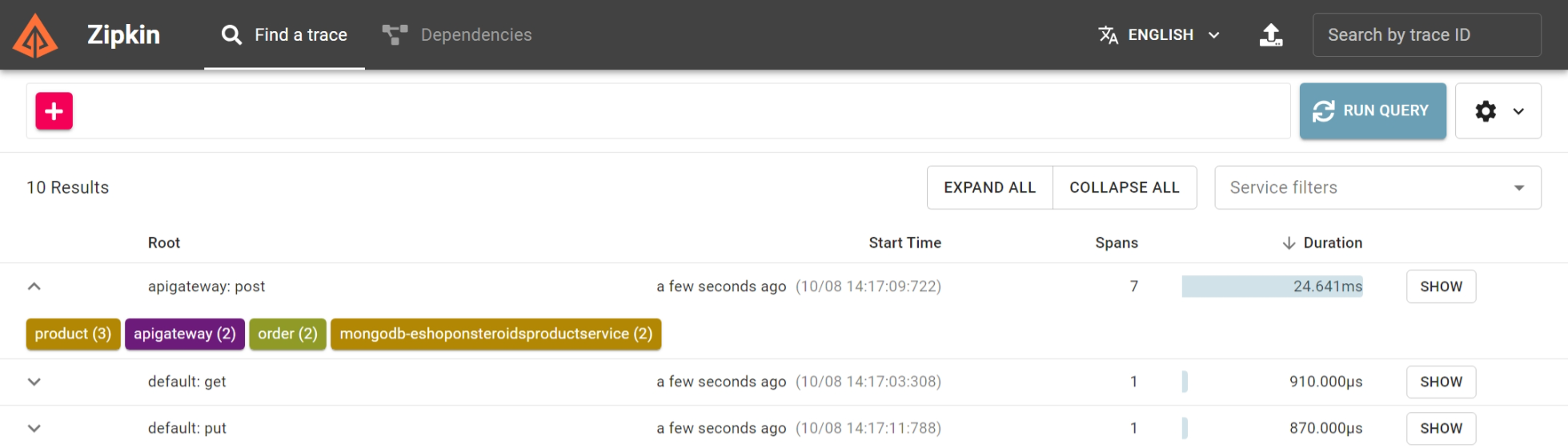
- Zipkin dashboard for tracing requests across microservices
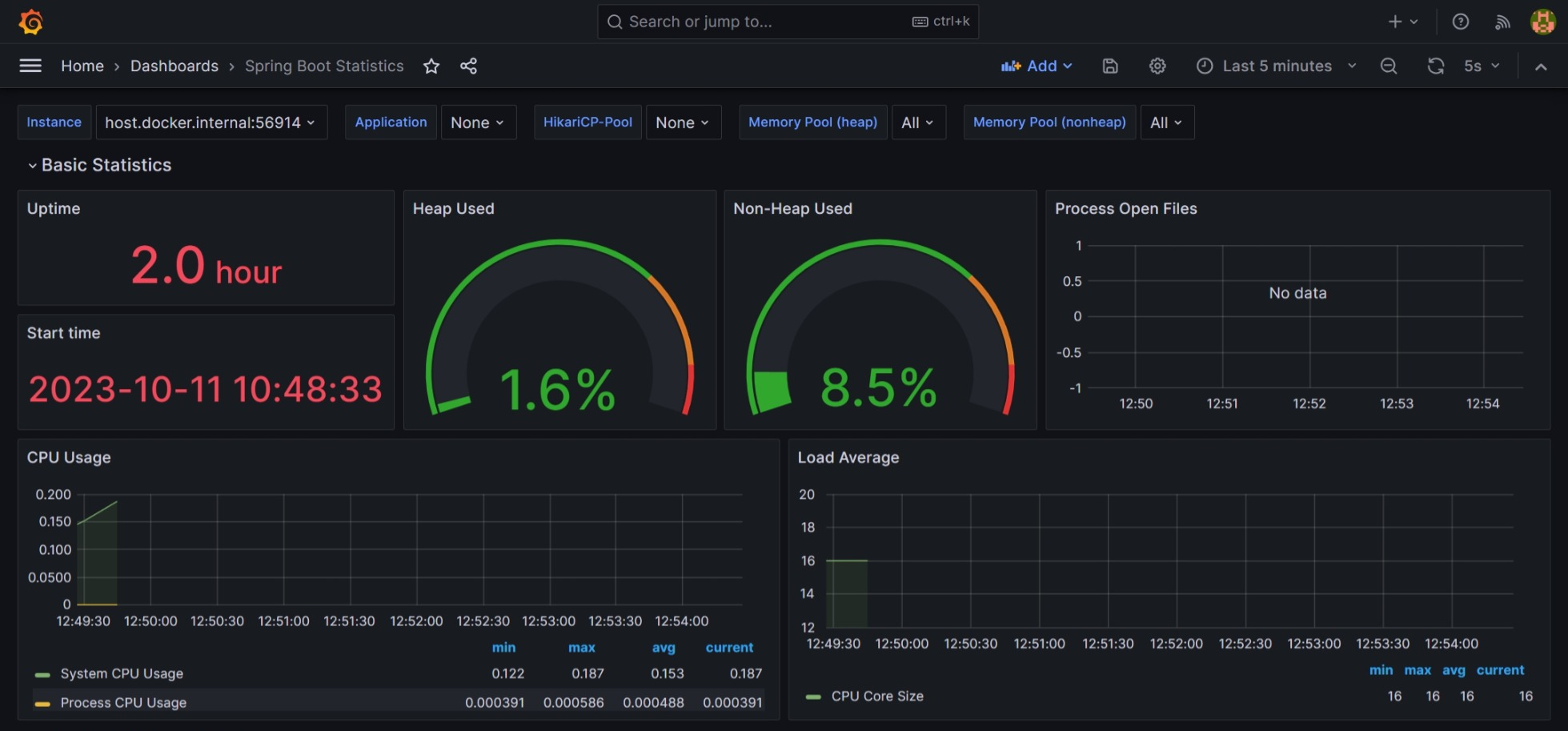
- Grafana dashboard for visualizing the metrics of microservices and setting up alerts for when a metric exceeds a threshold
Having Docker and Docker Compose installed, run the following command to start the application:
docker compose up -dIt will take a few minutes to download the required images and create the containers.
Ensure you have a Kubernetes cluster running, and run the following command to deploy the application:
kubectl apply -f k8sThe interface (a Single-Page Application) is still a work in progress, but the available endpoints can be found in the API documentation which post-deployment can be accessed at:
- Java 17+
- Docker
To run the unit tests, run the following command:
mvnw test- Make sure you have Docker installed and running
- Run the following command to start the testcontainers:
mvnw verify