forked from NVlabs/SPADE
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
49 additions
and
4 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1,9 +1,54 @@ | ||
| # SPADE: Semantic Image Synthesis with Spatially-Adaptive Normalization | ||
| ## Semantic Image Synthesis with Spatially-Adaptive Normalization | ||
|
|
||
| Taesung park, Ming-Yu Liu, Ting-Chun Wang, and Jun-Yan Zhu, CVPR 2019. | ||
| We will provide PyTorch implementation of the code soon, along with pretrained models that are needed to replicate the results of the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.07291). The work was done by [Taesung Park](http://taesung.me/), [Ming-Yu Liu](http://mingyuliu.net/), [Ting-Chun Wang](https://tcwang0509.github.io/), and [Jun-Yan Zhu](http://people.csail.mit.edu/junyanz/). | ||
|
|
||
| The code will be released soon. In the meantime, please visit our [project webpage](https://nvlabs.github.io/SPADE/). | ||
| In the meantime, please visit our [project webpage](https://nvlabs.github.io/SPADE/) for more information. | ||
|  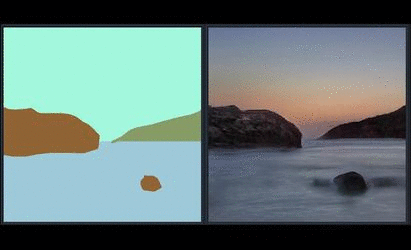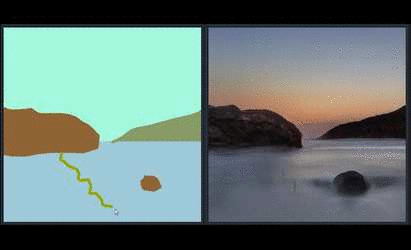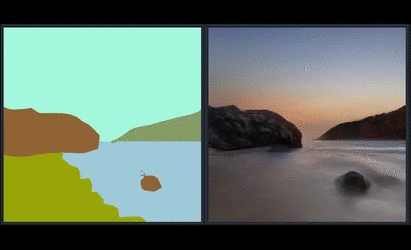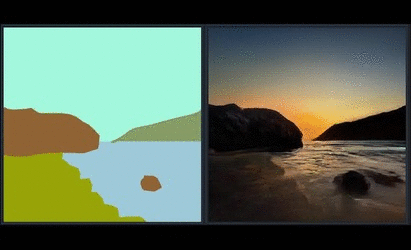 | ||
|
|
||
|   | ||
| ## Brief Description of the Method | ||
|
|
||
| <img src="https://nvlabs.github.io/SPADE/images/method.png" width="97%"> | ||
|
|
||
| In many common normalization techniques such as Batch Normalization (<a href="[https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167](https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167)"><span style="font-weight:normal">Ioffe et al., 2015</span></a>), there are learned affine layers (as in <a href="[https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html?highlight=batchnorm2d#torch.nn.BatchNorm2d](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html?highlight=batchnorm2d#torch.nn.BatchNorm2d)"><span style="font-weight:normal">PyTorch</span></a> and <a href="[https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/layers/batch_normalization](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/layers/batch_normalization)"><span style="font-weight:normal">TensorFlow</span></a>) that are applied after the actual normalization step. In SPADE, the affine layer is <i>learned from semantic segmentation map</i>. This is similar to Conditional Normalization (<a href="[https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.00683](https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.00683)"><span style="font-weight:normal">De Vries et al., 2017</span></a> and <a href="[https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.07629](https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.07629)"><span style="font-weight:normal">Dumoulin et al., 2016</span></a>), except that the learned affine parameters now need to be spatially-adaptive, which means we will use different scaling and bias for each semantic label. Using this simple method, semantic signal can act on all layer outputs, unaffected by the normalization process which may lose such information. Moreover, because the semantic information is provided via SPADE layers, random latent vector may be used as input to the network, which can be used to manipulate the style of the generated images. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Comparison to Existing Methods | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
| SPADE outperforms existing methods on the [COCO-Stuff dataset](https://github.com/nightrome/cocostuff), which is more challenging than [the Cityscapes dataset](https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com/) due to more diverse scenes and labels. The images above are the ones authors liked. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Applying on Flickr Images | ||
|
|
||
|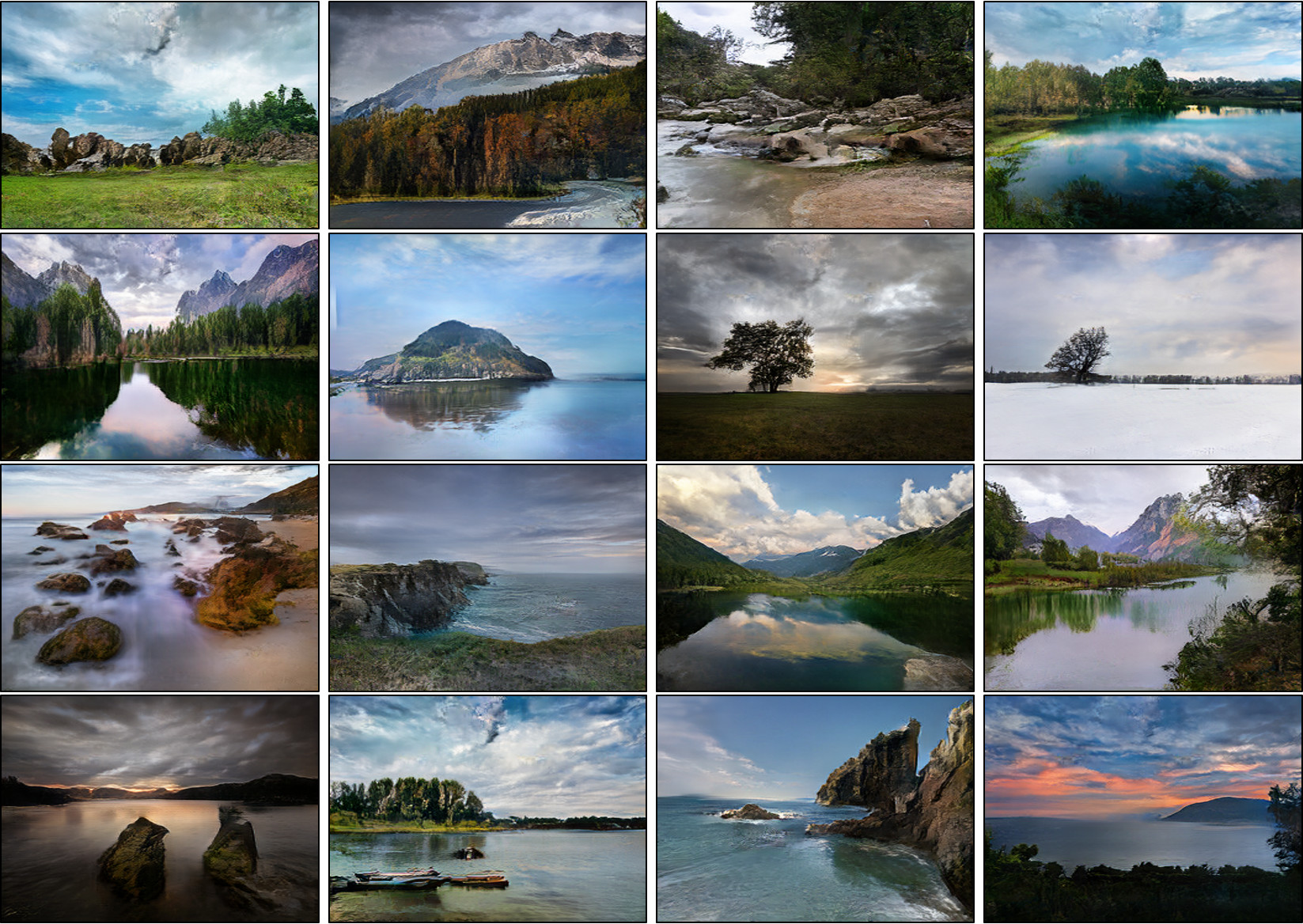  | ||
|
|
||
| Since SPADE works on diverse labels, it can be trained with [an existing semantic segmentation network](https://github.com/kazuto1011/deeplab-pytorch) to learn the reverse mapping from semantic maps to photos. These images were generated from SPADE trained on 40k images scraped from [Flickr](https://www.flickr.com/). | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Abstract | ||
|
|
||
| We propose spatially-adaptive normalization, a simple but effective layer for synthesizing photorealistic images given an input semantic layout. Previous methods directly feed the semantic layout as input to the network, which is then processed through stacks of convolution, normalization, and nonlinearity layers. We show that this is suboptimal because the normalization layers tend to wash away semantic information. To address the issue, we propose using the input layout for modulating the activations in normalization layers through a spatially-adaptive, learned transformation. Experiments on several challenging datasets demonstrate the advantage of the proposed method compared to existing approaches, regarding both visual fidelity and alignment with input layouts. Finally, our model allows users to easily control the style and content of synthesis results as well as create multi-modal results. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ### Paper | ||
|
|
||
| [arxiv](https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.07291), 2019. | ||
| [](https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.07291) | ||
|
|
||
| ### Citation | ||
|
|
||
| Taesung Park, Ming-Yu Liu, Ting-Chun Wang, and Jun-Yan Zhu. | ||
| "Semantic Image Synthesis with Spatially-Adaptive Normalization", in CVPR, 2019. [Bibtex](https://nvlabs.github.io/SPADE/SPADE.txt) | ||
|
|
||
| ## Acknowledgement | ||
|
|
||
| We thank Alyosha Efros and Jan Kautz for insightful advice. Taesung Park contributed to the work during his internship at NVIDIA. His Ph.D. is supported by Samsung Scholarship. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Related Work | ||
|
|
||
| - V. Dumoulin, J. Shlens, and M. Kudlur. [**"A learned representation for artistic style"**](https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.07629), in ICLR 2016. | ||
| - H. De Vries, F. Strub, J. Mary, H. Larochelle, O. Pietquin, and A. C. Courville. [**"Modulating early visual processing by language"**](https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.00683), in NeurIPS 2017. | ||
| - T. Wang, M. Liu, J. Zhu, A. Tao, J. Kautz, and B. Catanzaro. [**"High-Resolution Image Synthesis and Semantic Manipulation with Conditional GANs"**](https://tcwang0509.github.io/pix2pixHD/), in CVPR 2018. (pix2pixHD) | ||
| - P. Isola, J. Zhu, T. Zhou, and A. A. Efros. [**"Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks"**](https://phillipi.github.io/pix2pix/), in CVPR 2017. (pix2pix) | ||
| - Q. Chen and V. Koltun. [**"Photographic image synthesis with cascaded refinement networks.**](https://cqf.io/ImageSynthesis/), ICCV 2017. (CRN) | ||
|
|
||
|
|