Solid Errors is a DB-based, app-internal exception tracker for Rails applications, designed with simplicity and performance in mind. It uses the new Rails error reporting API to store uncaught exceptions in the database, and provides a simple UI for viewing and managing exceptions.
Install the gem and add to the application's Gemfile by executing:
$ bundle add solid_errorsIf bundler is not being used to manage dependencies, install the gem by executing:
$ gem install solid_errorsAfter installing the gem, run the installer:
$ rails generate solid_errors:installThis will copy the required migration over to your app.
Then mount the engine in your config/routes.rb file:
authenticate :user, -> (user) { user.admin? } do
mount SolidErrors::Engine, at: "/solid_errors"
endNote
Be sure to secure the dashboard in production.
All exceptions are recorded automatically. No additional code required.
Please consult the official guides for an introduction to the error reporting API.
There are intentionally few features; you can view and resolve errors. That’s it. The goal is to provide a simple, lightweight, and performant solution for tracking exceptions in your Rails application. If you need more features, you should probably use a 3rd party service like Honeybadger, whose MIT-licensed Ruby agent gem provided a couple of critical pieces of code for this project.
You can configure Solid Errors via the Rails configuration object, under the solid_errors key. Currently, only 3 configuration options are available:
connects_to- The database configuration to use for the Solid Errors database. See Database Configuration for more information.username- The username to use for HTTP authentication. See Authentication for more information.password- The password to use for HTTP authentication. See Authentication for more information.
config.solid_errors.connects_to takes a custom database configuration hash that will be used in the abstract SolidErrors::Record Active Record model. This is required to use a different database than the main app. For example:
# Use a single separate DB for Solid Errors
config.solid_errors.connects_to = { database: { writing: :solid_errors, reading: :solid_errors } }or
# Use a separate primary/replica pair for Solid Errors
config.solid_errors.connects_to = { database: { writing: :solid_errors_primary, reading: :solid_errors_replica } }Solid Errors does not restrict access out of the box. You must secure the dashboard yourself. However, it does provide basic HTTP authentication that can be used with basic authentication or Devise. All you need to do is setup a username and password.
There are two ways to setup a username and password. First, you can use the SOLIDERRORS_USERNAME and SOLIDERRORS_PASSWORD environment variables:
ENV["SOLIDERRORS_USERNAME"] = "frodo"
ENV["SOLIDERRORS_PASSWORD"] = "ikeptmysecrets"Second, you can set the SolidErrors.username and SolidErrors.password variables in an initializer:
# Set authentication credentials for Solid Errors
config.solid_errors.username = Rails.application.credentials.solid_errors.username
config.solid_errors.password = Rails.application.credentials.solid_errors.passwordEither way, if you have set a username and password, Solid Errors will use basic HTTP authentication. If you have not set a username and password, Solid Errors will not require any authentication to view the dashboard.
If you use Devise for authenctication in your app, you can also restrict access to the dashboard by using their authenticate contraint in your routes file:
authenticate :user, -> (user) { user.admin? } do
mount SolidErrors::Engine, at: "/solid_errors"
endThere are only two screens in the dashboard.
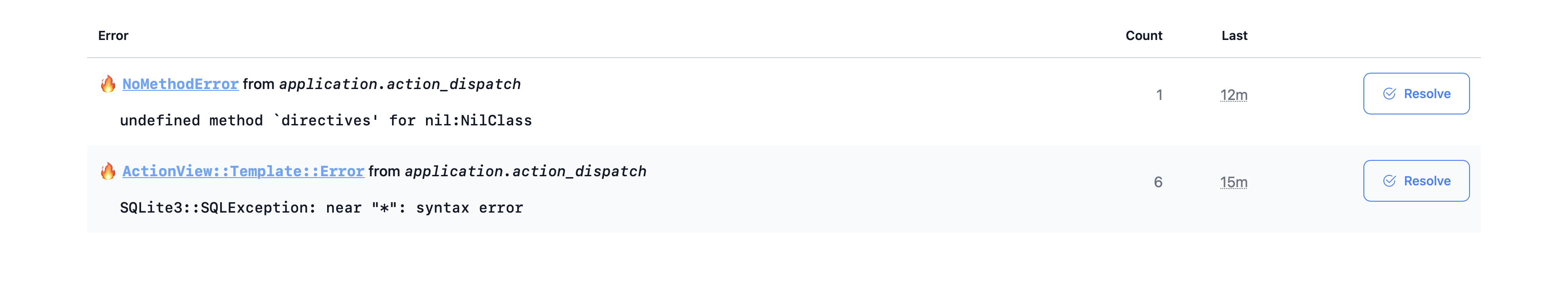
- the index view of all unresolved errors:
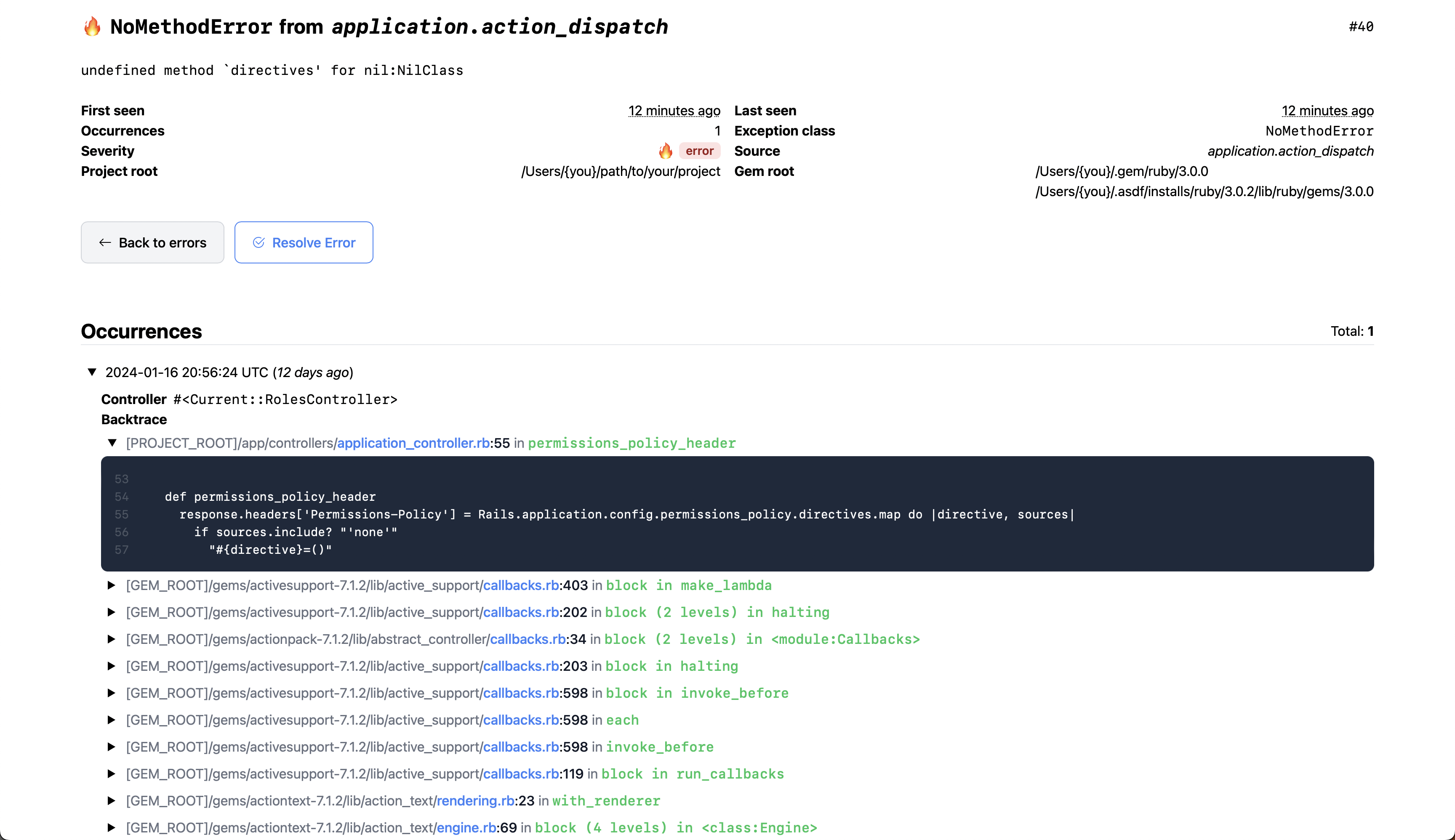
- and the show view of a particular error:
After checking out the repo, run bin/setup to install dependencies. Then, run rake test to run the tests. You can also run bin/console for an interactive prompt that will allow you to experiment.
To install this gem onto your local machine, run bundle exec rake install. To release a new version, update the version number in version.rb, and then run bundle exec rake release, which will create a git tag for the version, push git commits and the created tag, and push the .gem file to rubygems.org.
Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/fractaledmind/solid_errors. This project is intended to be a safe, welcoming space for collaboration, and contributors are expected to adhere to the code of conduct.
The gem is available as open source under the terms of the MIT License.
Everyone interacting in the SolidErrors project's codebases, issue trackers, chat rooms and mailing lists is expected to follow the code of conduct.