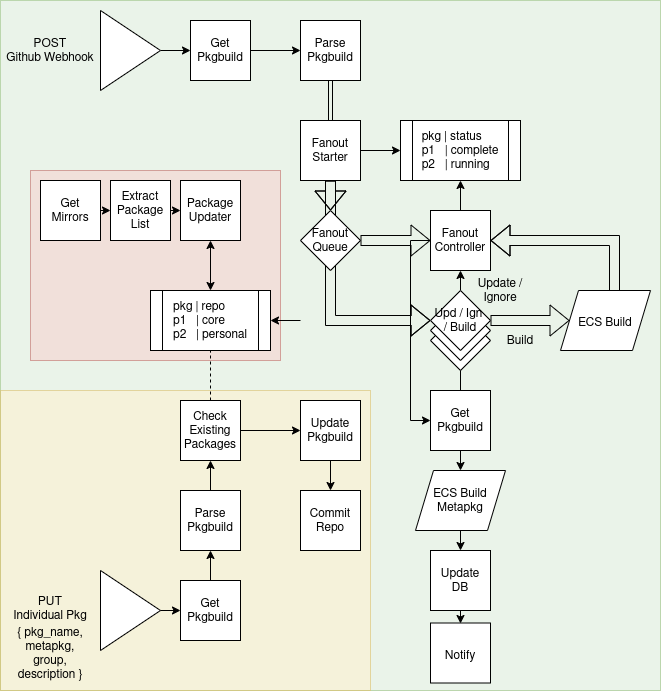
An AWS lambda service used to keep a personal repository of Arch packages up to date. This service automatically monitors a Github repository for AUR packages to build and store. An overview of the parts within the system are as follows:
.
├── event.json <-- Test JSON event for API Gateway
├── pkgbuild_retriever <-- Retrieves the PKGBUILD file from the repository once a
│ ├── commit_parser.py commit event has been passed to the API gateway
│ ├── github_token_validator.py
│ ├── requirements.txt
│ └── retrieve_pkgbuild.py
├── pkgbuild_parser <-- Parses the PKGBUILD file from the repository and extracts
│ ├── parse_pkgbuild.py any new files that are required to be built
│ └── requirements.txt
├── fanout_starter <-- Adds packages to the build queue if they need to be built
│ ├── requirements.txt
│ └── starter.py
├── fanout_controller <-- Lambda function used to control the packages being built
│ ├── controller.py and updating the status table
│ └── requirements.txt
├── metapackage_builder <-- Builds the metapackage once all other packages are complete
│ ├── metapackage.py
│ └── requirements.txt
├── pkg_builder <-- Starts an ECS task used to build the package
│ ├── build_package.py
│ └── requirements.txt
├── package_updater <-- Periodically updates the packages available in the official
│ ├── arch_packages.py repositories, as they do not need to be rebuilt
│ ├── best_mirror.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── reflector.py
│ ├── requirements.txt
│ └── update_packages.py
├── repo_updater <-- Periodically checks the repository for packages that need
│ ├── requirements.txt to be updated
│ └── update_repo.py
├── src <-- Shared packages used by all the lambda functions
│ └── python
│ ├── aws.py
│ ├── common.py
│ ├── enums.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── requirements.txt
├── template.yaml <-- SAM template
├── README.md <-- This instructions file
├── requirements.txt
└── tests <-- Unit tests
├── inputs
│ ├── fanout_starter_input.json
│ ├── package_checker_filesystem.json
│ ├── package_checker_ghidra.json
│ ├── parser_input.json
│ ├── retriever_input.json
│ └── webhook-old.json
├── tables
│ └── fanout-status.json
└── unit
├── __init__.py
└── test_handler.py
- AWS Administrator access
- Python 3
- Docker
- Pushover
- AWS SAM CLI
- Personal repository in S3
- Meta-packages stored in GitHub
Firstly we need to create an AWS account and configure it to be used on our Development system. We'll be
making use of S3 to store any built packages and be our repository as well as to store AWS SAM deployments,
and Lambda to handle building of new packages as they become available.
Create a new AWS account, and within the console create a new user with Administrator access. When given the
option ensure "Programmatic access" is selected, as we'll be using the AWS keys for deployment. Once created
use aws configure within the terminal to set up AWS on the local machine.
Follow the steps in Disconnected's blog post first, then resume here. An example repository can be found here.
Once the repository has been set up and added to Github, a new webhook is necessary for kicking off the build process. The PKGBUILD file is the main requirement here, as it's searched for when any commits are made. To add a webhook, navigate to Settings -> Webhooks. Create a new webhook and enter the following details:
- Payload URL:
https://example.com(this will need to be changed once the build service has been published) - Content-Type:
application/json - Secret: Create a new UUID -
uuidgencan be used if installed. This should be noted for future use - Event: Select
Just the push event
Pushover is used to send notifications of new/updated packages as well as failures. We need to create an account and set up an API key in order to use them. After creating an account, take note of the user key. Create a new application and note down the API key there. Also register a phone so notifications have somewhere to be sent.
A GPG key is used to sign packages and ensure they haven't been tampered with after being built. Create a GPG key with the following steps:
export GNUPGHOME=/tmp # Create a temporary GPG directory (if required)
gpg --full-generate-key
gpg --export-secret-keys --armor > aur_key.gpgThe key must then be exported as text, which can then be uploaded to SSM as described below. Alternatively if a key is already available, simply export the secret key to a text file and upload it to SSM using the steps below.
All the keys that have been generated need to be uploaded to SSM with the following commands, taking note of the variables that will need to be populated by the keys created above:
aws ssm put-parameter --name aur_key --value $(cat aur_key.gpg) --type SecureString
aws ssm put-parameter --name githubToken --value $GITHUB_TOKEN
aws ssm put-parameter --name pushoverUser --value $PUSHOVER_USER
aws ssm put-parameter --name pushoverToken --value $PUSHOVER_TOKENOnce the SSM values are placed into AWS, a KMS key is created to enable encryption/decryption. The ID of this key is needed so as the values can be used on demand. This can be retrieved by using the following command:
echo "key/$(aws kms describe-key --key-id 'alias/aws/ssm' | jq -r '.KeyMetadata.KeyId')"Clone the repository, create a new Python virtual environment and install the requirements:
git clone https://github.com/kontax/repo-build-service.git
cd repo-build-service
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txtAWS Lambda generally seems to be behind Arch Linux when it comes to Python versions - at the time of writing the latest version available within AWS is 3.7, however Arch is running 3.8.1 locally. This causes issues when building and deploying as there is a version mismatch, so docker is required to do this within a container. If both local and remote options are the same then this step isn't necessary.
When installing docker, ensure to add the local user to the docker group with the command
usermod -a -G docker <username> and re-login. Occasionally the PC needs to be restarted to fix the group
issue. Once done, enable and start the docker service with systemctl enable --now docker.service.
If using docker, build the application with:
sam build -uThe first time this is run, the lambci/lambda:build-python3.7 (or equivalent) container needs to be
downloaded, which can take some time. Once complete, go through the deployment steps with the command:
sam deploy --guidedName the application however you want, same with the region. For the rest of the options, check out the list of Template Paramters section below. Once "Allow SAM CLI IAM role creation" pops up, choose "n" and then "CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM" within the "Capabilities" option. This is required as the roles used within the deployment are named.
Occasionally an error will occur stating that the "S3 Bucket does not exist". If this happens, simply look at the option under "Deployment s3 bucket" and create that bucket with the following command:
aws s3api create-bucket --bucket <bucket_name> --region <aws_region>An alternative would be to modify "samconfig.toml" (assuming saving the arguments was selected during the deployment) with an existing S3 bucket name and running:
sam deployOnce deployment has been completed the deployment is ready to go. Any changes to the PKGBUILD file in the packages repository will send a message via the webhook, kicking off the process. If any AUR packages need to be built that will happen first using the ECS containers, then the metapackages will be updated. Any of these processes will cause a push notification to be sent to Pushover.
- PersonalRepository: Full URL to the AUR repository DB eg.
https://s3.us-west-1.amazonaws.com/my-aur-bucket/x86_64/my-aur-repo.db - PersonalRepoBucket: Name of the S3 bucket containing the repostitory eg.
my-aur-bucket - RepoName: Name of the repository as set up in pacman eg.
my-aur-repo - RepoArch: Architecture of the repository eg.
x86_64 - AurPackager: Name/email assigned to the package build eg.
Package Builder <[email protected]>
- PackageTable: Name of the DynamoDB table storing package details, defaults to
package-list - FanoutStatusTable: Name of the table used to control the fan-in / fan-out status of package building, defaults to
fanout-status - FanoutController: Name of the lambda function used to control fan-in / fan-out state, defaults to
fanout-controller - BuildQueueName: Name of the queue that the ECS tasks use to pull package details from to build, defaults to
fanout-queue
- RepositoryCountries: Comma-separated country codes used for finding the best mirror for package downloads, defaults to
IE,GB
- GithubWebhookSecret: Secret key set up within the Github repository containing the PKGBUILD meta-package, defaults to
{{resolve:ssm:githubToken:1}}which needs to be set up as described above - PushoverToken: Token used to notify built packages via pushover, defaults to
{{resolve:ssm:pushoverToken:1}}, however this needs to be set up within AWS SSM as outlined above - PushoverUser: Username created within Pushover, defaults to
{{resolve:ssm:pushoverUser:1}}, which needs to be set up as described above - AurKeyParam: Name of the private key within the Paramter Store used to sign built packages, defaults to
aur_key - AurKeyDecrypt: The KMS key used to encrypt/decrypt the parameter store above, eg.
key/abcdef-1234-5678-ghijkl123456
- ECSCluster: Name of the cluster used to contain the packages building ECS tasks, defaults to
aur-pkgbuild-cluster - TaskDefinition: Name of the ECS task used to build packages, defaults to
aur-pkgbuild-task - RepoUpdater: Name of the ECS task used to update the full repository, defaults to
aur-repo-update-task - MaxTaskCount: Maximum number of ECS tasks to run simultaneously, defaults to 4