An extensible, modular GNU Emacs front-end for interacting with external debuggers, brought to you by Rocky Bernstein (@rocky) and Clément Pit-Claudel (@cpitclaudel).
You can install RealGUD from MELPA, a repository of Emacs packages. If you don't have MELPA set up, add the following to your .emacs and restart Emacs:
(require 'package)
(add-to-list 'package-archives '("melpa" . "http://melpa.org/packages/") t)
(package-initialize)You can then run the following commands to install RealGUD:
M-x package-refresh-contents RET (to refresh your package database)
M-x package-install RET realgud RET (to install and compile `realgud` and its dependencies)
Alternatively, you can install RealGUD using el-get or from source directly. See this article in our wiki for more info.
Use M-x load-library RET realgud RET to load RealGUD.
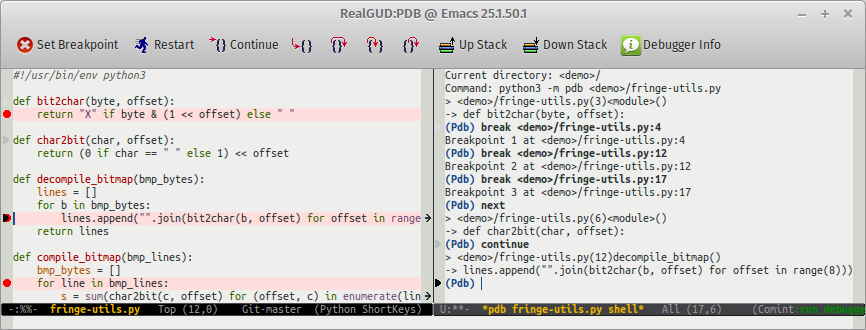
Open a source file, then use M-x realgud:<debugger-name> to start your favorite debugger (for example, you can use M-x realgud:pdb to launch PDB, a Python debugger). RealGUD opens two windows: the command window (showing the debugger's REPL), and the source window, showing your code (with some debuggers, such as realgud:gdb, this window does not appear until you type start in the command window). An solid arrow ▶ indicates the current line in the source window. Grayed out arrows indicate previous positions.
All usual debugger commands work in the command window: for example, you can type n RET in the command window to step forward one source line. But RealGUD's power lies in the source window: in it, most single keys correspond to a debugger action. For example, you can press n in the source window to step forward.
Here is a quick rundown of the most useful commands. “🐁” indicates mouse commands (commands that can be run by clicking on a variable or in the margins). Many of the commands are accessible from the tool bar (tool-bar-mode) and the menu (menu-bar-mode).
-
Motion commands
Command Action n, F10 Next (aka “step over”, “step through”) s, SPC, F11 Step (aka “step into”) f, S-F11 Finish (aka “step out”, “return”) c, F5 Continue (run to next break point) -
Using breakpoints
Command Action b, F9 Set breakpoint 🐁 D Clear breakpoint 🐁 (by number) -
Inspecting variables
Command Action mouse-2 (middle button) Inspect variable under cursor (in tooltip) 🐁 e Evaluate expression -
Control commands
Command Action q, S-F5 Quit R, r Run (aka “restart”) S Go to command window
RealGUD supports many external debuggers. Help us support even more!
“⚙” indicates a work-in-progress (contributions welcome!)
| Command | Action |
|---|---|
| U | Until (run to a greater source line) |
| u, > | Up stack (move to older stack frame) |
| d, < | Down stack (move to younger stack frame) |
| X | Clear breakpoint (by line) |
| j | Jump to current line ⚙ |
| - | Disable breakpoint ⚙ |
| + | Enable breakpoint ⚙ |
Use M-x realgud-track-mode inside an existing shell, or eshell buffer to track an already-running debugger process.
Browse the wiki for more information about setting up, using realgud, exploring features, and lots more.