📌 Protocol Agnostic - Currently supporting HTTP, HTTPS, HTTP/2. Other protocols are on the way.
📌 Scenario-Based - Create your flow in a JSON file. Without a line of code!
📌 Different Load Types - Test your system's limits across different load types.
📌 Parameterization - Use dynamic variables just like on Postman.
ddosify is available via Docker, Docker Extension, Homebrew Tap, and downloadable pre-compiled binaries from the releases page for macOS, Linux and Windows.
docker run -it --rm ddosify/ddosifyRun Ddosify open-source on Docker Desktop with Ddosify Docker extension. More: https://hub.docker.com/extensions/ddosify/ddosify-docker-extension
brew install ddosify/tap/ddosify- For arm architectures change
ddosify_amd64toddosify_arm64orddosify_armv6. - Superuser privilege is required.
# For Redhat based (Fedora, CentOS, RHEL, etc.)
rpm -i https://github.com/ddosify/ddosify/releases/latest/download/ddosify_amd64.rpm
# For Debian based (Ubuntu, Linux Mint, etc.)
wget https://github.com/ddosify/ddosify/releases/latest/download/ddosify_amd64.deb
dpkg -i ddosify_amd64.deb
# For Alpine
wget https://github.com/ddosify/ddosify/releases/latest/download/ddosify_amd64.apk
apk add --allow-untrusted ddosify_amd64.apk
# For Arch Linux
git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/ddosify.git
cd ddosify
makepkg -sri
# For FreeBSD
pkg install ddosifyWindows exe from the releases page
- Download *.zip file for your architecture. For example download ddosify version vx.x.x with amd64 architecture: ddosify_x.x.x.zip_windows_amd64
- Unzip
ddosify_x.x.x_windows_amd64.zip - Open Powershell or CMD (Command Prompt) and change directory to unzipped folder:
ddosify_x.x.x_windows_amd64 - Run ddosify:
.\ddosify.exe -t target_site.com- The script requires root or sudo privileges to move ddosify binary to
/usr/local/bin. - The script attempts to detect your operating system (macOS or Linux) and architecture (arm64, x86, amd64) to download the appropriate binary from the releases page.
- By default, the script installs the latest version of
ddosify. - If you have problems, check common issues
- Required packages:
curlandsudo
curl -sSfL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ddosify/ddosify/master/scripts/install.sh | shgo install -v go.ddosify.com/ddosify@latestThis section aims to show you how to use Ddosify without deep dive into its details easily.
-
ddosify -t target_site.comThe above command runs a load test with the default value that is 100 requests in 10 seconds.
-
ddosify -t target_site.com -n 1000 -d 20 -p HTTPS -m PUT -T 7 -P http://proxy_server.com:80Ddosify sends a total of 1000 PUT requests to https://target_site.com over proxy http://proxy_server.com:80 in 20 seconds with a timeout of 7 seconds per request.
-
ddosify -t target_site.com -o stdout-json | jq .avg_durationDdosify outputs the result in JSON format. Then
jq(or any other command-line JSON processor) fetches theavg_duration. The rest depends on your CI/CD flow logic. -
ddosify -config config_examples/config.jsonDdosify first sends HTTP/2 POST request to https://test_site1.com/endpoint_1 using basic auth credentials test_user:12345 over proxy http://proxy_host.com:proxy_port and with a timeout of 3 seconds. Once the response is received, HTTPS GET request will be sent to https://test_site1.com/endpoint_2 along with the payload included in config_examples/payload.txt file with a timeout of 2 seconds. This flow will be repeated 20 times in 5 seconds and response will be written to stdout.
-
ddosify -t target_site.com/{{_randomInt}} -d 10 -n 100 -h 'User-Agent: {{_randomUserAgent}}' -b '{"city": "{{_randomCity}}"}'Ddosify sends a total of 100 GET requests to https://target_site.com/{{_randomInt}} in 10 seconds.
{{_randomInt}}path generates random integers between 1 and 1000 in every request. Dynamic variables can be used in URL, headers, payload (body) and basic authentication. In this example, Ddosify generates a random user agent in the header and a random city in the body. The full list of the dynamic variables can be found in the docs.
You can configure your load test by the CLI options or a config file. Config file supports more features than the CLI. For example, you can't create a scenario-based load test with CLI options.
ddosify [FLAG]| Flag | Description | Type | Default | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
-t |
Target website URL. Example: https://ddosify.com | string |
- | Yes |
-n |
Total request count | int |
100 |
No |
-d |
Test duration in seconds. | int |
10 |
No |
-p |
Protocol of the request. Supported protocols are HTTP, HTTPS. HTTP/2 support is only available by using a config file as described. More protocols will be added. | string |
HTTPS |
No |
-m |
Request method. Available methods for HTTP(s) are GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, PATCH, OPTIONS | string |
GET |
No |
-b |
The payload of the network packet. AKA body for the HTTP. | string |
- | No |
-a |
Basic authentication. Usage: -a username:password |
string |
- | No |
-h |
Headers of the request. You can provide multiple headers with multiple -h flag. Usage: -h 'Accept: text/html' |
string |
- | No |
-T |
Timeout of the request in seconds. | int |
5 |
No |
-P |
Proxy address as host:port. -P 'http://user:pass@proxy_host.com:port' |
string |
- | No |
-o |
Test result output destination. Supported outputs are [stdout, stdout-json] Other output types will be added. | string |
stdout |
No |
-l |
Type of the load test. Ddosify supports 3 load types. | string |
linear |
No |
--config |
Config File of the load test. | string |
- | No |
--version |
Prints version, git commit, built date (utc), go information and quit | - | - | No |
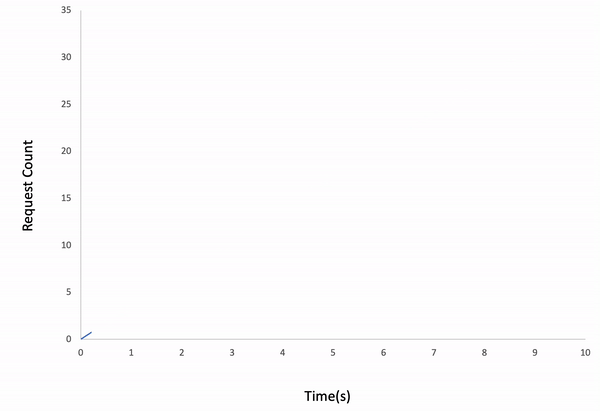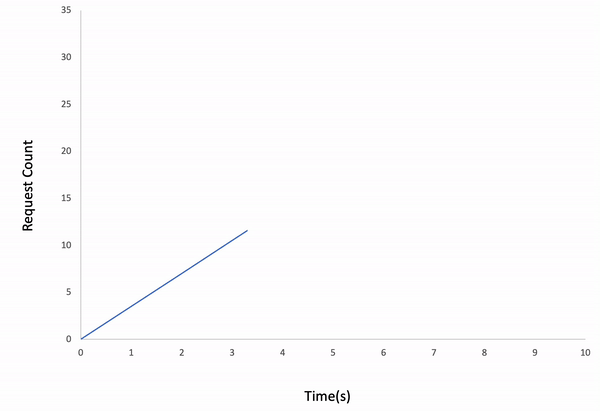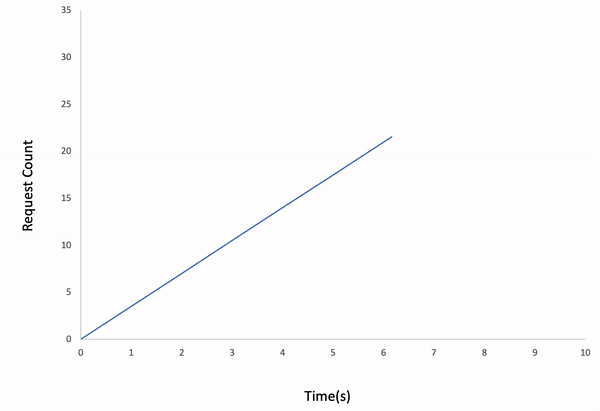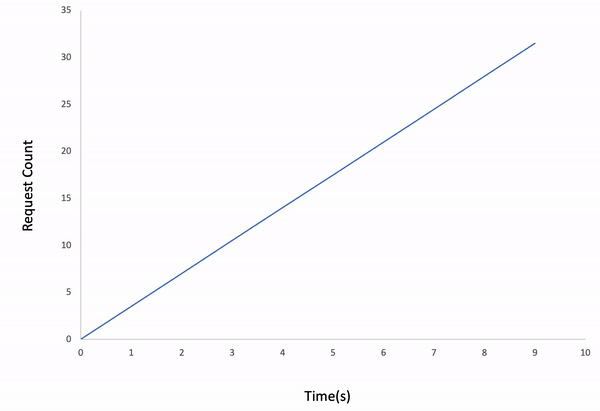
ddosify -t target_site.com -l linearResult:
Note: If the request count is too low for the given duration, the test might be finished earlier than you expect.
ddosify -t target_site.com -l incrementalResult:
ddosify -t target_site.com -l wavedResult:
Config file lets you use all capabilities of Ddosify.
The features you can use by config file;
- Scenario creation
- Custom load type creation
- Payload from a file
- Multipart/form-data payload
- Extra connection configuration, like keep-alive enable/disable logic
- HTTP2 support
Usage;
ddosify -config <json_config_path>
There is an example config file at config_examples/config.json. This file contains all of the parameters you can use. Details of each parameter;
-
request_countoptionalThis is the equivalent of the
-nflag. The difference is that if you have multiple steps in your scenario, this value represents the iteration count of the steps. -
load_typeoptionalThis is the equivalent of the
-lflag. -
durationoptionalThis is the equivalent of the
-dflag. -
manual_loadoptionalIf you are looking for creating your own custom load type, you can use this feature. The example below says that Ddosify will run the scenario 5 times, 10 times, and 20 times, respectively along with the provided durations.
request_countanddurationwill be auto-filled by Ddosify according tomanual_loadconfiguration. In this example,request_countwill be 35 and thedurationwill be 18 seconds. Alsomanual_loadoverridesload_typeif you provide both of them. As a result, you don't need to provide these 3 parameters when usingmanual_load."manual_load": [ {"duration": 5, "count": 5}, {"duration": 6, "count": 10}, {"duration": 7, "count": 20} ]
-
proxyoptionalThis is the equivalent of the
-Pflag. -
outputoptionalThis is the equivalent of the
-oflag. -
stepsmandatoryThis parameter lets you create your scenario. Ddosify runs the provided steps, respectively. For the given example file step id: 2 will be executed immediately after the response of step id: 1 is received. The order of the execution is the same as the order of the steps in the config file.
Details of each parameter for a step;
-
idmandatoryEach step must have a unique integer id.
-
urlmandatoryThis is the equivalent of the
-tflag. -
Name of the step.
-
protocoloptionalThis is the equivalent of the
-pflag. -
methodoptionalThis is the equivalent of the
-mflag. -
headersoptionalList of headers with key:value format.
-
payloadoptionalThis is the equivalent of the
-bflag. -
payload_fileoptionalIf you need a long payload, we suggest using this parameter instead of
payload. -
Use this for
multipart/form-dataContent-Type.Accepts list of
form-fieldobjects, structured as below;{ "name": [field-name], "value": [field-value|file-path|url], "type": <text|file>, // Default "text" "src": <local|remote> // Default "local" }Example: Sending form name-value pairs;
"payload_multipart": [ { "name": "[field-name]", "value": "[field-value]" } ]
Example: Sending form name-value pairs and a local file;
"payload_multipart": [ { "name": "[field-name]", "value": "[field-value]", }, { "name": "[field-name]", "value": "./test.png", "type": "file" } ]
Example: Sending form name-value pairs and a local file and a remote file;
"payload_multipart": [ { "name": "[field-name]", "value": "[field-value]", }, { "name": "[field-name]", "value": "./test.png", "type": "file" }, { "name": "[field-name]", "value": "http://test.com/test.png", "type": "file", "src": "remote" } ]
Note: Ddosify adds
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=[generated-boundary-value]header to the request when usingpayload_multipart. -
timeoutoptionalThis is the equivalent of the
-Tflag. -
Sleep duration(ms) before executing the next step. Can be an exact duration or a range.
Example: Sleep 1000ms after step-1;
"steps": [ { "id": 1, "url": "target.com/endpoint1", "sleep": "1000" }, { "id": 2, "url": "target.com/endpoint2", } ]
Example: Sleep between 300ms-500ms after step-1;
"steps": [ { "id": 1, "url": "target.com/endpoint1", "sleep": "300-500" }, { "id": 2, "url": "target.com/endpoint2", } ]
-
authoptionalBasic authentication.
"auth": { "username": "test_user", "password": "12345" }
-
othersoptionalThis parameter accepts dynamic key: value pairs to configure connection details of the protocol in use.
"others": { "keep-alive": true, // Default true "disable-compression": false, // Default true "h2": true, // Enables HTTP/2. Default false. "disable-redirect": true // Default false }
-
Just like the Postman, Ddosify supports parameterization (dynamic variables) on URL, headers, payload (body) and basic authentication. Actually, we support all the random methods Postman supports. If you use {{$randomVariable}} on Postman you can use it as {{_randomVariable}} on Ddosify. Just change $ to _ and you will be fine. To simulate a realistic load test on your system, Ddosify can send every request with dynamic variables.
The full list of dynamic variables can be found in the Ddosify Docs.
Ddosify sends 100 GET requests in 10 seconds with random string key parameter. This approach can be also used in cache bypass.
ddosify -t target_site.com/?key={{_randomString}} -d 10 -n 100Ddosify sends 100 GET requests in 10 seconds with random Transaction-Type and Country headers.
ddosify -t target_site.com -d 10 -n 100 -h 'Transaction-Type: {{_randomTransactionType}}' -h 'Country: {{_randomCountry}}'Ddosify sends 100 GET requests in 10 seconds with random latitude and longitude values in body.
ddosify -t target_site.com -d 10 -n 100 -b '{"latitude": "{{_randomLatitude}}", "longitude": "{{_randomLongitude}}"}'Ddosify sends 100 GET requests in 10 seconds with random username and password with basic authentication.
ddosify -t target_site.com -d 10 -n 100 -a '{{_randomUserName}}:{{_randomPassword}}'Dynamic variables can be used on config file as well. Ddosify sends 100 GET requests in 10 seconds with random string key parameter in URL and random User-Key header.
ddosify -config ddosify_config_dynamic.json// ddosify_config_dynamic.json
{
"request_count": 100,
"load_type": "linear",
"duration": 10,
"steps": [
{
"id": 1,
"url": "https://test_site1.com/?key={{_randomString}}",
"protocol": "https",
"method": "POST",
"headers": {
"User-Key": "{{_randomInt}}"
}
}
]
}"ddosify" can’t be opened because Apple cannot check it for malicious software.
- Open
/usr/local/bin - Right click
ddosifyand select Open - Select Open
- Close the opened terminal
You can join our Discord Server for issues, feature requests, feedbacks or anything else.
This repository includes the single-node version of the Ddosify Loader. For distributed and Geo-targeted Load Testing you can use Ddosify Cloud
Ddosify is created for testing the performance of web applications. Users must be the owner of the target system. Using it for harmful purposes is extremely forbidden. Ddosify team & company is not responsible for its’ usages and consequences.
Licensed under the AGPLv3: https://www.gnu.org/licenses/agpl-3.0.html