forked from 0voice/newsql_nosql_library
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
204 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1 +1,205 @@ | ||
| 这个博客记录了MySQL 5.7的物理和逻辑架构,还有其组件。在这个帖子中,我会尝试用图去说明SQL语句的执行流程和数据处理流程。MySQL的架构具备灵活性,因为它把不同的存储引擎作为插件。因此,MySQL的架构和行为也会随着存储引擎的改变而改变。 | ||
|
|
||
| 我们重点讨论InnoDB,因为它是MySQL的默认存储引擎。 | ||
|
|
||
| # **MySQL物理架构** | ||
| 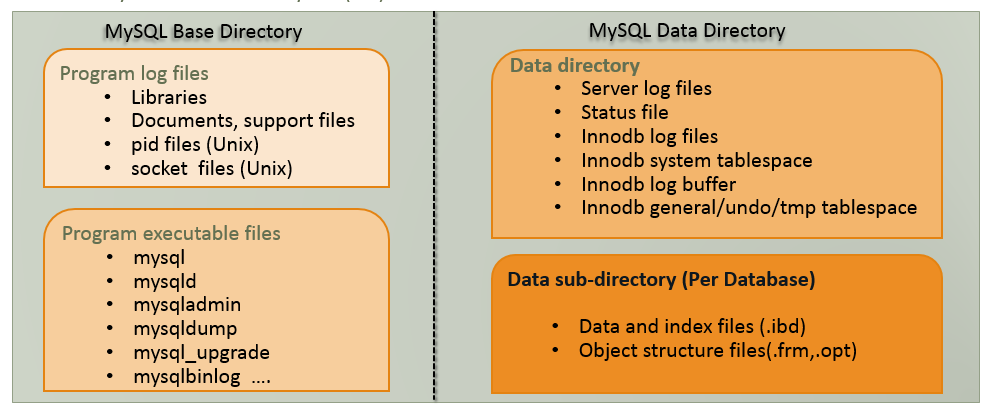 | ||
|
|
||
| # **配置文件** | ||
| * auto.cnf : 包含 server_uuid | ||
| * my.cnf : MySQL配置文件 | ||
|
|
||
| # **形形色色的其他文件** | ||
| ```C | ||
| –basedir=dir_name //MySQL安装目录路径 | ||
| –datadir=dir_name //数据目录的路径,数据目录存储数据,状态,日志等 | ||
| –pid-file=file_name //MySQL服务器写ProcessID的文件路径 | ||
| –socket=file_name, -S file_name //在Unix系统上,使用的Unix套接字文件的名字,用于通过管道与本地服务器建立连接 | ||
| –log-error=file_name //记录错误和启动信息的日志文件名 | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| # **MySQL逻辑架构** | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ## **Client** : | ||
| 提供连接MySQL服务器功能的常用工具集 | ||
| ## **Server** : | ||
| MySQL实例,真正提供数据存储和数据处理功能的MySQL服务器进程 | ||
| ## **mysqld**: | ||
| MySQL服务器守护程序,在后台运行。它管理着客户端请求。mysqld是一个多线程的进程,允许多个会话连接,端口监听连接,管理MySQL实例 | ||
| ## **MySQL memory allocation**: | ||
| MySQL的要求的内存空间是动态的,比如 innodb_buffer_pool_size (from 5.7.5), key_buffer_size。每个会话都有独一无二的执行计划,我们只能共享同一会话域内的数据集。 | ||
| ## **SESSION** | ||
| 为每个客户端连接分配一个会话,动态分配和回收。用于查询处理,每个会话同时具备一个缓冲区。每个会话是作为一个线程执行的 | ||
| ## **Parser** | ||
| 检测SQL语句语法,为每条SQL语句生成SQL_ID,用户认证也发生在这个阶段 | ||
| ## **Optimizer** | ||
| 创造一个有效率的执行计划(根据具体的存储引擎)。它将会重写查询语句。比如:InnoDB有共享缓冲区,所以,优化器会首先从预先缓存的数据中提取。使用 table statistics optimizer将会为SQL查询生成一个执行计划。用户权限检查也发生在这个阶段。 | ||
| ## **Metadata cache** | ||
| 缓存对象元信息和统计信息 | ||
| ## **Query cache** | ||
| 共享在内存中的完全一样的查询语句。如果完全相同的查询在缓存命中,MySQL服务器会直接从缓存中去检索结果。缓存是会话间共享的,所以为一个客户生成的结果集也能为另一个客户所用。查询缓存基于SQL_ID。将SELECT语句写入视图就是查询缓存最好的例子。 | ||
| ## **key cache** | ||
| 缓存表索引。MySQL keys是索引。如果索引数据量小,它将缓存索引结构和叶子节点(存储索引数据)。如果索引很大,它只会缓存索引结构,通常供MyISAM存储引擎使用 | ||
|
|
||
| # **SQL执行** | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| MySQL连接 | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| # **InnoDB存储引擎架构** | ||
| 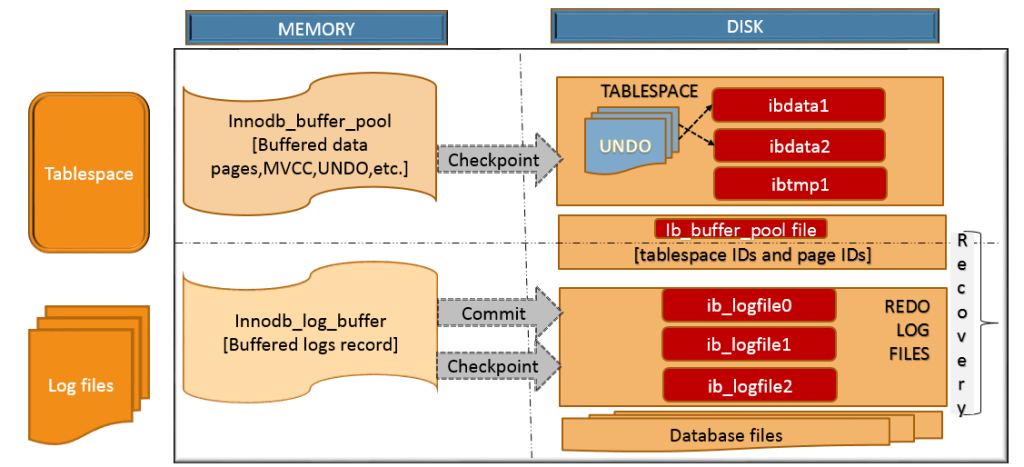 | ||
|
|
||
| # **TABLESPACE** | ||
| InnoDB存储空间被切分成tablespace,tablespace是一个与多个数据文件相关联的逻辑结构。 | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ## **Pages** | ||
| InnoDB最小的数据存储单元被也称作块。默认的页框是16KB,一个页包含多行。 | ||
| 可用页大小: 4kb,8kb,16kb,32kb,64kb | ||
| 配置变量名 : innodb_page_size,在初始化mysqld时配置 | ||
| ## **Extents** | ||
| 一组页组成一个区,InnoDB为了更好的I/O吞吐率,每次读写都是按照区为单位。 | ||
| 一组16KB的页,一个区可以1MB,双写缓冲区(Doublewrite buffer )每次分配/读/写都是以区为单位。 | ||
| ## **Segments** | ||
| 4个区构成一个Segments | ||
|
|
||
| # **InnoDB存储引擎** | ||
| * ACID事务支持 | ||
| * 行锁模式 | ||
| * 事务REDO&UNDO支持 | ||
| * 多数据文件 | ||
| * 逻辑对象结构(InnoDB数据和日志缓冲区) | ||
| * InnoDB数据是百分百的具备逻辑结构,数据物理存储。 | ||
| * InnoDB读取物理数据,创建逻辑结构[Blocks and Rows] | ||
| * 逻辑存储称为TABLESPACE | ||
|
|
||
| # **InnoDB 内存中组件** | ||
| * InnoDB buffer pool | ||
| InnoDB存储引擎的核心缓冲区。在这个缓冲区之中,加载表和索引数据 | ||
| * InnoDB缓存表数据和索引数据的主要区域 | ||
| 占据80%以上的物理内存,在专用数据库服务器中 | ||
| * 所有会话的共享缓冲区 | ||
| * InnoDB使用LRU页面置换算法 | ||
|
|
||
| ## **Change buffer** | ||
| ```C | ||
| In a memory change buffer is a part of InnoDB buffer pool and on disk, | ||
| it is part of system tablespace, so even after database restart index | ||
| changes remain buffered.Change buffer is a special data structure that | ||
| caches changes to secondary index pages when affected pages not in the | ||
| buffer pool. | ||
| memory change buffer是InnoDB buffer pool的一部分,在磁盘上,也是系统tablespace的一部分。送印即使数据库重启…毛意思啊!无力…保留原文 | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## **Redo log buffer** | ||
| redo logs缓冲区,保存写到redo log(重放日志)的数据。周期性的将缓冲区内的数据写入redo日志中。将内存中的数据写入磁盘的行为由innodb_log_at_trx_commit 和 innodb_log_at_timeout 调节。较大的redo日志缓冲区允许大型事务在事务提交前不进行写磁盘操作。 | ||
| 变量:innodb_log_buffer_size (default 16M) | ||
|
|
||
| # **在磁盘上的组件** | ||
| ## **系统表空间(tablespace)** | ||
| 除了存储表数据之外,InnoDB也支持查找表元信息,存储和检索MVCC信息以兑现服从ACID和事务隔离性等原则。它包含几种类型的InnoDB对象信息。 | ||
| 其包含的文件: | ||
| 1. Table Data Pages | ||
| 2. Table Index Pages | ||
| 3. Data Dictionary | ||
| 4. MVCC Control Data | ||
| 5. Undo Space | ||
| 6. Rollback Segments | ||
| 7. Double Write Buffer (Pages Written in the Background to avoid OS | ||
| caching) Insert Buffer (Changes to Secondary Indexes) | ||
| ```C | ||
| 变量: | ||
| innodb_data_file_path = /ibdata/ibdata1:10M:autoextend | ||
| 1 | ||
| 激活 | ||
| innodb_file_per_table选项,你可以将每个新创建的表存储到不同的tablespace中。这种做法的优点是减少磁盘上数据文件中的碎片 | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## **通用tablespace** | ||
| Shared tablespace to store multiple table data. Introduce in MySQL 5.7.6. A user has to create this using CREATE TABLESPACE syntax. TABLESPACE option can be used with CREATE TABLE to create a table and ALTER TABLE to move a table in general table. | ||
| 共享的tablespace存储多个表信息,在MySQL 5.7.6时引入。用户只能使用CREATE TABLESPACE创建一个这样的表空间。 TABLESPACE选项可以在使用CREATE TABLE命令创建一个表然后 ALTER TABLE 将表移入通用空间时发挥作用。 | ||
| ```C | ||
| – Memory advantage over innodb_file_per_table storage method. | ||
| – Support both Antelope and Barracuda file formats. | ||
| – Supports all row formats and associated features. | ||
| – Possible to create outside data directory. | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## **InnoDB数据字典** | ||
| 在系统tablespace中的存储区域,由系统内部表(供mysql服务器使用的表)和对象元数据(表,索引,列信息)组成 | ||
|
|
||
| ## **双写缓冲区(Double write buffer)** | ||
| 系统tablespace的存储区域,InnoDB在写入物理文件之前先将页从InnoDB buffer pool写入此空间。mysqld进程突然崩溃会导致部分写问题。InnoDB可以从这个区域拿到一个备份。 Variable: inndb_doublewrite (default enable) | ||
|
|
||
| ## **REDO logs** | ||
| 用于灾难恢复。mysqld启动的时候,InnoDB会尝试执行自动恢复,将不完整的事务更改矫正。还未完成更新数据文件的事务会在mysqld启动时会根据此日志记录中的信息被重放。它使用 LSN(Log Sequence Number)值来重放信息,因为mySQL会为每个事务赋予一个ID。因为大量数据更改不可能及时写道磁盘,所以得先记录到redo日志,然后再写入磁盘。 | ||
| 再redo日志,所有更改都会带有 row_id, 旧的列值,新的列值, session_id 和时间。 | ||
| ```C | ||
| Innodb_log_file_in_group= [# of redo file groups] | ||
| Innodb_log_file_size= [每个日志文件大小] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## **UNDO日志和UNDO表空间** | ||
| UNDO tablespace包含一个或多个undo日志文件。UNDO通过为事务(MVCC)保存被更改还未提交的值保持读一致性。未提交值从这个存储区域读取。UNDO日志也被叫做回滚数据段。 | ||
| 默认地,UNDO日志是系统表空间的一部分。但MySQL允许UNDO日志置于一个单独的表空间中 [Introduce in MySQL 5.6]。这需要在初始化mysqld之前进行更改才起作用。 | ||
| 当我们配置单独UNDO表空间时,系统表空间的UNDO日志就被抑制了,但是一旦配置成单独的,我们只能删除UNDO日志的一部分,比如过期日志,而不能删除它。 | ||
| ```C | ||
| – Variables : innodb_undo_tablespace : # of undo tablespaces, default | ||
| 0 innodb_undo_directory: | ||
| Location for undo tablespace,default is,data_dir with 10MB size. | ||
| innodb_undo_logs : | ||
| # of undo logs, default ,and max value is ‘128’ | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## **临时表空间** | ||
| 为临时表和相关对象提供存储功能,存储包括临时表未提交的数据。在MySQL 5.7.2引入,用于对临时表修改的回滚。 ibtmp1每次系统启动被重新创建,避免REDO日志对临时表的I/O操作。 | ||
| ```C | ||
| innodb_temp_data_file_path = ibtmp1:12M:autoextend (default) | ||
| ``` | ||
| And All SET !! | ||
|
|
||
| # **存储引擎** | ||
| ```C | ||
| Storage engine: | ||
| MySQL component that manages physical data (file management) and locations. Storage engine responsible for SQL statement execution and fetching data from data files. Use as a plugin and can load/unload from running MySQL server.Few of them as following, | ||
| InnoDB : | ||
| Fully transactional ACID. | ||
| Offers REDO and UNDO for transactions. | ||
| Data storage in tablespace: | ||
| Multiple data files | ||
| Logical object structure using InnoDB data and log buffer | ||
| Row-level locking. | ||
| NDB (For MySQL Cluster): | ||
| Fully Transactional and ACID Storage engine. | ||
| Distribution execution of data and using multiple mysqld. | ||
| NDB use logical data with own buffer for each NDB engine. | ||
| Offers REDO and UNDO for transactions. | ||
| Row-level locking. | ||
| MyISAM: | ||
| Non-transactional storage engine | ||
| Speed for read | ||
| Data storage in files and use key, metadata and query cache | ||
| – FRM for table structure | ||
| – MYI for table index | ||
| – MYD for table data | ||
| Table-level locking. | ||
| MEMORY: | ||
| Non-transactional storage engine | ||
| All data stored in memory other than table metadata and structure. | ||
| Table-level locking. | ||
| ARCHIVE: | ||
| Non-transactional storage engine, | ||
| Store large amounts of compressed and unindexed data. | ||
| Allow INSERT, REPLACE, and SELECT, but not DELETE or UPDATE sql operations. | ||
| Table-level locking. | ||
| CSV: | ||
| Stores data in flat files using comma-separated values format. | ||
| Table structure need be created within MySQL server (.frm) | ||
| ``` | ||
| 原文作者: lalit |