forked from MisterBooo/LeetCodeAnimation
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
1 parent
ab07ece
commit fb7c0a1
Showing
2 changed files
with
170 additions
and
3 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,165 @@ | ||
| # LeetCode 第 347 号问题:前 K 个高频元素 | ||
|
|
||
| > 本文首发于公众号「五分钟学算法」,是[图解 LeetCode ](<https://github.com/MisterBooo/LeetCodeAnimation>)系列文章之一。 | ||
| > | ||
| > 个人网站:[https://www.cxyxiaowu.com](https://www.cxyxiaowu.com) | ||
|
|
||
| 今天分享的题目来源于 LeetCode 上第 347 号问题:前 K 个高频元素。题目难度为 Medium,目前通过率为 56.9% 。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 题目描述 | ||
|
|
||
| 给定一个非空的整数数组,**返回其中出现频率前 k 高**的元素。 | ||
|
|
||
| **示例 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| 输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 | ||
| 输出: [1,2] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| **示例 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| 输入: nums = [1], k = 1 | ||
| 输出: [1] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| **说明:** | ||
|
|
||
| - 你可以假设给定的 k 总是合理的,且 1 ≤ k ≤ 数组中不相同的元素的个数。 | ||
| - 你的算法的时间复杂度必须优于 O(n log n) , n 是数组的大小。 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 题目解析 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 解法一:粗暴排序法 | ||
|
|
||
| 最简单粗暴的思路就是 **使用排序算法对元素按照频率由高到低进行排序**,然后再取前 k 个元素。 | ||
|
|
||
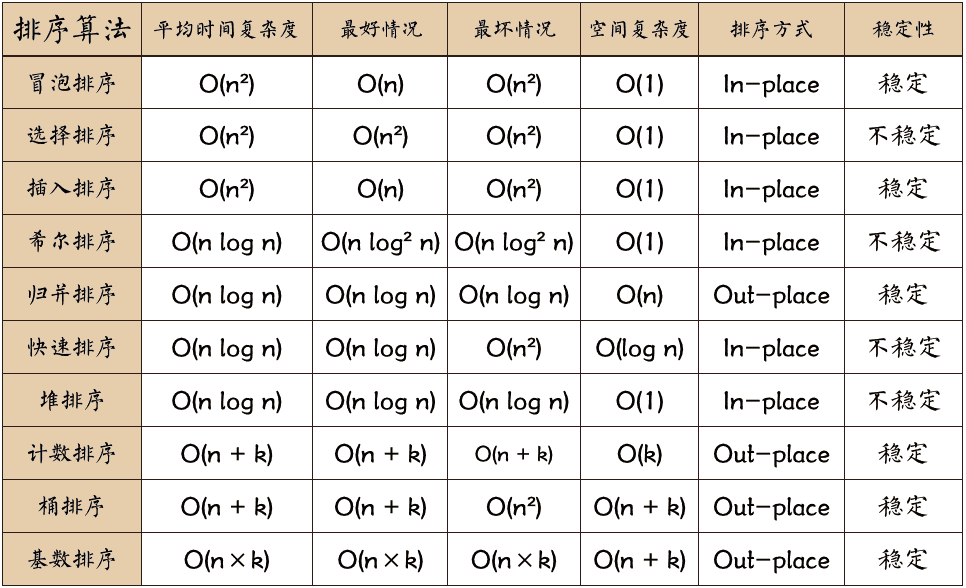
| 以下十种排序算法,任你挑选! | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 可以发现,使用常规的诸如 冒泡、选择、甚至快速排序都是不满足题目要求,它们的时间复杂度都是大于或者等于 O(n logn) ,而题目要求算法的时间复杂度必须优于 O(n log n) 。 | ||
|
|
||
| #### 复杂度分析 | ||
|
|
||
| - **时间复杂度**:O(nlogn),n 表示数组长度。首先,遍历一遍数组统计元素的频率,这一系列操作的时间复杂度是 O(n);接着,排序算法时间复杂度为O(nlogn) ;因此整体时间复杂度为 O(nlogn) 。 | ||
| - **空间复杂度**:O(n),最极端的情况下(每个元素都不同),用于存储元素及其频率的 Map 需要存储 n 个键值对。 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 解法二:最小堆 | ||
|
|
||
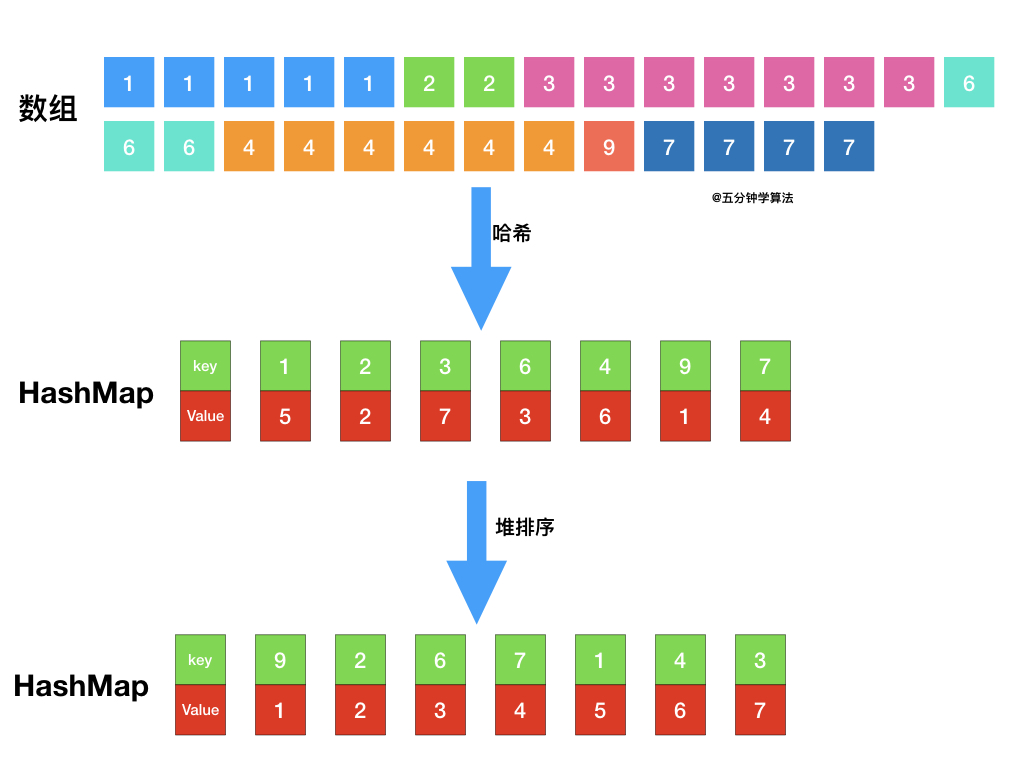
| 题目最终需要返回的是前 k 个频率最大的元素,可以想到借助堆这种数据结构,对于 k 频率之后的元素不用再去处理,进一步优化时间复杂度。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
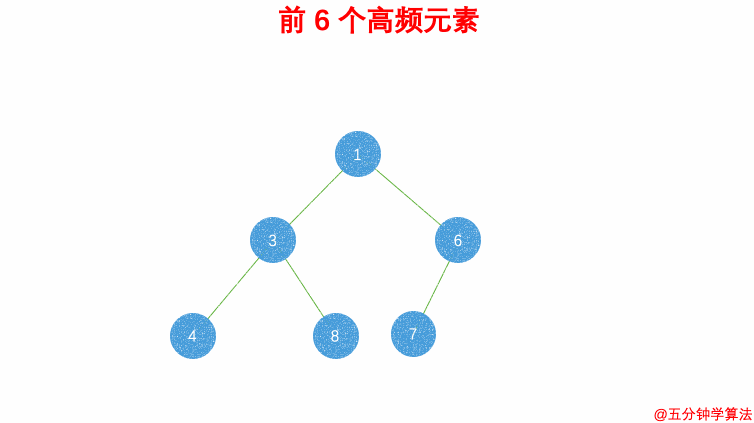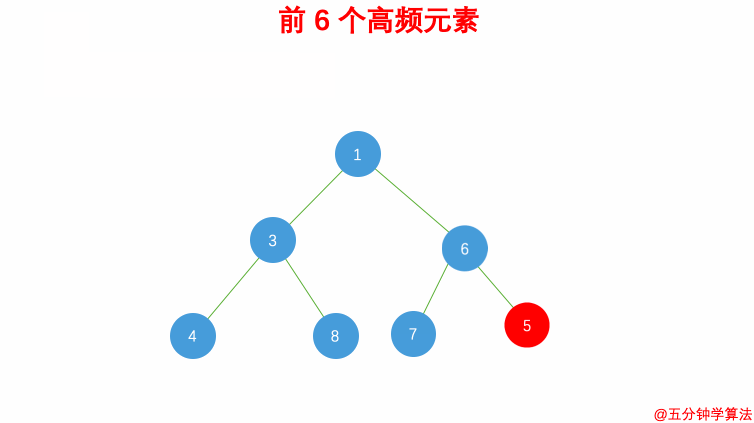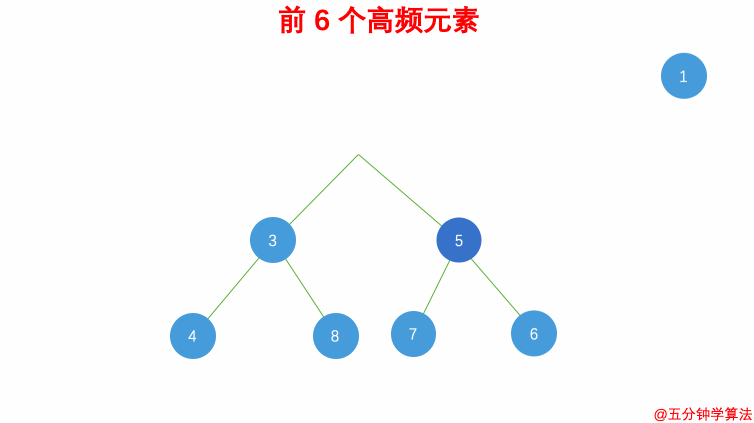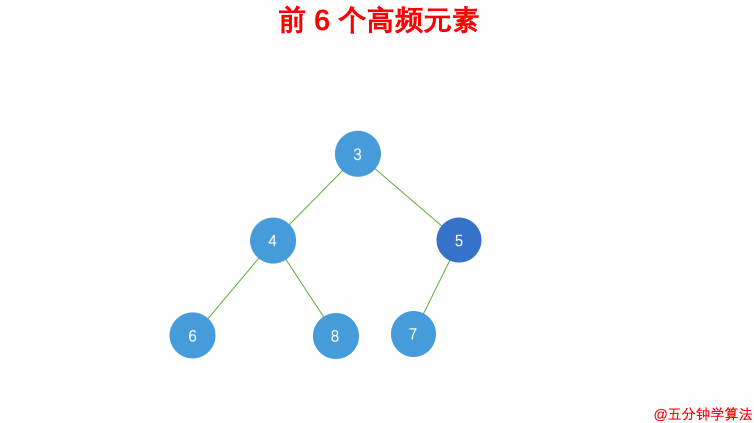
| 具体操作为: | ||
|
|
||
| - 借助 **哈希表** 来建立数字和其出现次数的映射,遍历一遍数组统计元素的频率 | ||
| - 维护一个元素数目为 k 的最小堆 | ||
| - 每次都将新的元素与堆顶元素(堆中频率最小的元素)进行比较 | ||
| - 如果新的元素的频率比堆顶端的元素大,则弹出堆顶端的元素,将新的元素添加进堆中 | ||
| - 最终,堆中的 k 个元素即为前 k 个高频元素 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 代码如下: | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| class Solution { | ||
| public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { | ||
| // 使用字典,统计每个元素出现的次数,元素为键,元素出现的次数为值 | ||
| HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap(); | ||
| for(int num : nums){ | ||
| if (map.containsKey(num)) { | ||
| map.put(num, map.get(num) + 1); | ||
| } else { | ||
| map.put(num, 1); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| // 遍历map,用最小堆保存频率最大的k个元素 | ||
| PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() { | ||
| @Override | ||
| public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) { | ||
| return map.get(a) - map.get(b); | ||
| } | ||
| }); | ||
| for (Integer key : map.keySet()) { | ||
| if (pq.size() < k) { | ||
| pq.add(key); | ||
| } else if (map.get(key) > map.get(pq.peek())) { | ||
| pq.remove(); | ||
| pq.add(key); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| // 取出最小堆中的元素 | ||
| List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); | ||
| while (!pq.isEmpty()) { | ||
| res.add(pq.remove()); | ||
| } | ||
| return res; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| #### 复杂度分析 | ||
|
|
||
| - **时间复杂度**:O(nlogk), n 表示数组的长度。首先,遍历一遍数组统计元素的频率,这一系列操作的时间复杂度是 O(n);接着,遍历用于存储元素频率的 map,如果元素的频率大于最小堆中顶部的元素,则将顶部的元素删除并将该元素加入堆中,**这里维护堆的数目是 k **,所以这一系列操作的时间复杂度是 O(nlogk)的;因此,总的时间复杂度是 O(nlogk) 。 | ||
| - **空间复杂度**:O(n),最坏情况下(每个元素都不同),map 需要存储 n 个键值对,优先队列需要存储 k个元素,因此,空间复杂度是 O(n)。 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ### 解法三:桶排序法 | ||
|
|
||
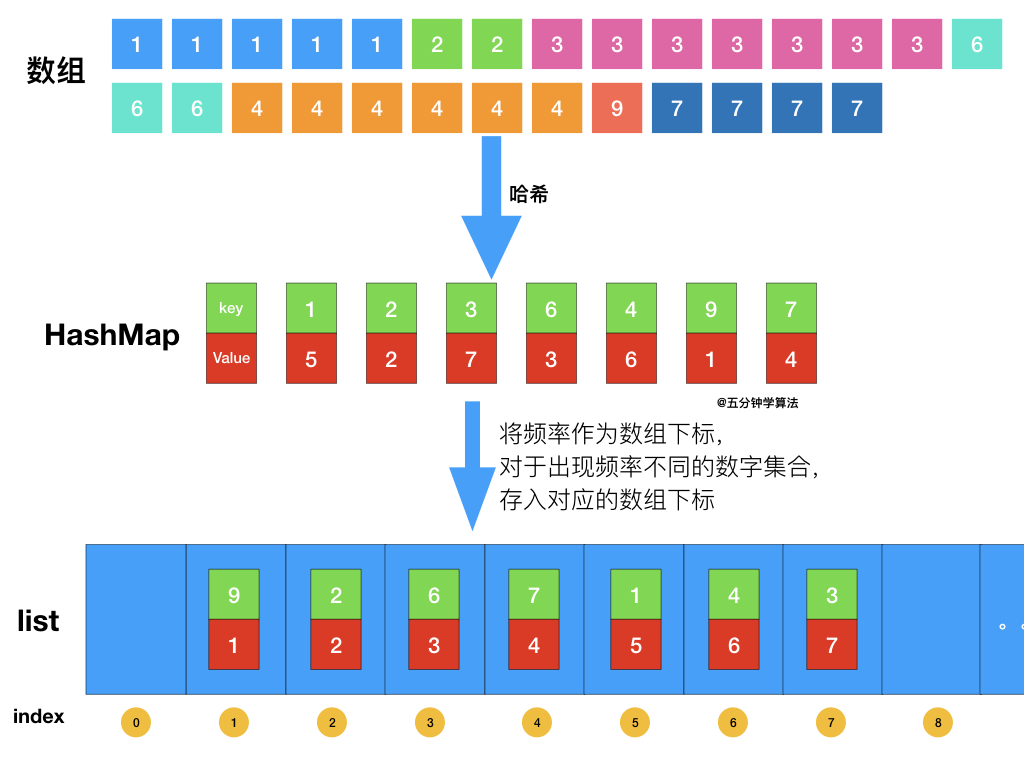
| 首先依旧使用哈希表统计频率,统计完成后,创建一个数组,将频率作为数组下标,对于出现频率不同的数字集合,存入对应的数组下标即可。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 代码实现如下: | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| //基于桶排序求解「前 K 个高频元素」 | ||
| class Solution { | ||
| public List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { | ||
| List<Integer> res = new ArrayList(); | ||
| // 使用字典,统计每个元素出现的次数,元素为键,元素出现的次数为值 | ||
| HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap(); | ||
| for(int num : nums){ | ||
| if (map.containsKey(num)) { | ||
| map.put(num, map.get(num) + 1); | ||
| } else { | ||
| map.put(num, 1); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| //桶排序 | ||
| //将频率作为数组下标,对于出现频率不同的数字集合,存入对应的数组下标 | ||
| List<Integer>[] list = new List[nums.length+1]; | ||
| for(int key : map.keySet()){ | ||
| // 获取出现的次数作为下标 | ||
| int i = map.get(key); | ||
| if(list[i] == null){ | ||
| list[i] = new ArrayList(); | ||
| } | ||
| list[i].add(key); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| // 倒序遍历数组获取出现顺序从大到小的排列 | ||
| for(int i = list.length - 1;i >= 0 && res.size() < k;i--){ | ||
| if(list[i] == null) continue; | ||
| res.addAll(list[i]); | ||
| } | ||
| return res; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| #### 复杂度分析 | ||
|
|
||
| - **时间复杂度**:O(n), n 表示数组的长度。首先,遍历一遍数组统计元素的频率,这一系列操作的时间复杂度是 O(n);桶的数量为 n + 1,所以桶排序的时间复杂度为 O(n);因此,总的时间复杂度是 O(n)。 | ||
| - **空间复杂度**:很明显为 O(n) | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|