A Package for managing cell type about color and markers while processing scRNA-seq data.
It's easy to install cellmanager via pip!
pip install cellmanager-
First, the user should prepare a TOML file as below.
[Immnue] [Immnue.Lyphoid] [Immnue.Lyphoid.T] color = "#1ba169" markers = ["CD3D", "CD3E", "CD3G", "CD8A", "TRBC2"] [Immnue.Lyphoid.T."CD8+ T"] markers = ["CD8A", "CD8B"] [Immnue.Lyphoid.T."CD4+ T"] markers = ["CD40LG", "FOXP3", "CD4"] [Immnue.Lyphoid.NK] color = "#014431" markers = ["GNLY", "NKG7", "FGFBP2", "FCGR3A", "CX3CR1", "KLRB1", "NCR1"]
Let me explain the basic logic of the data structure in the TOML file:
-
Top-level category (like [Immune] in the example above): The top-level category is indicated with square brackets []. In this case, [Immune] defines the main section of the file, grouping all immune-related data.
-
Nested subcategories [Immune.Lyphoid]: You can create nested sections by using dot notation (e.g., Lyphoid under Immune). This creates a hierarchical structure to organize related data within the top-level category.
-
Further sub-nesting [Immune.Lyphoid.T]: Further subcategories can be defined by continuing to nest sections using dots. For example, [Immune.Lyphoid.T] indicates a further refinement under Lyphoid.
-
Attributes: Inside each section, key-value pairs define attributes.
For most usage cases,
colorandmarkersare used frequently.color = "#1ba169" assigns a color attribute, and markers = [...] defines a list of markers.
[!TIP]
We have designed the # character as a placeholder to keep the hierarchy consistent. We will introduce this below, so don't worry.
-
-
Create a CellManager object
from cellmanager import CellManager manager = CellManager("data.toml") # Input your TOML file path here.
-
Visualize your cell-type view
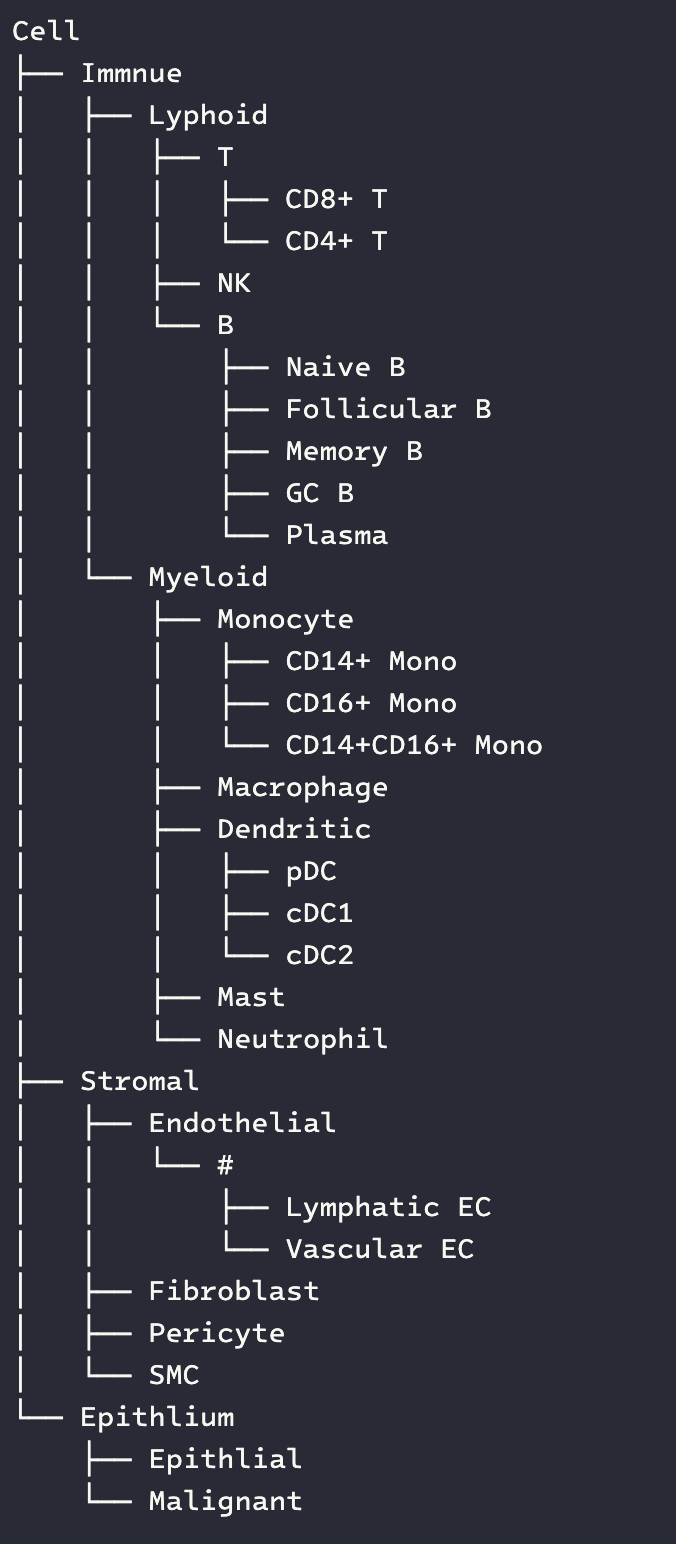
# tree manager.render_tree() # level group manager.render_lavel_table()
[!NOTE]
The # character is used as a placeholder to keep related cell types at the same level.
-
Visualize the markers of cell-type
# markers of all cell type manager.render_markers_table() # markers of specific cell type manager.render_markers_table(cluster="Endothelial")
-
Query information
-
byandkeyare the two most important parameters inCellManager.query()function. -
infocontrol to outputcolorormarkers, defaultmarkers -
output_formatcontrol to output asdictorlist, defaultdict.
We provide three query methods:
-
Query by cluster
by = "cluster"
key =
Which cluster do you want to know(like "T" as below)include_major is a bool parameter controlling whether to output the major cell type.
Example:
-
Query by level
[!WARNING]
If you want to query by level, you must first run the
CellManager.render_level_table()function to ensure that the user confirms the level informationby = "level"
key =
Which level do you want to knowExample:
As shown above, there are eight cell types in the level 3.
-
Query by a custom list
Also, if you want to query a custom list you are interested in, you can use this method
by = "list"
key = [...] everything you want to query
-