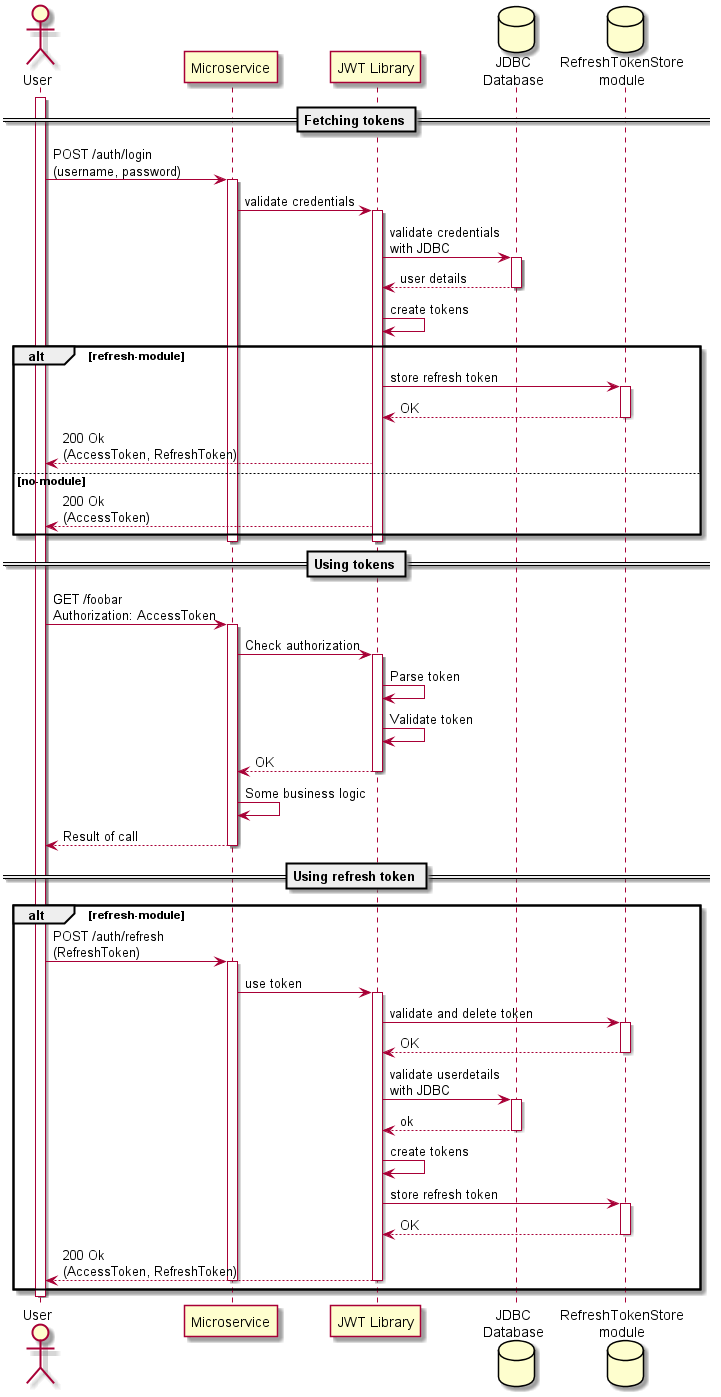
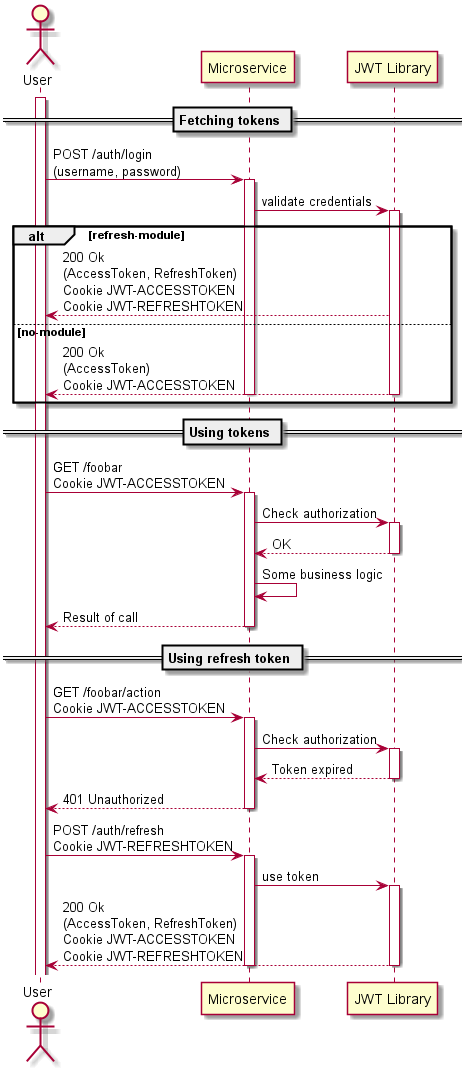
Providing a simple way to integrate JWT into your spring boot application.
This project is split into 4 parts:
- base: Basic integration of JWT into spring security (without refresh tokens)
- internal: Support for an in-memory cache (ExpiringMap) for refresh tokens
- memcache: Support for memcache to store refresh tokens
- hibernate: Support for hibernate to store refresh tokens
Simply use the dependencies within your build script, spring boot takes care of the rest. The default configuration should be sufficient for the most use cases.
- base:
- JWT Integration into Spring Security (including a REST-Controller to authenticate against)
- A CryptPasswordEncoder to generate / use linux system crypt(1)-hashes (supporting new
$5$ and$6$ hashes and rounds) - Full support for Swagger 2 documentation (REST Controller and DTO are annotated and described)
- module internal:
- Refresh token support through an internal, in-memory map
- module memcache:
- Refresh token support through an external memcache server
- module hibernate:
- Refresh token support using hibernate and a database table
<dependency>
<groupId>eu.fraho.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>security-jwt-base</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1</version>
</dependency>When you want to add refresh token support, then choose one of the following dependencies:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>eu.fraho.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>security-jwt-internal</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>eu.fraho.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>security-jwt-memcache</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>eu.fraho.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>security-jwt-hibernate</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>For details on the usage of the plugins please see the README within the relevant module directories.
Starting with version 1.0.0 there are two ways on how to use these libraries.
The old way is by directly using the libraries as dependencies and doing some manual configuration. The newer way used spring boot autoconfiguration and reduced the needed configuration a lot.
To see this library "in action", please take a look at the examples.
- Use any *-spring-boot-starter dependency you like
- Bouncycastle will be automagically loaded and installed if on classpath
- My enhanced PasswordEncoder (using Unix-Crypt-Style hashes) will be used as default
- Add the dependencies to your build script
- Configure your boot application to pick up our components (add "eu.fraho.spring.securityJwt" to the scanBasePackages field of your
@SpringBootApplication) - Optionally add the BouncyCastle Provider (e.g. within the main-Method)
- Hint: This is required if you would like to use the ECDSA signature algorithm!
- Optionally use my enhanced PasswordEncoder as a
@Bean - Optionally choose a refresh token store implementation and set it as
fraho.jwt.refresh.cache-impl
- Create an implementation of UserDetailsService that returns an instance of JwtUser
- By default, this service creates a random hmac secret for signatures on each startup. To stay consistent accross service restarts and not kicking clients out please either change the algorithm (recommended) or specifiy at least an hmac keyfile.
- Request new tokens by sending an authentication request to
/auth/login - Somehow store the received token(s)
- Or use the cookie flow so the browser can store the tokens safely
- To access a secured controller set the retrieved token as
Authorization: <TokenType> <Token>- When using cookies this is done automatically by your browser
This library will run out-of the box, but you should at least take a look at the different configuration properties. I tried to make them reasonable secure, but if you're really paranoid you can change them as you like.
By default, this library creates an hmac secret on startup. As this is no problem for testing and running your application you are strongly adviced to define a static key. Otherwise you will render all access tokens invalid upon service restart, thus requiring your clients to login again.
I recommend using ECDSA for tokens (you can use this class for that) and setting the algorithm field to something like ES256.
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| algorithm | HS256 | The signature algorithm used for the tokens. For a list of valid algorithms please see either the JWT spec or JWSAlgorithm |
| cookie.enabled | false | Enables support for tokens sent as a cookie |
| cookie.names | JWT-ACCESSTOKEN, XSRF-TOKEN | Sets the name of the cookie with the token. The first entry in this list is used when sending out the cookie, any other names are optionally taken when validating incoming requests. |
| cookie.domain | null | The issued tokens will only be valid for the specified domain. Defaults to the issuing server domain. |
| cookie.httpOnly | true | The cookie will not be accessible by client JavaScript if enabled (highly recommend) |
| cookie.path | / | The issued access token cookie will only be sent by the client to URIs matching this pattern |
| cookie.secure | true | The cookie will only be sent over an encrypted (https) connection (highly recommend) |
| expiration | 1 hour | The validity period of issued tokens. For details on how this field has to specified see TimeWithPeriod |
| header.enabled | true | Enables support for tokens sent as a header. (highly recommended) |
| header.names | Authorization | Sets the name of the headers which may contain the token. |
| hmac | null | Defines the key file when using a hmac signature method |
| issuer | fraho-security | Sets the issuer of the token. The issuer is used in the tokens iss field |
| path | /auth/login | Sets the path for the RestController, defining the endpoint for login requests. |
| priv | null | Defines the private key file when using a public / private key signature method. May be null if this service should only verify, but not issue tokens. In this case, any calls to generateToken or generateRefreshToken will throw an FeatureNotConfiguredException. To the caller, it will be shown as a UNAUTHORIZED Http StatusCode. |
| pub | null | Defines the public key file when using a public / private key signature method |
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cache-impl | null | Defines the implemenation for refresh token storage. The specified class has to implement the RefreshTokenStore Interface. To disable the refresh tokens at all use null as value. You have to add at least one of the optional dependencies below to add refresh token support. Please see module READMEs for valid values. |
| cookie.enabled | false | Enables support for tokens sent as a cookie |
| cookie.names | JWT-REFRESHTOKEN | Sets the name of the cookie with the token. The first entry in this list is used when sending out the cookie, any other names are optionally taken when validating incoming requests. |
| cookie.domain | null | If this value is not specified, then the redirect for refreshing the cookies will be sent only with the {@link #path} specified. Otherweise the domain will be prepended to the redirect, thus allowing to use an external refresh server. See javax.servlet.http.Cookie#setDomain(String) |
| cookie.httpOnly | true | The cookie will not be accessible by client JavaScript if enabled (highly recommend) |
| cookie.secure | true | The cookie will only be sent over an encrypted (https) connection (recommend) |
| cookie.path | /auth/refresh | The issued access token cookie will only be sent by the client to URIs matching this pattern. This path spec has to include the endpoint for refreshing tokens, otherwise this won't work! See javax.servlet.http.Cookie#setPath(String) |
| expiration | 1 day | How long are refresh tokens valid? For details on how this field has to specified see TimeWithPeriod |
| length | 24 | Defines the length of refresh tokens in bytes, without the base64 encoding |
| path | /auth/refresh | Sets the path for the RestController, defining the endpoint for refresh requests. |
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| fraho.totp.length | 16 | Defines the length of the generated TOTP secrets |
| fraho.totp.variance | 3 | Defines the allowed variance / validity of TOTP pins. The number defines how many "old / expired" pins will be considered valid. A value of "3" is the official suggestion for TOTP. This value is used to consider small clock-differences between the client and server. |
| fraho.crypt.algorithm | SHA512 | Configure the used crypt algorithm. For a list of possible values see CryptAlgorithm Please be aware that changing this parameter has a major effect on the strength of the hashed password! Do not use insecure algorithms (as DES or MD5 as time of writing) unless you really know what you do! |
| fraho.crypt.rounds | 10,000 | Defines the "strength" of the hashing function. The more rounds used, the more secure the generated hash. But beware that more rounds mean more cpu-load and longer computation times! This parameter is only used if the specified algorithm supports hashing rounds. |
# on linux:
./gradlew assemble
# on windows:
gradlew.bat assemble- This repository uses the git flow layout
- Changes are welcome, but please use pull requests with separate branches
- TravisCI has to pass before merging
- Code coverage should stay about the same level (please write tests for new features!)
- When writing new modules please use my abstract testclasses which provide a great base (see internal for an example)
# to local repository:
./gradlew install
# to central:
./gradlew -Prelease check uploadArchivesRequest a token (login):
> POST /auth/login HTTP/1.1
> Host: localhost:8080
> Content-Type: application/json
> Content-Length: 63
>
> {
> "username": "userA",
> "password": "userA"
> }
>
< HTTP/1.1 200
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
< Content-Length: 491
<
< {
< "accessToken": {
< "token": "eyJhbGciOiJFUzI1NiJ9.<some more token code>",
< "expiresIn": 3600,
< "type": "Bearer"
< },
< "refreshToken": {
< "token": "5bYNdXEGQRzz6xD4yFmw2wNPjXAh+wMc",
< "expiresIn": 604800
< }
< }
Usage of token to access some (secured) data:
> GET /users HTTP/1.1
> Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJFUzI1NiJ9...
>
< HTTP/1.1 200
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
< Content-Length: 42
<
< (some json content, result of request)
Use refresh token when token expired:
> POST /auth/refresh HTTP/1.1
> Content-Type: application/json
> Content-Length: 56
>
> {
> "refreshToken": "5bYNdXEGQRzz6xD4yFmw2wNPjXAh+wMc"
> }
>
< HTTP/1.1 200
< Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
< Content-Length: 491
< Date: Fri, 19 May 2017 08:05:19 GMT
<
< {
< "accessToken": {
< "token": "eyJhbGciOiJFUzI1NiJ9.<some more token code>",
< "expiresIn": 3600,
< "type": "Bearer"
< },
< "refreshToken": {
< "token": "U3LFL8dVZAeAp8Js6db2zrHGPfGslIeQ",
< "expiresIn": 604800
< }
< }