This thesis presents an innovative approach to audio chord recognition, aiming to automatically identify and classify fundamental chord structures within music pieces. Leveraging Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) with Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (biLSTM) layers, advanced feature engineering, and post-processing techniques rooted in music theory, our research enhances the accuracy and robustness of chord recognition systems. By extracting features from chord representations such as root, bass, and triad qualities, and segmenting the problem into distinct components, our framework creates a solid ground to enhance the accuracy of chord recognition. Ad- ditionally, we employ transfer learning techniques to capitalize on pre-trained models, fine-tuning them for our specific chord recognition task, thus improving generalization and robustness. Moreover, our exploration encompasses various Fourier transforms for feature extraction, including Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) and Constant Q Trans- form (CQT), to capture essential information from audio signals and optimize chord recog- nition performance. Through extensive experimentation and evaluation of different CNN and biLSTM configurations, as well as post-processing techniques, our approach demon- strates significant enhancements in several aspectes of chord recognition. Overall, this research contributes a comprehensive framework that leverages deep learning method- ologies, sophisticated feature engineering, and post-processing techniques, showcasing its potential to advance music information retrieval systems.
The preprocessing pipeline involves a series of steps to convert and transform the raw audio data into a format that can be used for further analysis or training. Below is a description of each preprocessing script and its purpose:
This script is responsible for converting .mp3 files to .wav format, which is a standard format for audio processing tasks.
Usage:
python convert_mp3_wav.py --directory path/to/files --mono- Converts MP3 audio files into WAV format for easier processing in subsequent steps.
This script applies a Constant-Q Transform (CQT) to the audio data, which is useful for time-frequency analysis. CQT is a type of Fourier transform that provides higher frequency resolution at lower frequencies and is typically used in music and audio signal processing.
Usage:
python cqt_transform.py --paths_txt path/to/paths_txt --dest_txt path/to/destination_txt - You can use pooling by adding the
--poolflag - You can use
--noskipto replace already transformed files - Performs a CQT on audio files for frequency domain analysis.
This script performs a standard Fourier transform on the audio data. The Fourier transform is useful for transforming the audio signal from the time domain into the frequency domain.
Usage:
python fourier_tr.py --paths_txt path/to/paths_txt --dest_txt path/to/destination_txt - You can use pooling by adding the
--poolflag - Transforms audio files using the Fourier Transform to obtain frequency components.
This script performs pitch shifting on the audio data, altering the pitch without affecting the tempo. Pitch shifting is commonly used for data augmentation in audio processing.
Usage:
python pitch_shifter.py --directory path/to/files --dest_dir path/to/destination --n_steps 5 --pool --noise- You can optionally use
poolandnoiseif you want to use pooling for parallel processing and to add Gaussian noise accordingly. - Shifts the pitch of audio files for augmentation or other tasks.
This script is similar to pitch_shifter.py, but it also adjusts the corresponding labels for the shifted audio. This ensures that the labels remain consistent with the pitch-shifted data.
Usage:
python pitch_shift_labels.py --directory path/to/files --dest_dir path/to/destination --n_steps 5 --pool- You can optionally use
poolif you want to use pooling for parallel processing. - Shifts the pitch of audio files and updates the corresponding labels accordingly.
This script creates the training and testing datasets in the form of pickles, which include X_train, y_train, and other necessary data splits.
Usage:
python create_train_test.py- Prepares pickled datasets for training and testing the model.
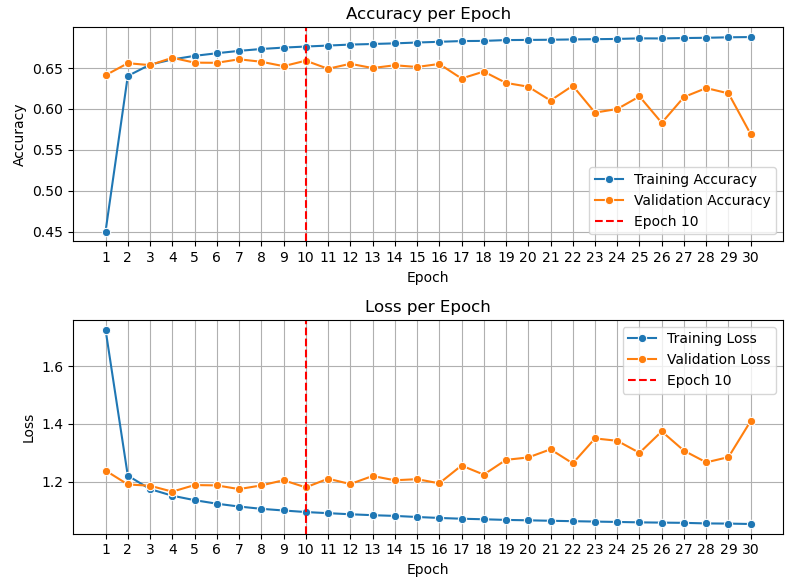
This script trains the 1D CNN model for the task of root prediction, using the pickled datasets created in the previous step.
Usage:
python fit_cnn.py- Trains the 1D CNN model for root prediction.
This script applies transfer learning to the model for the remaining tasks. You will need to adjust the parameters in the script for each task before running it.
Usage:
python run_transfer_learning.py- Trains the model for each additional task using transfer learning. Parameters must be adjusted for each task.
This script creates the training and testing datasets, including X_train and y_train. It ensures all chord types, including 7 chords, are properly included.
Usage:
python create_train_test.py- Prepares training and testing datasets in the form of pickles.
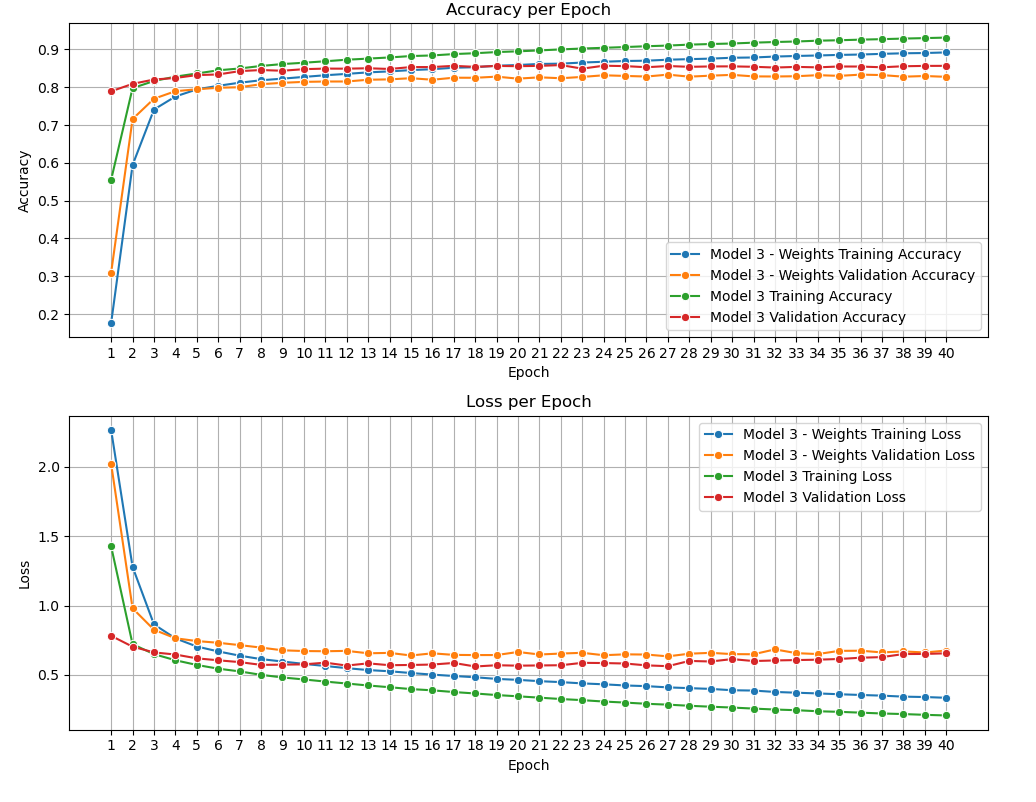
This script trains the 2D model for the task of root prediction, using the datasets created in the previous step.
Usage:
python fit_model.py- Trains the 2D model for chord classification.
This script applies transfer learning to the 2D model for additional tasks. You will need to adjust parameters in the script based on the task being performed.
Usage:
python run_transfer_learning.py- Trains the model for additional tasks using transfer learning. Adjust parameters as needed for each task.
This script runs inference on the trained 2D model to predict chords.
Usage:
python inference.py- Runs inference on the trained 2D model and generates chord predictions.
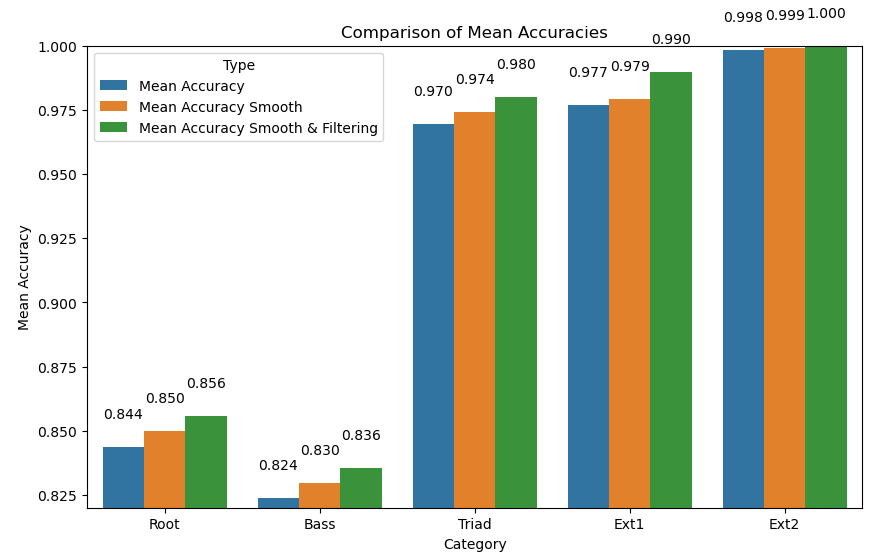
This script assembles predictions for chord classification and implements metrics for evaluating parts of chords.
Usage:
python assemble_preds.py- Assembles model predictions and evaluates chord-related metrics.
Results comparing model outputs with model outputs using post processing techniques (see src/post_processing).