This is the project web for the study titled "Predicting Myocardial Infarction through Retinal Scans and Minimal Personal Information". This study is accepted for publication in Nature Machine Intelligence.
Retinal images are routinely obtained in ophthalmologic practice to aid diagnosis and monitoring of both primary eye diseases and systemic conditions affecting the eye, such as diabetic retinopathy. Recent studies have shown that biomarkers on retinal images, e.g. retinal blood vessels density or tortuosity, are associated with cardiac function and may be used to identify patients at risk of coronary artery disease. In this work, we investigate the use of retinal images together with relevant patient metadata, to estimate left ventricular mass (LVM) and left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV), and subsequently, predict incident myocardial infarction. We trained a multi-channel variational autoencoder (mcVAE) and a deep regressor model to estimate LVM (4.4 (-32.30, 41.1) g) and LVEDV (3.02 (-53.45, 59.49) ml) and predict risk of myocardial infarction (AUC=0.80+/-0.02, Sensitivity=0.76+/-0.02, Specificity=0.73+/-0.05) using just the retinal images and demographic data. Our results indicate that routine retinal imaging could be used to identify patients at high-risk of future myocardial infarction.
We used the UK Biobank dataset UKB (application # 11350 PDF) to train and validate the proposed method. Our method is based on the work published in ICML by Antelmi et al. PDF. External validation was performed on AREDS dataset.
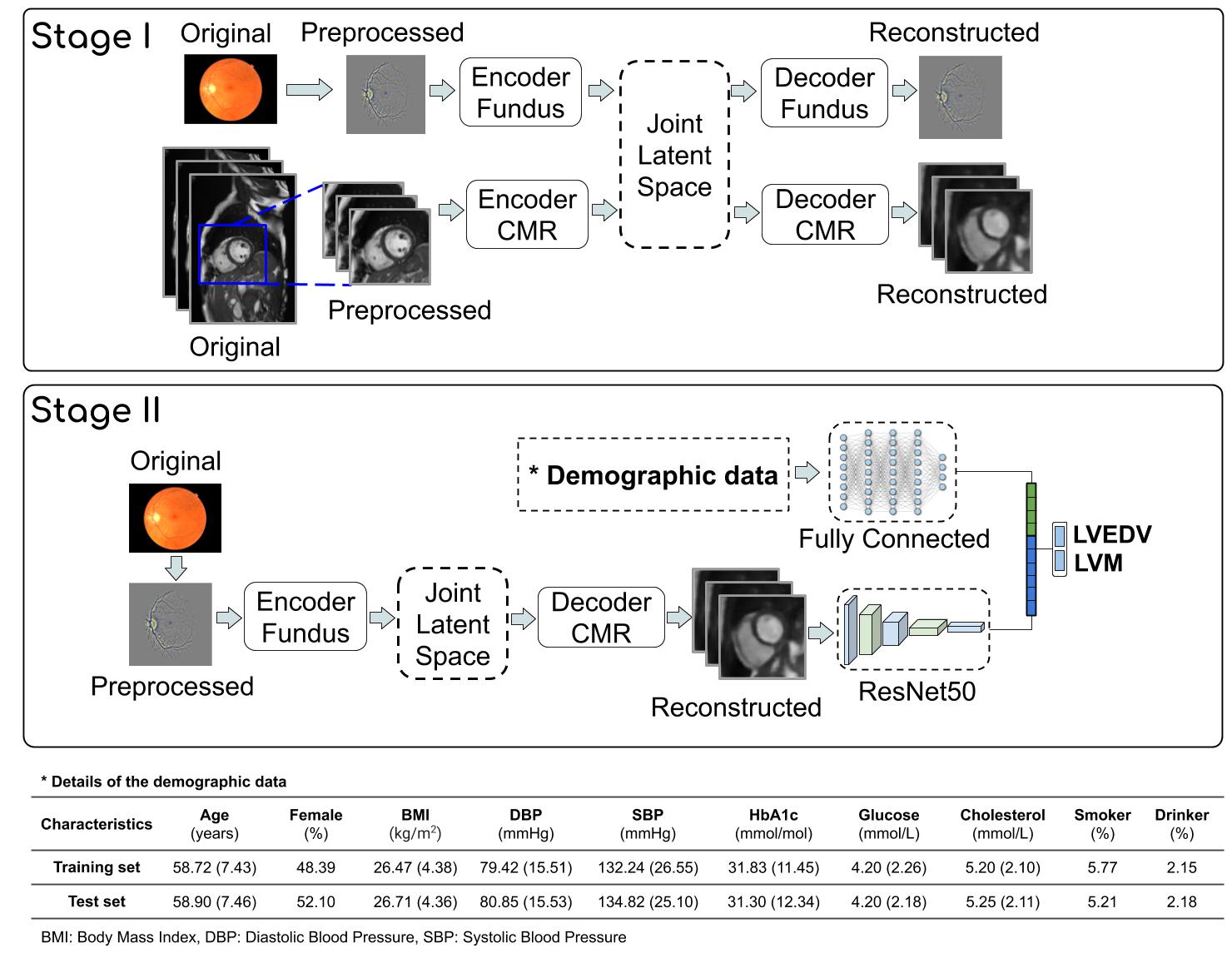
Schema of the proposed method: This system is composed of two main components, a multi-channel VAE and a deep regressor network. During Stage I, a joint latent space is created with two channels: Retinal and cardiac MR. Then, during Stage II a deep regressor is trained on the reconstructed CMR plus demographic data to estimate LVM and LVEDV. Demographic data: Summary of the subjects metadata used in this study to train (5097 participants) and test (566 participants) the proposed method. All continuous values are reported in mean and standard deviation (in parenthesis) while categorical data are reported in percentage.
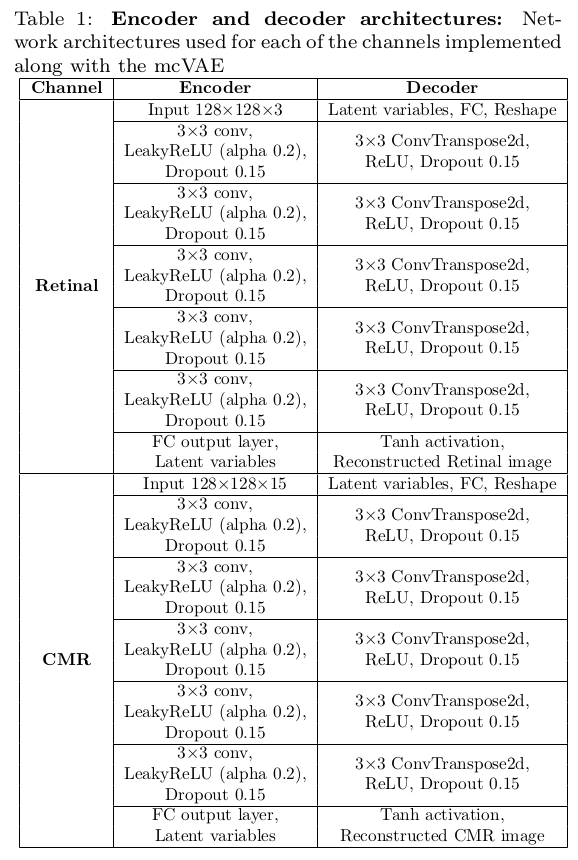
Encoder and Decoder Architectures: The following are the layers used for the decoder and decoder of both channels.
- dataloader: All dataloaders used in this study. Dataloaders to train and test the system with retinal images, cardiac MR and both image modalities.
- mcvae: Multi-channel VAE model.
- networks: Networks used as encoder and decoder in the mcVAE
- statistical_analysis: Jupyter Notebook used to perform the myocardial infarction predcition based on the cardiac indices and demographic data.
- csvPreparation: Scripts used to prepare input csv files (This bit is based on the UK Biobank data).
The package development version is tested on Linux operating systems. The developmental version of the package has been tested on the following systems:
Linux: CentOS Linux 7
We used Python 3.6.5. File requirements.txt contains the list of python libraries/packages used to train our approach.
The weights of the trained models (~5GB) could be download from this link.
Users have two options: (1) create a Python virtual environment and then install all the libraries listed in requirements.txt file using the command "pip install -r requirements.txt". This will take about 10 mins to install. (2) Use the Docker recipe to create a Docker container.
Secondly, users should download the weights inside the main folder.
Finally, users should run the script mcVAE_4_test.py to test on new retinal images. For testing, users may want to use the UK Biobank dataset or other publicly available datasets such as HRF
For training the system, users should load the cardiac MR, retinal images and demographic data inside the "./input_data" folder. Then, run the script "main_mcVAE.py" to train the mcVAE.
- Scripts main_mcVAE.py, mcVAE_4_test.py were used to train and test the Multi-channel VAE, respectively. (Stage I)
- Script main_deep_regressor.py was used to train the Stage II.
- Scripts main_only_fundus.py and main_only_mtdt.py were used to analyse contribuntion made by retinal and demographic data respectively.
- All scripts used to address reviewers comments are available in the branch externalValidation
If you are having an issue that you believe to be tied to software versioning issues, please drop us an Issue.
Please cite the following paper if you use this code:
[1] Diaz-Pinto A, Attar R, Ravikumar N, Suinesiaputra A, Zhao Y, Levelt E, Dall'Armellina E, Lorenzi M, Chen Q, Keenan T D L, Agrón E, Chew E Y, Lu Z, Gale C P, Gale R P, Plein S and Frangi A F. "Predicting Myocardial Infarction through Retinal Scans and Minimal Personal Information". Nature Machine Intelligence. Under review. July 2021.
Update log:
- 20.08.14: Code released.
- 20.09.15: Network weights uploaded. Article under review.
- 21.06.02: Update Abstract and Readme file
- 21.07.19: Update title and abstract for second review