A blazingly fast JSON serializing & deserializing library, accelerated by JIT(just-in-time compiling) and SIMD(single-instruction-multi-data).
WARNING: This is still in alpha stage, use with care !
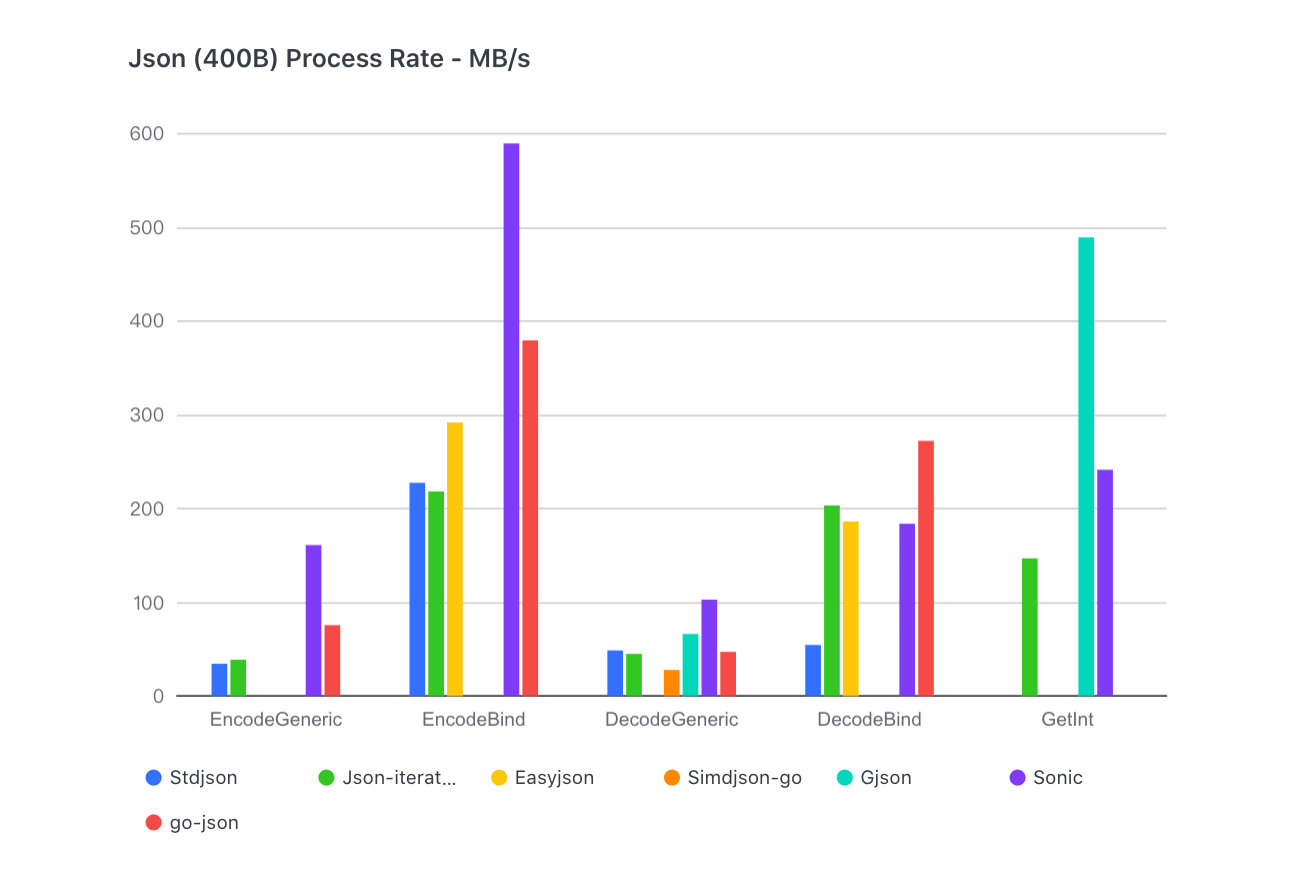
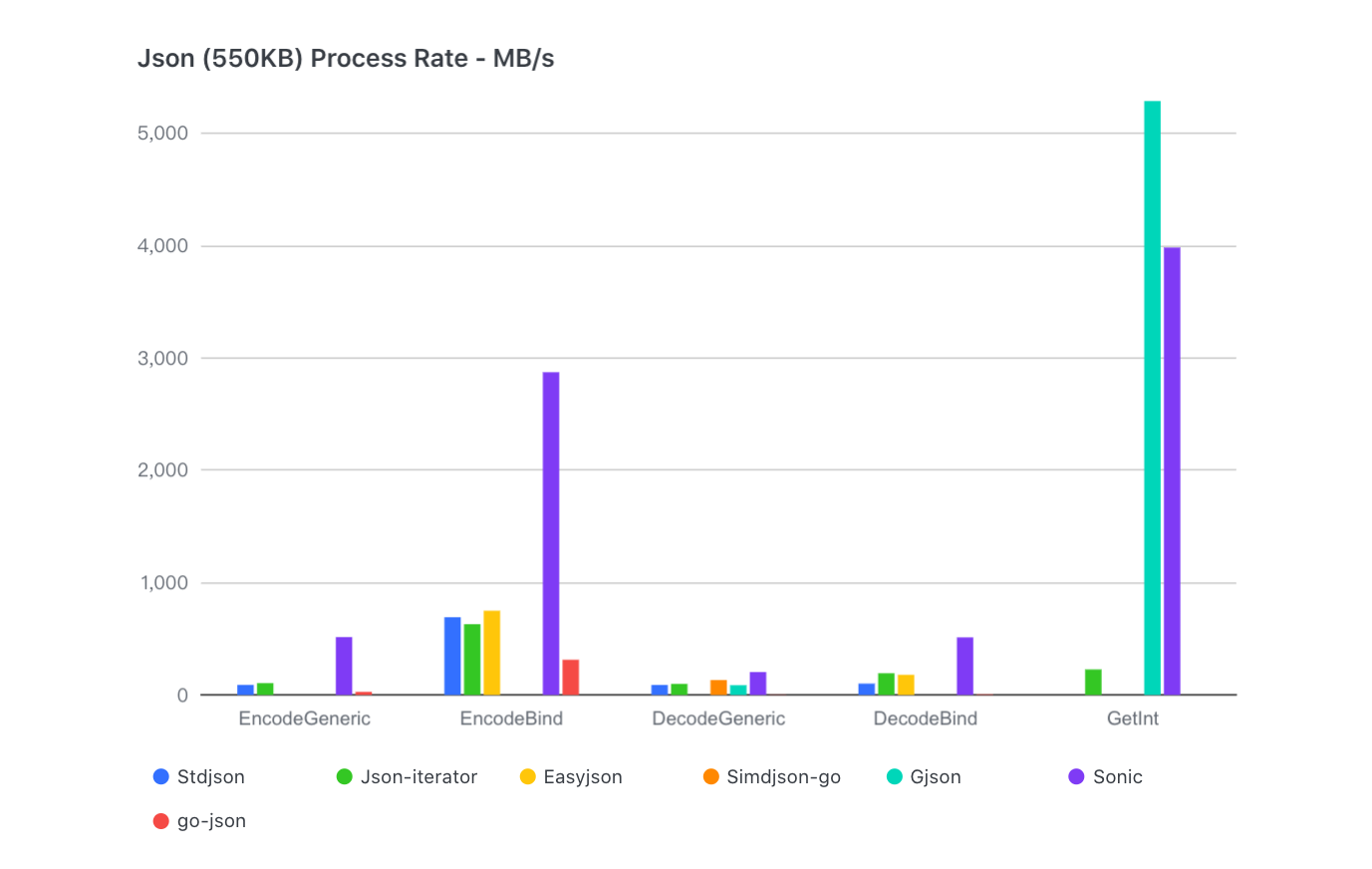
For all sizes of json and all scenes of usage, Sonic performs almost best.
For a 13KB TwitterJson, Sonic is 1.5x faster than json-iterator in decoding, 2.5x faster in encoding.
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
pkg: github.com/bytedance/sonic/encoder
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-9880H CPU @ 2.30GHz
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_Sonic-16 100000 24174 ns/op 539.22 MB/s 17757 B/op 42 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_JsonIter-16 100000 44613 ns/op 292.18 MB/s 13433 B/op 77 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_GoJson-16 100000 87898 ns/op 148.30 MB/s 13234 B/op 39 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_StdLib-16 100000 133512 ns/op 97.63 MB/s 48177 B/op 827 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_Sonic-16 100000 6058 ns/op 2151.73 MB/s 13481 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_JsonIter-16 100000 21223 ns/op 614.20 MB/s 9488 B/op 2 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_GoJson-16 100000 10186 ns/op 1279.74 MB/s 9480 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_StdLib-16 100000 17741 ns/op 734.75 MB/s 9479 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_Sonic-16 100000 53344 ns/op 244.36 MB/s 50158 B/op 313 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_StdLib-16 100000 141006 ns/op 92.44 MB/s 50898 B/op 772 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_JsonIter-16 100000 106386 ns/op 122.53 MB/s 55785 B/op 1068 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_GoJson-16 100000 107184 ns/op 121.61 MB/s 65678 B/op 944 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_Sonic-16 100000 30039 ns/op 433.94 MB/s 25259 B/op 34 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_StdLib-16 100000 131088 ns/op 99.44 MB/s 10560 B/op 207 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_JsonIter-16 100000 37988 ns/op 343.13 MB/s 14674 B/op 385 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_GoJson-16 100000 33741 ns/op 386.33 MB/s 22047 B/op 49 allocs/opMore detail see decoder/decoder_test.go, encoder/encoder_test.go, ast/search_test.go, ast/parser_test.go
The behaviors are mostly consistent with encoding/json, except some uncommon escaping and key sorting (see issue4)
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
// Marshal
output, err := sonic.Marshal(&data)
// Unmarshal
err := sonic.Unmarshal(input, &data) Search partial json by given pathes, which must be non-negative integer or string or nil
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
input := []byte(`{"key1":[{},{"key2":{"key3":[1,2,3]}}]}`)
// no path, returns entire json
root, err := sonic.Get(input)
raw := root.Raw() // == string(input)
// multiple pathes
root, err := sonic.Get(input, "key1", 1, "key2")
sub := root.Get("key3").Index(2).Int64() // == 3Returned ast.Node supports:
- secondary search:
Get(),Index(),GetByPath() - type assignment:
Int64(),Float64(),String(),Number(),Bool(),Map(),Array() - children traversal:
Values(),Properties() - supplement:
Set(),SetByIndex(),Add(),Cap(),Len()
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
input := `1`
var data interface{}
// default float64
dc := decoder.NewDecoder(input)
dc.Decode(&data) // data == float64(1)
// use json.Number
dc = decoder.NewDecoder(input)
dc.UseNumber()
dc.Decode(&data) // data == json.Number("1")
// use int64
dc = decoder.NewDecoder(input)
dc.UseInt64()
dc.Decode(&data) // data == int64(1)
root, err := sonic.GetFromString(input)
// Get json.Number
jn := root.Number()
jm := root.InterfaceUseNumber().(json.Number) // jn == jm
// Get float64
fn := root.Float64()
fm := root.Interface().(float64) // jn == jmSince Sonic uses JIT(just-in-time) compiling for decoder/encoder, huge schema may cause request-timeout. For better stability, we suggest to use Pretouch() for more-than-10000-field schema(struct) before Marshal()/Unmarshal().
import (
"reflect"
"github.com/bytedance/sonic"
)
func init() {
var v HugeStruct
err := sonic.Pretouch(reflect.TypeOf(v))
}For alignment to encoding/json, we provide API to pass []byte as arguement, but the string-to-bytes copy is conducted at the same time considering safety, which may lose performance when origin json is huge. Therefore, you can use UnmarshalString, GetFromString to pass string, as long as your origin data is string or nocopy-cast is safe for your []byte.
Get() overlapping pathes from the same root may cause repeating parsing. Instead of using Get() several times, you can use parser and searcher together like this:
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
root, err := sonic.GetFromString(_TwitterJson, "statuses", 3, "user")
a = root.GetByPath( "entities","description")
b = root.GetByPath( "entities","url")
c = root.GetByPath( "created_at")No need to worry about the overlaping or overparsing of a, b and c, because the inner parser of their root is lazy-loaded.
In most cases of fully-load generic json, Unmarshal() performs better than ast.Loads(). But if you only want to search a partial json and convert it into interface{} (or map[string]interface{}, []interface{}), we advise you to combine Get() and Unmarshal():
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
node, err := sonic.GetFromString(_TwitterJson, "statuses", 3, "user")
var user interface{}
err = sonic.UnmarshalString(node.Raw(), &user)