| title | description | services | ms.service | author | ms.reviewer | ms.custom | ms.topic | ms.date | ms.author |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Install Jupyter locally and connect to Spark in Azure HDInsight |
Learn how to install Jupyter notebook locally on your computer and connect it to an Apache Spark cluster. |
hdinsight |
hdinsight |
hrasheed-msft |
jasonh |
hdinsightactive |
conceptual |
11/28/2017 |
hrasheed |
In this article you learn how to install Jupyter notebook, with the custom PySpark (for Python) and Apache Spark (for Scala) kernels with Spark magic, and connect the notebook to an HDInsight cluster. There can be a number of reasons to install Jupyter on your local computer, and there can be some challenges as well. For more on this, see the section Why should I install Jupyter on my computer at the end of this article.
There are three key steps involved in installing Jupyter and the Spark magic on your computer.
- Install Jupyter notebook
- Install the PySpark and Spark kernels with the Spark magic
- Configure Spark magic to access Spark cluster on HDInsight
For more information about the custom kernels and the Spark magic available for Jupyter notebooks with HDInsight cluster, see Kernels available for Jupyter notebooks with Apache Spark Linux clusters on HDInsight.
The prerequisites listed here are not for installing Jupyter. These are for connecting the Jupyter notebook to an HDInsight cluster once the notebook is installed.
- An Azure subscription. See Get Azure free trial.
- An Apache Spark cluster on HDInsight. For instructions, see Create Apache Spark clusters in Azure HDInsight.
You must install Python before you can install Jupyter notebooks. Both Python and Jupyter are available as part of the Anaconda distribution. When you install Anaconda, you install a distribution of Python. Once Anaconda is installed, you add the Jupyter installation by running appropriate commands.
-
Download the Anaconda installer for your platform and run the setup. While running the setup wizard, make sure you select the option to add Anaconda to your PATH variable.
-
Run the following command to install Jupyter.
conda install jupyterFor more information on installing Jupyter, see Installing Jupyter using Anaconda.
For instructions on how to install the Spark magic, the PySpark and Spark kernels, follow the installation instructions in the sparkmagic documentation on GitHub. The first step in the Spark magic documentation asks you to install Spark magic. Replace that first step in the link with the following commands, depending on the version of the HDInsight cluster you will connect to. After that, follow the remaining steps in the Spark magic documentation. If you want to install the different kernels, you must perform Step 3 in the Spark magic installation instructions section.
-
For clusters v3.4, install sparkmagic 0.2.3 by executing
pip install sparkmagic==0.2.3 -
For clusters v3.5 and v3.6, install sparkmagic 0.11.2 by executing
pip install sparkmagic==0.11.2
In this section you configure the Spark magic that you installed earlier to connect to an Apache Spark cluster that you must have already created in Azure HDInsight.
-
The Jupyter configuration information is typically stored in the users home directory. To locate your home directory on any OS platform, type the following commands.
Start the Python shell. On a command window, type the following:
pythonOn the Python shell, enter the following command to find out the home directory.
import os print(os.path.expanduser('~')) -
Navigate to the home directory and create a folder called .sparkmagic if it does not already exist.
-
Within the folder, create a file called config.json and add the following JSON snippet inside it.
{ "kernel_python_credentials" : { "username": "{USERNAME}", "base64_password": "{BASE64ENCODEDPASSWORD}", "url": "https://{CLUSTERDNSNAME}.azurehdinsight.net/livy" }, "kernel_scala_credentials" : { "username": "{USERNAME}", "base64_password": "{BASE64ENCODEDPASSWORD}", "url": "https://{CLUSTERDNSNAME}.azurehdinsight.net/livy" } } -
Substitute {USERNAME}, {CLUSTERDNSNAME}, and {BASE64ENCODEDPASSWORD} with appropriate values. You can use a number of utilities in your favorite programming language or online to generate a base64 encoded password for your actual password.
-
Configure the right Heartbeat settings in
config.json. You should add these settings at the same level as thekernel_python_credentialsandkernel_scala_credentialssnippets your added earlier. For an example on how and where to add the heartbeat settings, see this sample config.json.-
For
sparkmagic 0.2.3(clusters v3.4), include:"should_heartbeat": true, "heartbeat_refresh_seconds": 5, "heartbeat_retry_seconds": 1 -
For
sparkmagic 0.11.2(clusters v3.5 and v3.6), include:"heartbeat_refresh_seconds": 5, "livy_server_heartbeat_timeout_seconds": 60, "heartbeat_retry_seconds": 1
[!TIP] Heartbeats are sent to ensure that sessions are not leaked. When a computer goes to sleep or is shut down, the heartbeat is not sent, resulting in the session being cleaned up. For clusters v3.4, if you wish to disable this behavior, you can set the Livy config
livy.server.interactive.heartbeat.timeoutto0from the Ambari UI. For clusters v3.5, if you do not set the 3.5 configuration above, the session will not be deleted. -
-
Start Jupyter. Use the following command from the command prompt.
jupyter notebook -
Verify that you can connect to the cluster using the Jupyter notebook and that you can use the Spark magic available with the kernels. Perform the following steps.
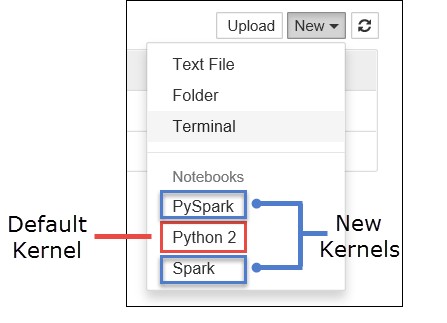
a. Create a new notebook. From the right-hand corner, click New. You should see the default kernel Python2 and the two new kernels that you install, PySpark and Spark. Click PySpark.
b. Run the following code snippet.
%%sql SELECT * FROM hivesampletable LIMIT 5If you can successfully retrieve the output, your connection to the HDInsight cluster is tested.
[!TIP] If you want to update the notebook configuration to connect to a different cluster, update the config.json with the new set of values, as shown in Step 3 above.
There can be a number of reasons why you might want to install Jupyter on your computer and then connect it to an Apache Spark cluster on HDInsight.
- Even though Jupyter notebooks are already available on the Spark cluster in Azure HDInsight, installing Jupyter on your computer provides you the option to create your notebooks locally, test your application against a running cluster, and then upload the notebooks to the cluster. To upload the notebooks to the cluster, you can either upload them using the Jupyter notebook that is running or the cluster, or save them to the /HdiNotebooks folder in the storage account associated with the cluster. For more information on how notebooks are stored on the cluster, see Where are Jupyter notebooks stored?
- With the notebooks available locally, you can connect to different Spark clusters based on your application requirement.
- You can use GitHub to implement a source control system and have version control for the notebooks. You can also have a collaborative environment where multiple users can work with the same notebook.
- You can work with notebooks locally without even having a cluster up. You only need a cluster to test your notebooks against, not to manually manage your notebooks or a development environment.
- It may be easier to configure your own local development environment than it is to configure the Jupyter installation on the cluster. You can take advantage of all the software you have installed locally without configuring one or more remote clusters.
Warning
With Jupyter installed on your local computer, multiple users can run the same notebook on the same Spark cluster at the same time. In such a situation, multiple Livy sessions are created. If you run into an issue and want to debug that, it will be a complex task to track which Livy session belongs to which user.
- Apache Spark with BI: Perform interactive data analysis using Spark in HDInsight with BI tools
- Apache Spark with Machine Learning: Use Spark in HDInsight for analyzing building temperature using HVAC data
- Apache Spark with Machine Learning: Use Spark in HDInsight to predict food inspection results
- Website log analysis using Apache Spark in HDInsight
- Create a standalone application using Scala
- Run jobs remotely on an Apache Spark cluster using Apache Livy
- Use HDInsight Tools Plugin for IntelliJ IDEA to create and submit Spark Scala applications
- Use HDInsight Tools Plugin for IntelliJ IDEA to debug Apache Spark applications remotely
- Use Apache Zeppelin notebooks with an Apache Spark cluster on HDInsight
- Kernels available for Jupyter notebook in Apache Spark cluster for HDInsight
- Use external packages with Jupyter notebooks