This repository was forked in June 2024 because it could only be compiled on Ubuntu 18.04 with glibc version <=2.27. Benedict patched this to work on Xubuntu 24.04. Install instructions for Xubuntu 24.04:
# install git
sudo apt install -y git
# clone this repo
cd ~ && git clone [email protected]:fuenfeinhalb-untrusted/MoonGen.git
# install dependencies
sudo apt install dpdk dpdk-dev dpdk-kmods-dkms libluajit-5.1-dev libssl-dev libssl-dev libhighwayhash-dev libtbb-dev cmake gcc-12 g++-12
# link python3 to python
sudo ln /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/python
# build MoonGen (without sudo)
cd ~/MoonGen && ./build.sh
# now resume in the testbed repository ...LuaJIT + DPDK = fast and flexible packet generator for 10 Gbit/s Ethernet and beyond. MoonGen uses hardware features for accurate and precise latency measurements and rate control.
Skip to Installation and Usage if you just want to send some packets.
Detailed evaluation: Paper (IMC 2015, BibTeX entry)
MoonGen is a scriptable high-speed packet generator built on libmoon. The whole load generator is controlled by a Lua script: all packets that are sent are crafted by a user-provided script. Thanks to the incredibly fast LuaJIT VM and the packet processing library DPDK, it can saturate a 10 Gbit/s Ethernet link with 64 Byte packets while using only a single CPU core. MoonGen can achieve this rate even if each packet is modified by a Lua script. It does not rely on tricks like replaying the same buffer.
MoonGen can also receive packets, e.g., to check which packets are dropped by a system under test. As the reception is also fully under control of the user's Lua script, it can be used to implement advanced test scripts. E.g. one can use two instances of MoonGen that establish a connection with each other. This setup can be used to benchmark middle-boxes like firewalls.
MoonGen focuses on four main points:
- High performance and multi-core scaling: > 20 million packets per second per CPU core
- Flexibility: Each packet is crafted in real time by a user-provided Lua script
- Precise and accurate timestamping: Timestamping with sub-microsecond precision on commodity hardware
- Precise and accurate rate control: Reliable generation of arbitrary traffic patterns on commodity hardware
You can have a look at our slides from a talk or read our paper [1] for a more detailed discussion of MoonGen's internals.
MoonGen is built on libmoon, a Lua wrapper for DPDK.
Users can write custom scripts for their experiments. It is recommended to make use of hard-coded setup-specific constants in your scripts. The script is the configuration, it is beside the point to write a complicated configuration interface for a script. Alternatively, there is a simplified (and less powerful) command-line interface available for quick tests.
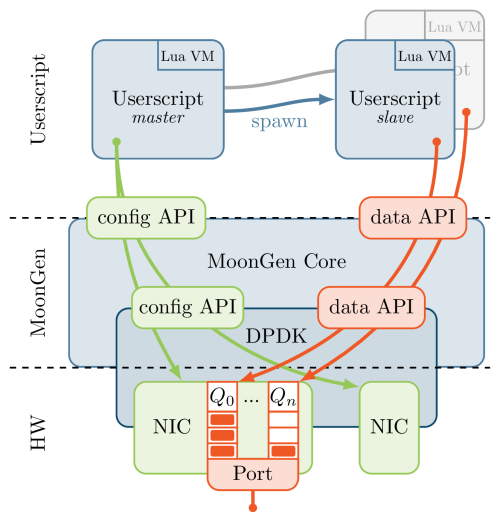
The following diagram shows the architecture and how multi-core support is handled.
Execution begins in the master task that must be defined in the userscript. This task configures queues and filters on the used NICs and then starts one or more slave tasks.
Note that Lua does not have any native support for multi-threading. MoonGen therefore starts a new and completely independent LuaJIT VM for each thread. The new VMs receive serialized arguments: the function to execute and arguments like the queue to send packets from. Threads only share state through the underlying library.
The example script quality-of-service-test.lua shows how this threading model can be used to implement a typical load generation task. It implements a QoS test by sending two different types of packets and measures their throughput and latency. It does so by starting two packet generation tasks: one for the background traffic and one for the prioritized traffic. A third task is used to categorize and count the incoming packets.
Intel commodity NICs from the igb, ixgbe, and i40e families support timestamping in hardware for both transmitted and received packets. The NICs implement this to support the IEEE 1588 PTP protocol, but this feature can be used to timestamp almost arbitrary UDP packets. MoonGen achieves a precision and accuracy of below 100 ns.
Use test-timestamping-capabilities.lua in examples/timestamping-tests to test your NIC's timestamping capabilities.
A more detailed evaluation can be found in our paper [1].
- Install the dependencies (see below)
- ./build.sh
- sudo ./bind-interfaces.sh
- sudo ./setup-hugetlbfs.sh
- sudo ./build/MoonGen examples/l3-load-latency.lua 0 1
Note: You need to bind NICs to DPDK to use them. bind-interfaces.sh does this for all unused NICs (no routing table entry in the system).
Use libmoon/deps/dpdk/usertools/dpdk-devbind.py to manage NICs manually.
If you have secure boot enabled (by default in ubuntu 20.04 LTS), you will get a permission denied error on the insmod command of the kernel module when running sudo ./bind-interfaces.sh. You can temporarely disable secure boot on ubuntu with the steps described here to permit the unsigned driver to load.
- gcc >= 4.8
- make
- cmake
- libnuma-dev
- kernel headers (for the DPDK igb-uio driver)
- lspci (for
dpdk-devbind.py) - additional dependencies for Mellanox NICs
Run the following command to install these on Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install -y build-essential cmake linux-headers-`uname -r` pciutils libnuma-dev
You have to write a simple script for your use case. The example l3-load-latency.lua is a good starting point as it makes use of a lot of different features of MoonGen.
The simplest way to get started is using the simple command line interface. For example:
sudo ./moongen-simple start load-latency:0:1:rate=10Mp/s,time=3m
This sends packets with a rate of 10 million packets per second for 3 minutes from port 0 to port 1 and outputs the latency at the end of the run. Available DPDK ports are printed on startup.
load-latency is a flow that is defined in flows/examples.lua.
Have a look at this file to see how flows are defined. You can add your own flow definitions to any file in the flows subdirectory.
Run ./moongen-simple list to see all available flows.
It's also helpful to run a flow with debug instead of start to print packet contents instead of sending them.
See the documentation for the simple CLI for more details and instructions.
You can also check the help command or run any subcommand with -h.
This API comes with a small performance overhead compared to the full API. You can enable multi-threading on a single port by specifying the same port multiple times separated with commas.
Using the full API gives you complete control over MoonGen, this is recommended for more complex test setups. This means that you'll have to write a custom script to use MoonGen in this mode.
MoonGen comes with examples in the examples folder which can be used as a basis for custom scripts. Reading the example script l3-load-latency.lua or quality-of-service-test.lua is a good way to learn more about our scripting API as these scripts uses most features of MoonGen.
You can run a script like this:
./build/MoonGen ./examples/l3-load-latency.lua 0 1
The two command line arguments are the transmission and reception ports, see script (or run with -h) for CLI parameter handling.
MoonGen prints all available ports on startup, so adjust this if necessary.
You can also check out the examples of the libmoon project. All libmoon scripts are also valid MoonGen scripts as MoonGen extends libmoon.
Basic functionality is available on all NICs supported by DPDK.
Hardware timestamping is currently supported and tested on Intel igb, ixgbe, and i40e NICs. However, support for specific features vary between models.
Use test-timestamping-capabilities.lua in examples/timestamping-tests to find out what your NIC supports.
Hardware rate control is supported and tested on Intel ixgbe and i40e NICs.
MoonGen builds on libmoon by extending it with features for packet generators such as software rate control and software timestamping.
If you want to write a packet generator or test your application: use MoonGen. If you want to prototype DPDK applications: use libmoon.
[1] Paul Emmerich, Sebastian Gallenmüller, Daniel Raumer, Florian Wohlfart, and Georg Carle. MoonGen: A Scriptable High-Speed Packet Generator, 2015. IMC 2015. Available online. BibTeX.