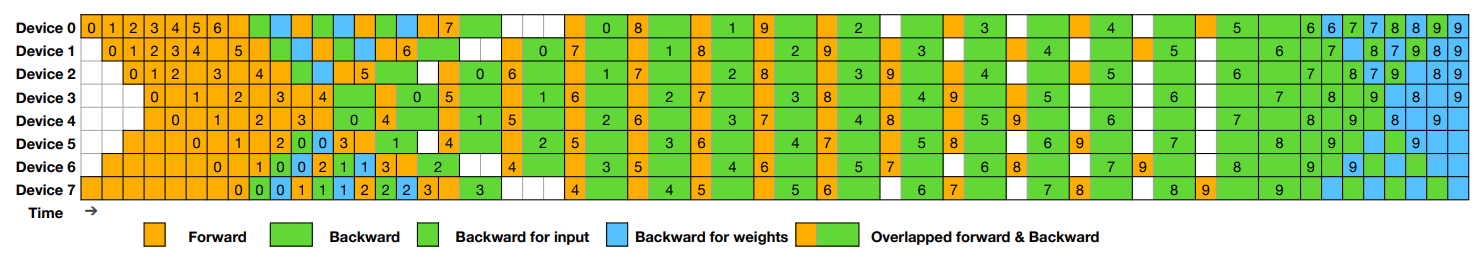
DualPipe is an innovative bidirectional pipeline parallelism algorithm introduced in the DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report. It achieves full overlap of forward and backward computation-communication phases, also reducing pipeline bubbles. For detailed information on computation-communication overlap, please refer to the profile data.
Example DualPipe scheduling for 8 PP ranks and 20 micro-batches in two directions. The micro-batches in the reverse direction are symmetric to those in the forward direction, so we omit their batch ID for illustration simplicity. Two cells enclosed by a shared black border have mutually overlapped computation and communication
| Method | Bubble | Parameter | Activation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1F1B | (PP-1)(𝐹+𝐵) | 1× | PP |
| ZB1P | (PP-1)(𝐹+𝐵-2𝑊) | 1× | PP |
| DualPipe | (PP/2-1)(𝐹&𝐵+𝐵-3𝑊) | 2× | PP+1 |
𝐹 denotes the execution time of a forward chunk, 𝐵 denotes the execution time of a full backward chunk, 𝑊 denotes the execution time of a "backward for weights" chunk, and 𝐹&𝐵 denotes the execution time of two mutually overlapped forward and backward chunks.
- Full Computation-Communication Overlap - DualPipe ensures that computation and communication phases fully overlap, maximizing GPU utilization.
- Reduced Pipeline Bubbles - The algorithm significantly reduces pipeline bubbles compared to traditional pipeline parallelism strategies.
- Model Adapters - Built-in adapters to automatically partition models from popular architectures (transformers, vision models, etc.).
- Framework Integration - Seamless integration with PyTorch, PyTorch Lightning, and Hugging Face Transformers.
- Performance Profiling - Comprehensive profiling tools to analyze and optimize performance.
The basic usage is shown in the following example:
python example.pyFor more advanced usage, check out these examples:
-
Transformer Model Example:
python examples/transformer_example.py --num-gpus 2
-
PyTorch Lightning Integration:
python examples/lightning_example.py --num-gpus 2
Note: For real-world applications, you will need to implement a custom overlapped_forward_backward method tailored to your specific module, or use one of the pre-built model adapters.
You can install DualPipe directly from the repository:
pip install git+https://github.com/your-repo/DualPipe.gitOr for local development:
git clone https://github.com/your-repo/DualPipe.git
cd DualPipe
pip install -e .DualPipe provides model adapters that make it easy to use with different model architectures:
import torch
from dualpipe import DualPipe, set_p2p_tensor_shapes, set_p2p_tensor_dtype
from dualpipe.adapters import get_model_adapter
# Create your model
model = YourModel(...)
# Get the appropriate adapter for your model
adapter = get_model_adapter(model)
# Partition the model
partitions = adapter.partition(num_partitions=4) # Must be even for DualPipe
# Set tensor shapes for communication
set_p2p_tensor_shapes([(batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size)])
set_p2p_tensor_dtype(torch.float32)
# Create DualPipe
local_rank = dist.get_rank()
local_module = partitions[local_rank].cuda()
dualpipe_model = DualPipe([local_module, local_module])
# Run the model
loss, outputs = dualpipe_model.step(inputs, num_chunks=8, criterion=your_loss_fn, labels=(labels,))DualPipe includes a profiling utility to help you optimize your implementation:
from dualpipe.utils import enable_profiling, get_profiler
# Enable profiling before your training loop
enable_profiling(log_dir="./profiles")
# Training loop
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch in dataloader:
# ... Run your model with DualPipe
# Get profiling results
profiler = get_profiler()
profiler.print_summary()
profiler.save_to_file("dualpipe_profile.json")from dualpipe.compat import DualPipeLightningModule
class YourLightningModule(DualPipeLightningModule):
def __init__(self, model, learning_rate=1e-3):
super().__init__(model=model, num_chunks=8)
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
def configure_optimizers(self):
return torch.optim.Adam(self.dualpipe_wrapper.local_module.parameters(), lr=self.learning_rate)
def criterion(self, outputs, targets):
return your_loss_function(outputs, targets)from transformers import AutoModel, TrainingArguments
from dualpipe.compat import DualPipeTrainer
# Create a model
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("your-model")
# Create training arguments
training_args = TrainingArguments(...)
# Create DualPipe trainer
trainer = DualPipeTrainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
num_chunks=8,
enable_profiling=True
)
# Train the model
trainer.train()- PyTorch 2.0 and above
- CUDA-capable GPU
- Optional dependencies:
- PyTorch Lightning (for Lightning integration)
- Hugging Face Transformers (for Transformers integration)
DualPipe was created and developed by Jiashi Li and Chengqi Deng and Wenfeng Liang.
@misc{deepseekai2024deepseekv3technicalreport,
title={DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report},
author={DeepSeek-AI},
year={2024},
eprint={2412.19437},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.19437},
}