In this repository, I worked with the KITTI semantic segmentation dataset [1] to explore both binary and multi-class segmentation of autonomous driving scenes.
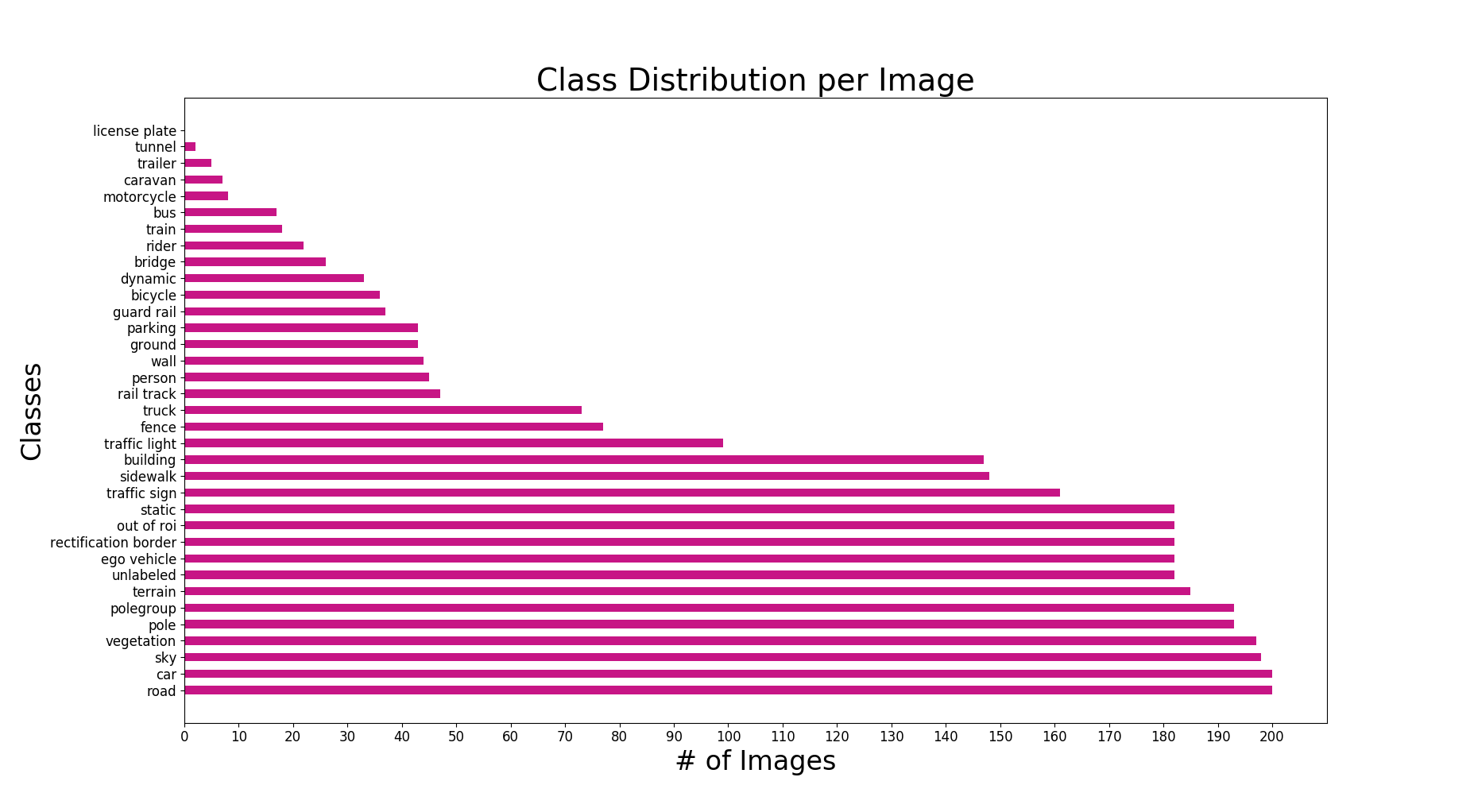
The semantic segmentation dataset consists of 200 train and test images (each) and can be downloaded here. Additionally, a development kit is provided, which offers helper functions that map pixel colours to class labels. There are a total of 35 labeled classes that are unevenly distributed throughout the dataset. The figures below show the distribution of classes on both a per image and per pixel basis.
I used an encoder-decoder architecture that was based on the popular U-Net architecture[2]. The network accepts as an input a 3-channel Height x Width x 3 RGB image, downsamples the image with the encoder branch of the network and then recovers the image's original resolution using the network's decoder branch. The final output is a tensor of size Height x Width x NClasses. For binary segmentation, NClasses = 2.
For training, I used the Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of 1e-4. The learning rate was decreased by a factor of 10 if the model's validation loss did not decrease after 10 epochs.
The training set was divided into a modified 90% / 10% train/val split. To reduce training time, the train/val images were resized to a resolution of 400 x 112, maintaining the approximate ~3.3 aspect width-to-height ratio from the original resolution.
[1]: Geiger, Andreas, et al. "Vision meets robotics: The KITTI dataset." The International Journal of Robotics Research 32.11 (2013): 1231-1237.
[2]: Ronneberger, Olaf, Philipp Fischer, and Thomas Brox. "U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation." International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, Cham, 2015.