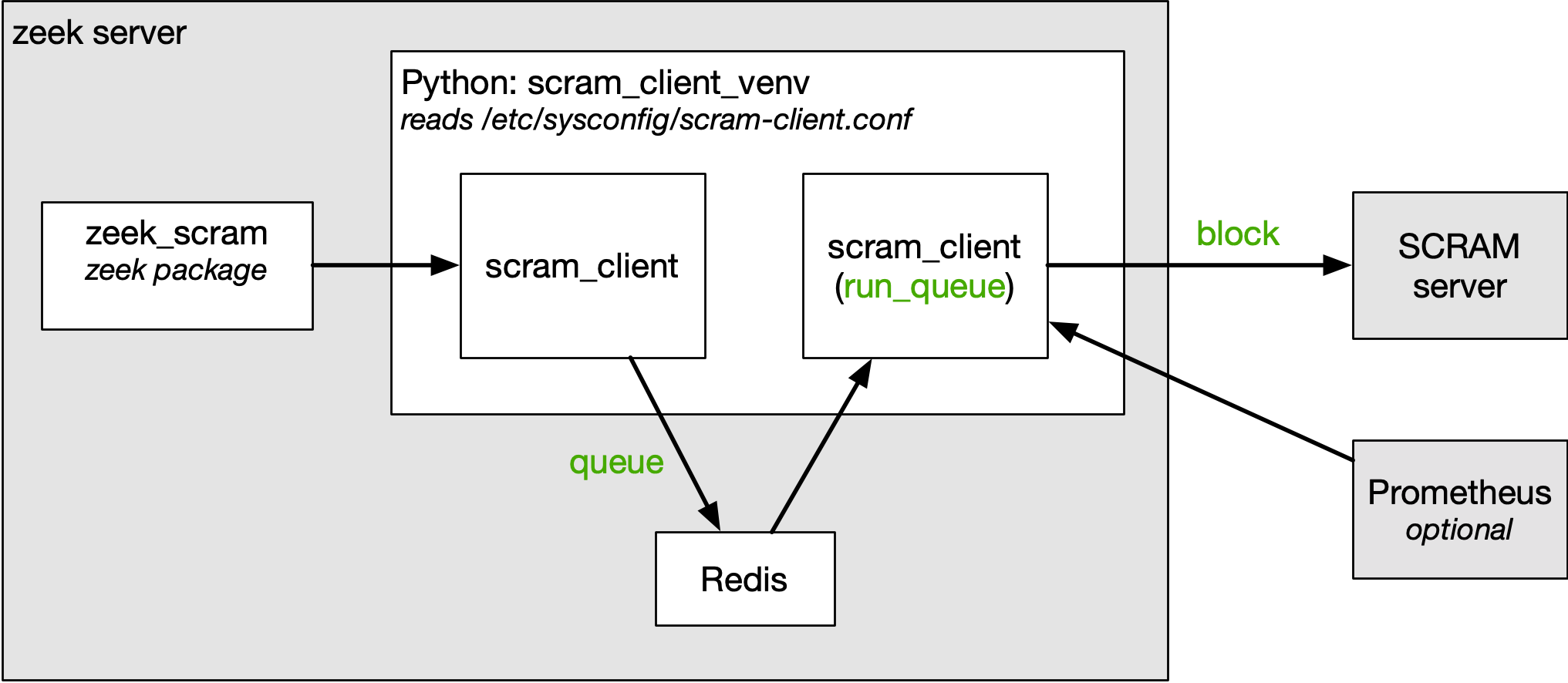
This is the client python script that needs to be installed on a system in order to inject blackhole router blocks w/ SCRAM.
The scram-client requires a locally running Redis server if you intend to use the queue mode. There are also several python module dependencies (see below).
The scram-client is generally installed into a python3 virtual environment via:
(scram_client_venv)$ pip install git+https://github.com/esnet-security/scram-client.git#egg=scram_client
or via ansible, similar to:
- name: Install Shared Pip Dependencies
pip:
name: "{{ item }}"
virtualenv: "{{ scram_client_venv }}"
loop:
- "git+https://github.com/esnet-security/scram-client.git#egg=scram_client"
- "requests"
- "prometheus-client"
- "walrus"
become: true
become_user: "{{ scram_client_user }}"
If you will be using the queue manager functionality as well, a template systemd file would look as follows:
[Unit]
Description=scram queue management
After=network.target
[Service]
User={{ scram_client_user }}
EnvironmentFile=/etc/sysconfig/scram-client.conf
ExecStart={{ scram_client_venv }}/bin/scram-client run_queue
Restart=always
RestartSec=10s
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
The scram client requires a few variables to be set either in the environment or in a configuration file at /etc/sysconfig/scram-client.conf.
[SCRAM]
SCRAM_HOST=scram-server.my.network
SCRAM_UUID=012a3f45-6789-1234-ab56-7890b12c345d
SCRAM_PROMETHEUS_PORT=9115
SCRAM_LOGLEVEL=INFO
The UUID can either be assigned by the SCRAM administrator or a client can register itself using the API. A registered client still needs to have the SCRAM administrator authorize the client.
Auto-registration:
$ source scram_client_venv/bin/activate
(scram_client_venv)$ scram-client register [server hostname]
The simplest mode is 'block.' As the name implies this allows you to send a block directly to SCRAM without any queue'ing taking place. It's also a good way to make sure your client is configured and working properly.
$ source scram_client_venv/bin/activate
(scram_client_venv)$ cat testblock
10.1.1.4
my_note
my_msg
my_sub
600
(scram_client_venv)$ scram_client block < testblock
INFO:root:Successfully blocked 10.1.1.4 for my_note: my_msg my_sub.
Queue mode works in much the same way from the user perspective, but instead of directly blocking the IP, the block request is added to a queue via Redis.
Run_queue mode is generally managed via systemd and simply reads the Redis queue and then performs the 'block' mode operation.
The register comand simply generates a new UUID and sends it to the SCRAM server to initliaze a new client. The SCRAM admin then needs to authorize the client as well as allow whichever actiontypes for that client in the SCRAM admin webUI.
We use zeek here as an example service that uses the scram-client: