springboot_01_hello是依赖整个SpringBoot的
pom.xml文件的一下内容;但是以后的springboot_02...我都是使用springInitializr创建的,所以不依赖SpringBoot(整个大项目)
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version> </parent>
- 简化
Spring应用开发的一个框架、整个Spring技术栈的一个大整合; J2EE开发的一站式解决方案;
优点:
- 快速创建独立运行的
Spring项目以及与主流框架集成; - 使用嵌入式的
Servlet容器,应用无需打成WAR包; starters自动依赖与版本控制;- 大量的自动配置,简化开发,也可修改默认值;
- 无需配置
XML,无代码生成,开箱即用; - 准生产环境的运行时应用监控;
- 与云计算的天然集成;
- martin fowler论文提出。
- 微服务:架构风格(服务微化)
- 一个应用应该是一组小型服务;可以通过
HTTP的方式进行互通; - 单体应用:
ALL IN ONE - 微服务:每一个功能元素最终都是一个可独立替换和独立升级的软件单元;
给maven 的settings.xml配置文件的profiles标签添加下面的代码:
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>表示maven使用jdk1.8。
实现功能:
浏览器发送
hello请求,服务器接受请求并处理,响应Hello Springboot!字符串;即浏览器输入localhost:8080/hello可以看到浏览器显示Hello SpringBoot!字符串;
① 创建一个maven工程(jar);
② 导入spring boot相关的依赖;
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>③ 编写一个主程序,启动Spring Boot应用
/**
* @SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类,说明这是一个Spring Boot应用
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloWorldMainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Spring应用启动起来
SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldMainApplication.class, args);
}
}④ 编写相关的Controller
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "Hello SpringBoot!";
}
}⑤ 运行主程序测试
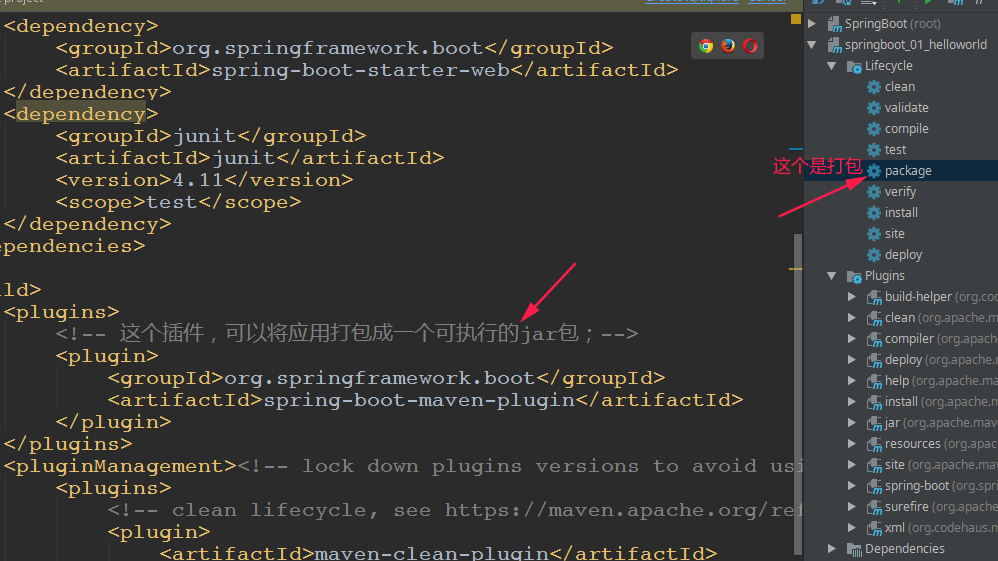
⑥简化部署
将这个应用打成jar包,直接使用java-jar的命令进行执行;
<!-- 这个插件,可以将应用打包成一个可执行的jar包;-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>结果:
父项目
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
</parent>他的父项目:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath>
</parent>他来真正管理Spring Boot应用里面的所有依赖版本;
也就是Spring Boot的版本仲裁中心;
以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;(没有在dependencies里面管理的依赖自然需要声明版本号)
启动器:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>spring-boot-starter-web:
spring-boot-starter:spring-boot场景启动器;帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件;
Spring Boot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starters(启动器),只需要在项目里面引入这些starter相关场景的所有依赖都会导入进来。要用什么功能就导入什么场景的启动器。
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloWorldMainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Spring应用启动起来
SpringApplication.run(HelloWorldMainApplication.class,args);
}
}① @SpringBootApplication: Spring Boot应用标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类,SpringBoot就应该运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用;这是一个组合注解。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
...
}下面看里面的每个注解含义:
@SpringBootConfiguration:Spring Boot的配置类,标注在某个类上,表示这是一个Spring Boot的配置类,里面包含这个@Configuration(也就是Spring里面的配置类);
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
}配置类 -----> 配置文件;配置类也是容器中的一个组件:@Component
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component //组件注解
public @interface Configuration {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}② @EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能;
以前我们需要配置的东西,Spring Boot帮我们自动配置;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能,这样自动配置才能生效;
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
}-
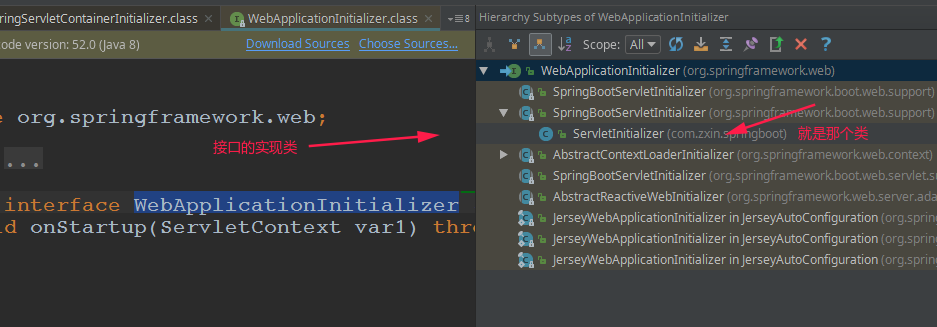
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class):Spring的底层注解@Import,给容器中导入一个组件;导入的组件由AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class指定。 也就是: 将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication标注的类)的所在包及下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器;,所以如果上面的controller如果不是在主配置类所在的包(或者子包)下,就不能扫描到。
-
@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class): 给容器中导入组件(不在同一个包下面的)EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector:导入哪些组件的选择器;将所有需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回,这些组件就会被添加到容器中;会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration);就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件,并配置好这些组件;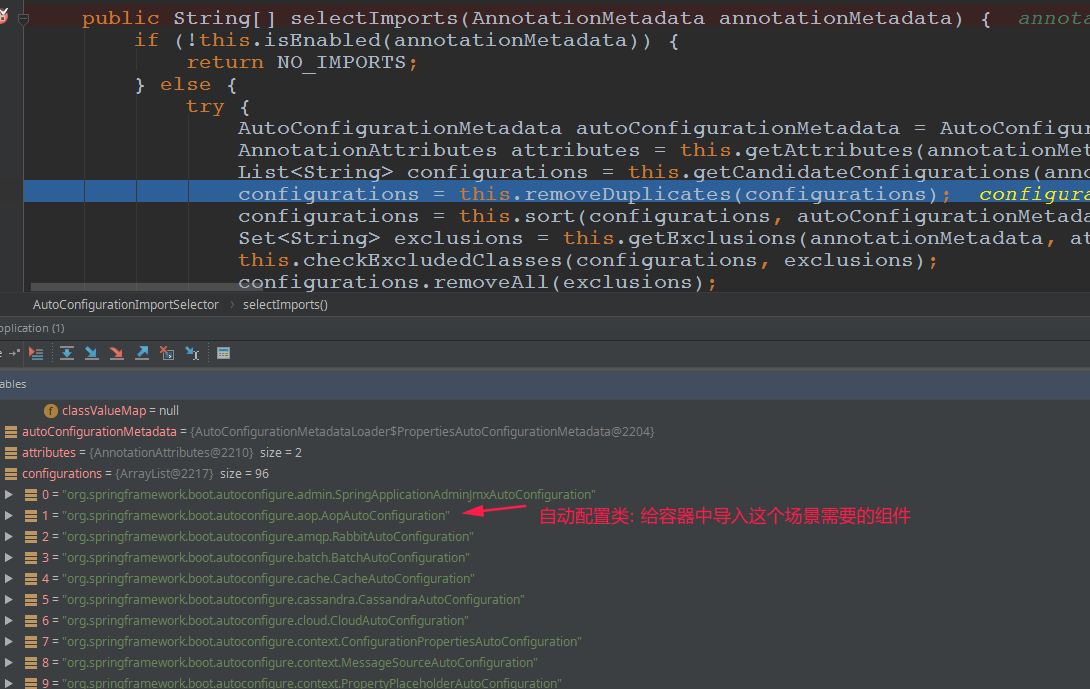
有了自动配置类,免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作; 里面的
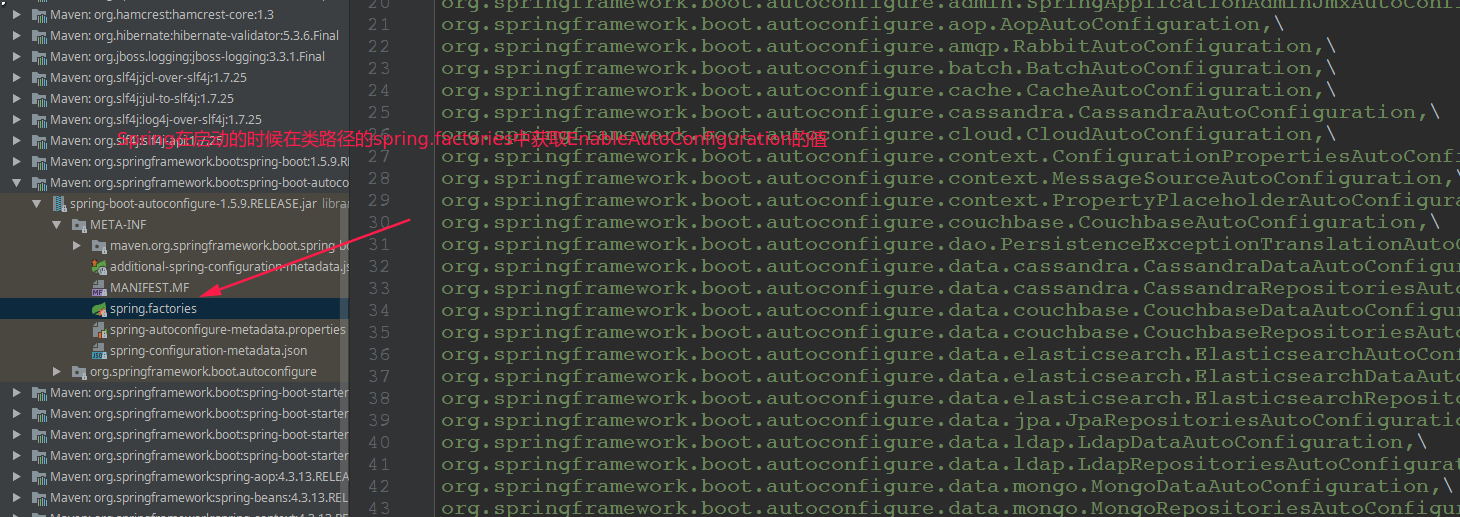
getCandidateConfigurations调用了下面的一个方法:SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(EnableAutoConfiguration.class,classLoader)Spring Boot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值,将这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中,自动配置类就生效,帮我们进行自动配置工作;以前我们需要自己配置的东西,自动配置类都帮我们;J2EE的整体整合解决方案和自动配置都在
spring-boot-autoconfigure-xxx.RELEASE.jar;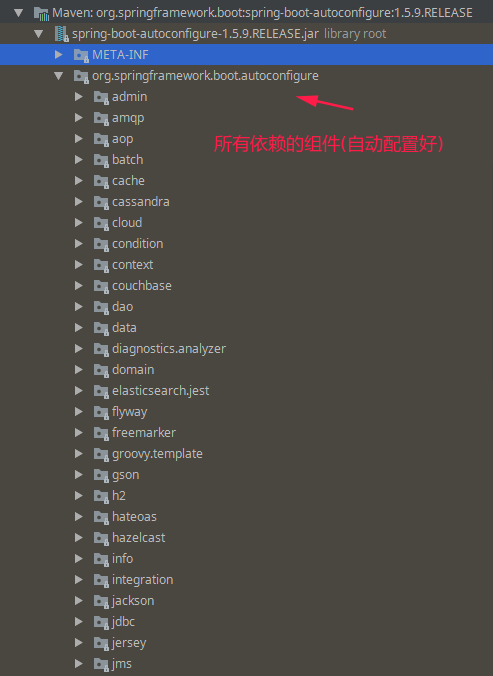
IDE都支持使用Spring的项目创建向导快速创建一个Spring Boot项目。选择我们需要的模块,向导会联网创建Spring Boot项目,默认生成的Spring Boot项目; 主程序生成好了,我们只需要我们自己的逻辑。
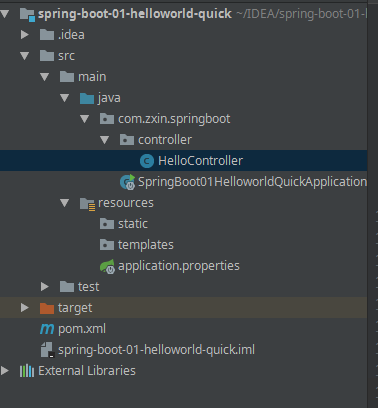
resources: 文件夹中目录结构static:保存所有的静态资源;js css images;templates:保存所有的模板页面;(Spring Boot默认jar包使用嵌入式的Tomcat,默认不支持JSP页 面);可以使用模板引擎(freemarker、thymeleaf);application.properties:Spring Boot应用的配置文件,可以修改一些默认设置;
结构目录:
简单Controller,注意@RestController注解。
package com.zxin.springboot.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
//@ResponseBody // 这个类的所有方法返回的数据直接写给浏览器(如果是对象 -> 转成json)
//@Controller
@RestController // 这个注解的作用和上面两个一起的作用相同 (就是 ResponseBody和Controller的合体)
public class HelloController {
@ResponseBody //如果每个类都需要写,麻烦
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello quick SpringBoot!";
}
}SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件,下面两者都会当做是配置文件,配置文件名是固定的;
application.properties;application.yml;
配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值,SpringBoot在底层都给我们自动配置好;
YAML(YAML Ain't Markup Language)
YAML A Markup Language:是一个标记语言
YAML isn't Markup Language:不是一个标记语言标记语言:
以前的配置文件,大多都使用的是 xxxx.xml文件;
YAML:以数据为中心,比json、xml等更适合做配置文件;
yaml配置例子:
server:
port: 8081对应xml配置例子:
<server>
<port>8081</port>
</server>基本语法:
k:(空格)v:表示一对键值对( 空格必须有);- 以空格的缩进来控制层级关系;只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的;
- 属性和值也是大小写敏感;
值的写法:
-
字面量:普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔);
-
k: v: 字面直接来写;
字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号;
""双引号:不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符,特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思。name: "zhangsan \n lisi"输出 :zhangsan 换行 lisi;''单引号:会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据。name: ‘zhangsan \n lisi’输出 :zhangsan \n lisi;
对象、Map(属性和值)(键值对):
k: v:在下一行来写对象的属性和值的关系,注意缩进。
对象还是k: v的方式
friends:
lastName: zhangsan
age: 20行内写法:
friends: {lastName: zhangsan,age: 18 }数组(List、Set):
用- 值(注意有空格)表示数组中的一个元素
pets:
‐ cat
‐ dog
‐ pig行内写法
pets: [cat,dog,pig]JavaBean配置:
/**
* 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中
* @ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关 的配置进行绑定;
* prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射
* 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能使用容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能;
* 所以需要使用@Component注解;
* @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")默认从全局配置文件中获取值(也可以指定文件);
*/
@Component("myPerson")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String lastName;
private Integer age;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
}application.yml文件配置
server:
port: 8081
person:
lastName: zhangsan
age: 18
boss: false
birth: 2018/01/02
maps: {k1 : v1, k2 : 100}
lists:
- lisi
- wangwu
dog:
name: 小狗
age: 5可以导入配置文件处理器,以后编写配置就有提示了。
<!--导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>上面的application.yml配置文件也可以使用application.properties文件来替换:
server.port=8081
# 乱码问题
spring.http.encoding.force=true
spring.http.encoding.charset=UTF-8
spring.http.encoding.enabled=true
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8
# 配置person的值
person.last-name=zhangsan
person.age=18
person.birth=2018/01/02
person.boss=false
person.maps.k1=v1
person.maps.k2=100
person.lists=lisi,wangwu
person.dog.name=小狗
person.dog.age=5| @ConfigurationProperties | @Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 功能 | 批量注入配置文件中的属性 | 一个个指定 |
松散绑定(松散语法-) |
支持 | 不支持 |
| SpEL(Spring表达式) | 不支持 | 支持 |
| JSR303数据校验 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 复杂类型封装 | 支持 | 不支持 |
配置文件yml还是properties他们都能获取到值;
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
对应项目:
springboot_02_config_3_propertysource_importresource
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件。
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"})
@Component("myPerson")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String lastName;
private Integer age;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上。
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"})
导入Spring的配置文件让其生效。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--如果不使用ImportResource注解,这个配置文件默认是不会被扫描到的,也就是这个Service不会注入到容器中-->
<bean id = "helloService" class="com.zxin.springboot.service.HelloService">
</bean>
</beans>SpringBoot推荐给容器中添加组件的方式;推荐使用全注解的方式
1、配置类@Configuration------> Spring配置文件;
2、使用@Bean给容器中添加组件;
/**
* @Configuration:指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件
* 类似 : 在配置文件中用<bean><bean/>标签添加组件
*/
@Configuration
public class MyAppConfig {
//将方法的返回值添加到容器中;容器中这个组件默认的id就是方法名
@Bean
public HelloService helloService01(){
System.out.println("配置类@Bean给容器中添加组件了...");
return new HelloService();
}
}测试类:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBoot02Config3PropertySourceImportResourceApplicationTests {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("myPerson")
private Person person;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext ioc;
@Test
public void testIsContainHelloService(){
boolean b = ioc.containsBean("helloService01");
System.out.println(b);
}
}没有专门写一个项目。
1、这些表达式可以出现在配置文件中:
例如application.properties
${random.value}、${random.int}、${random.long}
${random.int(10)}、${random.int[1024,65536]}2、占位符获取之前配置的值,如果没有可以是用:指定默认值
比如:
person.last-name=张三${random.uuid}
person.age=${random.int} # 生成随机数
person.birth=2017/12/15
person.boss=false
person.maps.k1=v1
person.maps.k2=14
person.lists=a,b,c
person.dog.name=${person.hello:hello}_dog #如果没有定义person.hello,就使用默认的hello
person.dog.age=15springboot_02_config_4_profile项目。
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml
默认使用application.properties的配置;
server:
port: 8080
spring: #指定使用哪个环境
profiles:
active: prod
---
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: prod这种方式也是和properties配置文件的指定方式差不多。
1、在配置文件中指定 spring.profiles.active=dev
例如项目中有三个properties文件,分别是application.properties、application-dev.properties、application-prod.properties:
内容如下:
application.properties:
# 默认环境的配置文件
server.port=80
# 默认用的就是 application.properties, 但是也可以通过下面的方法来指定别的(对于properties,对于yml是别的方式)
# 使用第二个(生产环境的)
spring.profiles.active=prodapplication-dev.properties:
# 开发环境的配置文件
server.port=8081application-prod.properties:
# 生产环境的配置文件
server.port=8082因为在application.properties中配置了使用prod环境,所以最终项目在8082端口启动了。
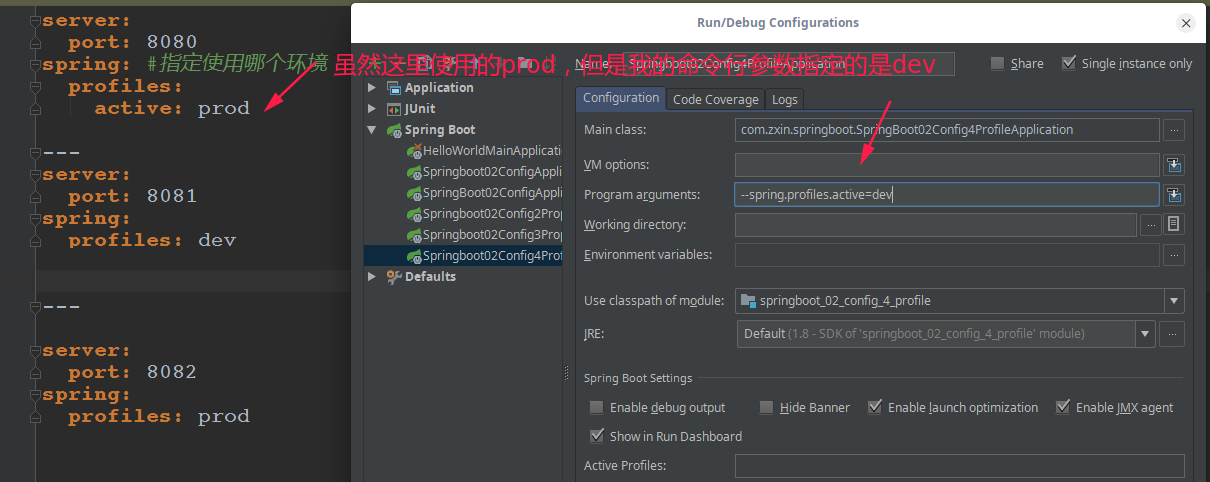
2、IDEA中配置命令行参数--spring.profiles.active=dev
o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8081 最终下面显示还是在dev这个环境中启动,所以说命令行参数的优先级>配置文件的优先级
3、命令行:java -jar springboot_02_config_4_profile-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev
可以直接在测试的时候,配置传入命令行参数
4、虚拟机参数: -Dspring.profiles.active=dev
项目:
springboot_02_config_5_locationofproperties
SpringBoot 启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为Spring boot的默认配置文件
–file:./config/
–file:./
–classpath:/config/
–classpath:/优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置;
SpringBoot会从这四个位置全部加载主配置文件;互补配置;
例如:
这里使用–classpath:/config/和–classpath:/下的两个application.properties来测试一下:
相关代码:
classpath:/config/application.properties:
server.port=8082classpath:/application.properties:
server.port=8081
# 配置项目的访问路径
server.servlet.context-path=/springboot_02_config_5_locationofpropertiesTestController:
package com.zxin.springboot.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
}我们还可以通过spring.config.location来改变默认的配置文件位置;
项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;指定配置文件和默认加载的这些配置文件共同起作用形成互补配置;
java -jar springboot_02_config_5_locationofproperties-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.config.location=/home/zxzxin/IDEA/application.properties
SpringBoot也可以从以下位置加载配置; 优先级从高到低;高优先级的配置覆盖低优先级的配置,所有的配置会形成互补配置,下面的11个配置重点是5个加粗样式的。
1.命令行参数
所有的配置都可以在命令行上进行指定
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8087 --server.context-path=/abc
多个配置用空格分开; --配置项=值
2.来自java:comp/env的JNDI属性
3.Java系统属性(System.getProperties())
4.操作系统环境变量
5.RandomValuePropertySource配置的random.*属性值
由jar包外向jar包内进行寻找;
优先加载带profile
6.jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
7.jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
再来加载不带profile
8.jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
9.jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
10.@Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource
11.通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的默认属性
所有支持的配置加载来源;
配置文件到底能写什么?怎么写?自动配置原理;
1)、SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能 @EnableAutoConfiguration
2)、@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用:
-
利用
EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入一些组件; -
可以查看
selectImports()方法的内容; -
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);获取候选的配置:-
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader()); 即SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() 扫描所有jar包SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象 从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器中
-
将 类路径下
META-INF/spring.factories里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中;以下是spring.factories的内容。
-
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceResolverAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceDelegatingViewResolverAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.SitePreferenceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.ReactorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.FallbackWebSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.OAuth2AutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.SocialWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.FacebookAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.LinkedInAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.TwitterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration每一个这样的xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
3)、每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能;
4)、以**HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)**为例解释自动配置原理;
@Configuration //表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class) //启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;将配置文件中对应的值和HttpEncodingProperties绑定起来;并把HttpEncodingProperties加入到ioc容器中
@ConditionalOnWebApplication //Spring底层@Conditional注解(Spring注解版),根据不同的条件,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效; 判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效
@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器;
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true) //判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置 spring.http.encoding.enabled;如果不存在,判断也是成立的
//即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的;
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
//它已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了
private final HttpEncodingProperties properties;
//只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿 (放到ioc)
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Bean //给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断容器没有这个组件?
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST));
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效。
一旦这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
5)、所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装者;配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http.encoding") //从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定
public class HttpEncodingProperties {
public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
}SpringBoot精髓:
1)、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2)、我们看我们需要的功能有没有SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类;
3)、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件有,我们就不需要再来配置了)
4)、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从xxxProperties类中获取某些属性。我们就可以在配置文件中指定这些属性的值;
① xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类 ---> 给容器中添加组件;
② xxxxProperties : 封装配置文件中相关属性;
作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;
| @Conditional扩展注解 | 作用(判断是否满足当前指定条件) |
|---|---|
| @ConditionalOnJava | 系统的java版本是否符合要求 |
| @ConditionalOnBean | 容器中存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean | 容器中不存在指定Bean; |
| @ConditionalOnExpression | 满足SpEL表达式指定 |
| @ConditionalOnClass | 系统中有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnMissingClass | 系统中没有指定的类 |
| @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate | 容器中只有一个指定的Bean,或者这个Bean是首选Bean |
| @ConditionalOnProperty | 系统中指定的属性是否有指定的值 |
| @ConditionalOnResource | 类路径下是否存在指定资源文件 |
| @ConditionalOnWebApplication | 当前是web环境 |
| @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication | 当前不是web环境 |
| @ConditionalOnJndi | JNDI存在指定项 |
自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效;
我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效;
我们可以通过启用 debug=true属性;来让控制台打印自动配置报告,这样我们就可以很方便的知道哪些自动配置类生效;
=========================
AUTO-CONFIGURATION REPORT
=========================
Positive matches:(自动配置类启用的)
-----------------
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnClass found required class 'org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet'; @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class (OnClassCondition)
- @ConditionalOnWebApplication (required) found StandardServletEnvironment (OnWebApplicationCondition)
...等等
Negative matches:(没有启动,没有匹配成功的自动配置类)
-----------------
ActiveMQAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required classes 'javax.jms.ConnectionFactory', 'org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory' (OnClassCondition)
AopAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required classes 'org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect', 'org.aspectj.lang.reflect.Advice' (OnClassCondition)
...等等
一个小故事:
小张;开发一个大型系统;
1、System.out.println("");将关键数据打印在控制台;去掉?写在一个文件?
2、框架来记录系统的一些运行时信息;日志框架 ; zhanglogging.jar;
3、高大上的几个功能?异步模式?自动归档?xxxx? zhanglogging-good.jar?
4、将以前框架卸下来?换上新的框架,重新修改之前相关的API;zhanglogging-prefect.jar;
5、JDBC---数据库驱动;
写了一个统一的接口层;日志门面(日志的一个抽象层);logging-abstract.jar;
给项目中导入具体的日志实现就行了;我们之前的日志框架都是实现的抽象层;
**市面上的日志框架 : **
JUL、JCL、Jboss-logging、logback、log4j、log4j2、slf4j....
| 日志门面 (日志的抽象层) | 日志实现 |
|---|---|
| Log4j JUL(java.util.logging) Log4j2 Logback |
左边选一个门面(抽象层)、右边来选一个实现;
我们最终选用的是:
- 日志门面: SLF4J;
- 日志实现:Logback;
SpringBoot:底层是Spring框架,Spring框架默认是用JCL;SpringBoot选用 SLF4j和logback;
如何在系统中使用SLF4j https://www.slf4j.org
以后开发的时候,日志记录方法的调用,不应该来直接调用日志的实现类,而是调用日志抽象层里面的方法;
给系统里面导入slf4j的jar和 logback的实现jar
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);
logger.info("Hello World");
}
}图示;
每一个日志的实现框架都有自己的配置文件。使用slf4j以后,配置文件还是做成日志实现框架自己本身的配置文件;
SpringBoot(slf4j+logback)、Spring(commons-logging)、Hibernate(jboss-logging)、MyBatis、xxxx
统一日志记录,即使是别的框架和我一起统一使用slf4j进行输出?
如何让系统中所有的日志都统一到slf4j;
1、将系统中其他日志框架先排除出去;
2、用中间包来替换原有的日志框架;
3、我们导入slf4j其他的实现
首先依赖于spring-boot-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>其中spring-boot-starter又包含spring-boot-starter-logging,使用它来做日志功能;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</dependency>底层依赖关系:
总结:
1)、SpringBoot底层也是使用slf4j+logback的方式进行日志记录;
2)、SpringBoot也把其他的日志都替换成了slf4j;
3)、中间替换包:jcl-over-slf4j.jar、log4j-over-slf4j.jar、jul-to-slf4j.jawr等;
public abstract class LogFactory {
static String UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION_IN_JCL_OVER_SLF4J = "http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#unsupported_operation_in_jcl_over_slf4j";
static LogFactory logFactory = new SLF4JLogFactory();
public static final String PRIORITY_KEY = "priority";
public static final String TCCL_KEY = "use_tccl";
public static final String FACTORY_PROPERTY = "org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory";
public static final String FACTORY_DEFAULT = "org.apache.commons.logging.impl.SLF4JLogFactory";
public static final String FACTORY_PROPERTIES = "commons-logging.properties";
protected static final String SERVICE_ID = "META-INF/services/org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory";
public static final String DIAGNOSTICS_DEST_PROPERTY = "org.apache.commons.logging.diagnostics.dest";
public static final String HASHTABLE_IMPLEMENTATION_PROPERTY = "org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory.HashtableImpl";
protected static Hashtable factories = null;
protected static LogFactory nullClassLoaderFactory = null;
protected LogFactory() {
}
} 4)、如果我们要引入其他框架,一定要把这个框架的默认日志依赖移除掉;
Spring框架用的是commons-logging;(这里如果是前面1.5版本的会有下面的代码,但是2.0+版本的没有)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>SpringBoot能自动适配所有的日志,而且底层使用slf4j+logback的方式记录日志,引入其他框架的时候,只需要把这个框架依赖的日志框架排除掉即可;
springboot_03_logging项目。
SpringBoot默认帮我们配置好了日志;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBoot03LoggingApplicationTests {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
//记录器
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
// 日志的级别, 这些日志的级别 由低到高 trace < debug < info < warn < error
// 可以调整输出的日志级别, 日志就只会在这个级别 级 以后的高级别生效
logger.trace("这是trace日志...");
logger.debug("这是debug日志...");
// SpringBoot默认给我们使用的是info级别, 没有指定级别的就用SpringBoot指定的默认级别(root级别)
logger.info("这是info日志...");
logger.warn("这是warn日志...");
logger.error("这是error日志");
}
}SpringBoot修改日志的默认配置
# 将com.zxin包的日志级别调成 trace 级别
logging.level.com.zxin=trace
#logging.path=
# 不指定路径在当前项目下生成springboot.log日志
# 可以指定完整的路径;
#logging.file=G:/springboot.log
# 在当前磁盘的根路径下创建spring文件夹和里面的log文件夹;使用 spring.log 作为默认文件
logging.path=/spring/log
# 在控制台输出的日志的格式
logging.pattern.console=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
# 指定文件中日志输出的格式
logging.pattern.file=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} === [%thread] === %-5level === %logger{50} ==== %msg%n| logging.file | logging.path | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| (none) | (none) | 只在控制台输出 | |
| 指定文件名 | (none) | my.log | 输出日志到my.log文件 |
| (none) | 指定目录 | /var/log | 输出到指定目录的 spring.log 文件中 |
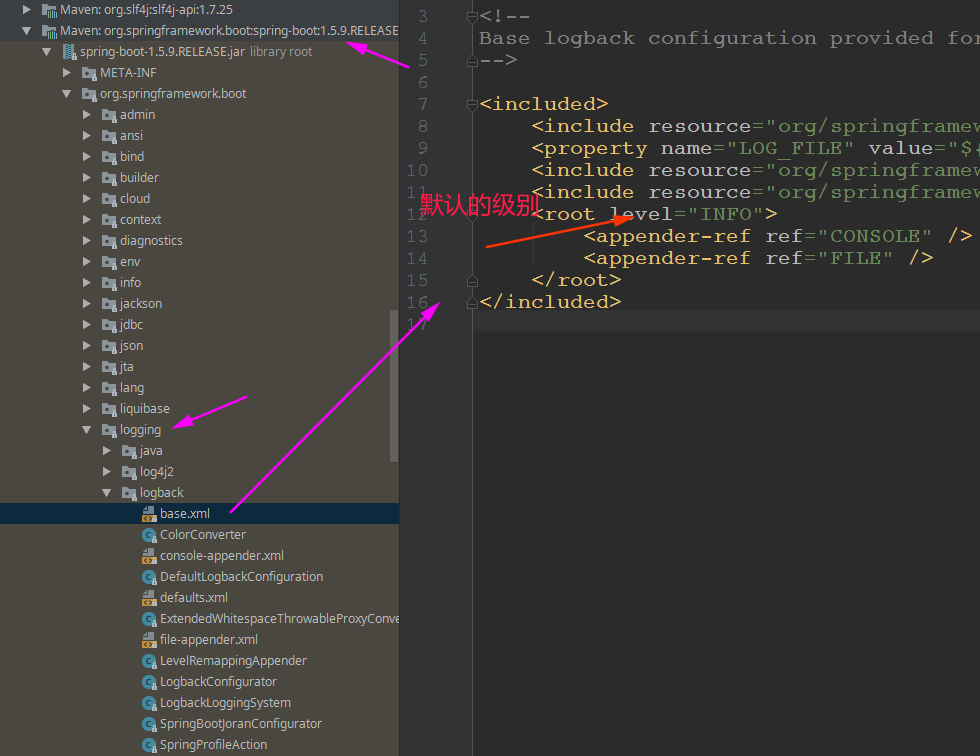
默认配置文件位置:
指定配置
给类路径下放上每个日志框架自己的配置文件即可;SpringBoot就不使用他默认配置的了
| Logging System | Customization |
|---|---|
| Logback | logback-spring.xml, logback-spring.groovy, logback.xml or logback.groovy |
| Log4j2 | log4j2-spring.xml or log4j2.xml |
| JDK (Java Util Logging) | logging.properties |
logback.xml:直接就被日志框架识别了;
logback-spring.xml:日志框架就不直接加载日志的配置项,由SpringBoot解析日志配置,可以使用SpringBoot的高级Profile功能
<springProfile name="staging">
<!-- configuration to be enabled when the "staging" profile is active -->
可以指定某段配置只在某个环境下生效
</springProfile>
logback-spring.xml配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--
scan:当此属性设置为true时,配置文件如果发生改变,将会被重新加载,默认值为true。
scanPeriod:设置监测配置文件是否有修改的时间间隔,如果没有给出时间单位,默认单位是毫秒当scan为true时,此属性生效。默认的时间间隔为1分钟。
debug:当此属性设置为true时,将打印出logback内部日志信息,实时查看logback运行状态。默认值为false。
-->
<configuration scan="false" scanPeriod="60 seconds" debug="false">
<!-- 定义日志的根目录 -->
<property name="LOG_HOME" value="log/zxlog" />
<!-- 定义日志文件名称 -->
<property name="appName" value="zxin-springboot"></property>
<!-- ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender 表示控制台输出 -->
<appender name="stdout" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<!--
日志输出格式:
%d表示日期时间,
%thread表示线程名,
%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度
%logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。
%msg:日志消息,
%n是换行符
-->
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<springProfile name="dev">
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ----> [%thread] ---> %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</springProfile>
<springProfile name="!dev">
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ==== [%thread] ==== %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</springProfile>
</layout>
</appender>
<!-- 滚动记录文件,先将日志记录到指定文件,当符合某个条件时,将日志记录到其他文件 -->
<appender name="appLogAppender" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<!-- 指定日志文件的名称 -->
<file>${LOG_HOME}/${appName}.log</file>
<!--
当发生滚动时,决定 RollingFileAppender 的行为,涉及文件移动和重命名
TimeBasedRollingPolicy: 最常用的滚动策略,它根据时间来制定滚动策略,既负责滚动也负责出发滚动。
-->
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--
滚动时产生的文件的存放位置及文件名称 %d{yyyy-MM-dd}:按天进行日志滚动
%i:当文件大小超过maxFileSize时,按照i进行文件滚动
-->
<fileNamePattern>${LOG_HOME}/${appName}-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}-%i.log</fileNamePattern>
<!--
可选节点,控制保留的归档文件的最大数量,超出数量就删除旧文件。假设设置每天滚动,
且maxHistory是365,则只保存最近365天的文件,删除之前的旧文件。注意,删除旧文件是,
那些为了归档而创建的目录也会被删除。
-->
<MaxHistory>365</MaxHistory>
<!--
当日志文件超过maxFileSize指定的大小是,根据上面提到的%i进行日志文件滚动 注意此处配置SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy是无法实现按文件大小进行滚动的,必须配置timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy
-->
<timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedFNATP">
<maxFileSize>100MB</maxFileSize>
</timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy>
</rollingPolicy>
<!-- 日志输出格式: -->
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [ %thread ] - [ %-5level ] [ %logger{50} : %line ] - %msg%n</pattern>
</layout>
</appender>
<!--
logger主要用于存放日志对象,也可以定义日志类型、级别
name:表示匹配的logger类型前缀,也就是包的前半部分
level:要记录的日志级别,包括 TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR
additivity:作用在于children-logger是否使用 rootLogger配置的appender进行输出,
false:表示只用当前logger的appender-ref,true:
表示当前logger的appender-ref和rootLogger的appender-ref都有效
-->
<!-- hibernate logger -->
<logger name="com.zxin" level="debug" />
<!-- Spring framework logger -->
<logger name="org.springframework" level="debug" additivity="false"></logger>
<!--
root与logger是父子关系,没有特别定义则默认为root,任何一个类只会和一个logger对应,
要么是定义的logger,要么是root,判断的关键在于找到这个logger,然后判断这个logger的appender和level。
-->
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="stdout" />
<appender-ref ref="appLogAppender" />
</root>
</configuration> 运行项目:
如果使用logback.xml作为日志配置文件,还要使用profile功能,会有以下错误:
可以按照slf4j的日志适配图,进行相关的切换;
slf4j+log4j的方式;
在sjf4j中使用log4j(而不是logback):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>log4j-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</dependency>切换为log4j2(可能用到)
springboot_03_logging_2_uselog4j2项目。
pom.xml改动:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions> <!--排除默认的logging-->
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--导入log4j2-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-log4j2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>效果:
使用SpringBoot:
1)、创建SpringBoot应用,选中我们需要的模块;
2)、SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来;
3)、自己编写业务代码即可;
自动配置原理?
这个场景SpringBoot帮我们配置了什么?能不能修改?能修改哪些配置?能不能扩展?xxx
xxxxAutoConfiguration:帮我们给容器中自动配置组件;xxxxProperties: 配置类来封装配置文件的内容;
和SpringMVC的自动配置都在WebMVCAutoConfiguration类中。下面是对静态资源的一些配置:
具体代码如下:
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
} else {
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(
registry.addResourceHandler(
new String[]{"/webjars/**"}).addResourceLocations(
new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"}).setCachePeriod(
this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(
registry.addResourceHandler(
new String[]{staticPathPattern}).addResourceLocations(
getResourceLocations(
this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations())).setCachePeriod(
this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
}对这对代码的总结:
1)、所有 /webjars/** ,都去classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/找资源;
webjars:以jar包的方式引入静态资源;http://www.webjars.org/
导入之后,查看maven依赖的目录结果,就是上面的classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/目录:
<!--导入静态资源jquery-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1-1</version>
</dependency>启动项目之后,可以直接在浏览器访问到jquery: 输入http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.3.1-1/jquery.js
2)、"/**" 访问当前项目的任何资源(自己添加的静态资源),都去(静态资源的文件夹)找映射
比如在上面的代码中还有一个行Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
这个resourceProperties是类ResourceProperties的对象,可以设置和静态资源有关的参数,比如缓存时间等。相关代码如下:
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.resources",
ignoreUnknownFields = false
)
public class ResourceProperties {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS
= new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/",
"classpath:/public/"};
private String[] staticLocations;
private boolean addMappings;
private final ResourceProperties.Chain chain;
private final ResourceProperties.Cache cache;
public ResourceProperties() {
this.staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
this.addMappings = true;
this.chain = new ResourceProperties.Chain();
this.cache = new ResourceProperties.Cache();
}
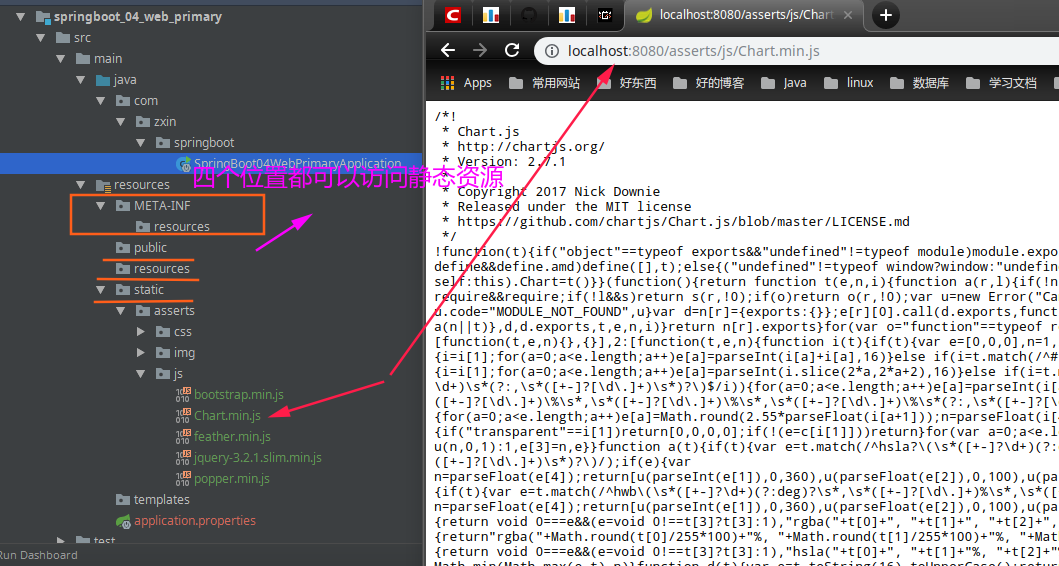
}下面就是几个静态资源的文件夹
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/",
"classpath:/public/"
"/":当前项目的根路径例如,访问项目的下静态资源http://localhost:8080/asserts/js/Chart.min.js去静态资源文件夹里面找Chart.min.js:
也可以在
application.properties中定义自己的静态资源文件夹:spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/zxzxin/,classpath:/test/
3)、欢迎页; 静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面,被"/**"映射;
localhost:8080/ 找index.html页面
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(
ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
return new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(
new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(
applicationContext), applicationContext,
this.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
}4)、所有的 **/favicon.ico 都是在静态资源文件下找;
下面是WebMVCAutoConfiguration里面的内部类FaviconConfiguration:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(
value = {"spring.mvc.favicon.enabled"},
matchIfMissing = true
)
public static class FaviconConfiguration implements ResourceLoaderAware {
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
public FaviconConfiguration(ResourceProperties resourceProperties) {
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
}
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
@Bean
public SimpleUrlHandlerMapping faviconHandlerMapping() {
SimpleUrlHandlerMapping mapping = new SimpleUrlHandlerMapping();
mapping.setOrder(-2147483647);
// 所有的**/favicon.ico,还是在静态资源文件夹
mapping.setUrlMap(Collections.singletonMap("**/favicon.ico", this.faviconRequestHandler()));
return mapping;
}
@Bean
public ResourceHttpRequestHandler faviconRequestHandler() {
ResourceHttpRequestHandler requestHandler = new ResourceHttpRequestHandler();
requestHandler.setLocations(this.resolveFaviconLocations());
return requestHandler;
}
private List<Resource> resolveFaviconLocations() {
String[] staticLocations = WebMvcAutoConfiguration.WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter.getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
List<Resource> locations = new ArrayList(staticLocations.length + 1);
Stream var10000 = Arrays.stream(staticLocations);
ResourceLoader var10001 = this.resourceLoader;
this.resourceLoader.getClass();
var10000.map(var10001::getResource).forEach(locations::add);
locations.add(new ClassPathResource("/"));
return Collections.unmodifiableList(locations);
}
}测试: 将favicon.ico放在META-INF/resources下(也是静态资源文件夹):
模板引擎的作用: 将页面模板和组装的数据交给模板引擎,模板引擎将页面中的表达式解析,填充到指定的位置,生成我们想要的内容。
SpringBoot推荐Thymeleaf,语法更简单,功能更强大。
(1)、引入thymeleaf
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<thymeleaf.version>3.0.9.RELEASE</thymeleaf.version>
<!--布局功能的支持程序: thymeleaf3 == layout2版本-->
<!-- thymeleaf2 == layout1 版本-->
<thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.1.1</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--导入thymeleaf-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>但是像上面那样配置之后项目启动会出错:
原因就是不能自己覆盖那个版本,但是教程上覆盖貌似是可以。。
所以pom.xml还是不能将thymeleaf的版本更改,直接用springboot默认的版本即可。
测试结果: (classpath:/tmplates/success.html)
(2)、Thymeleaf使用
默认规则:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf")
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private static final MimeType DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = MimeType.valueOf("text/html");
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
//
}只要我们把HTML页面放在classpath:/templates/,thymeleaf就能自动渲染;
使用:
1、导入thymeleaf的名称空间
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">一个关于IDE的问题: Thymeleaf在IDEA中的红色波浪线问题
2、使用thymeleaf语法;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!--suppress ALL--> <!--解决thymeleaf红线问题-->
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>成功!</h1>
<!--th:text将div里面的内容设置成-->
<div th:text="${hello}">这是显示欢迎信息</div> <!--后面的"这是显示欢迎信息"经过模板引擎解析后不会显示出来-->
</body>
</html>(3)、语法规则
1)、th:text;改变当前元素里面的文本内容;
th:任意html属性;来替换原生属性的值
2)、表达式语法
具体参见: 在线文档
1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法; 2)、使用内置的基本对象; 3)、内置的一些工具对象;
Simple expressions:
- Variable Expressions:
${...} - Selection Variable Expressions:
*{...} - Message Expressions: #{...}
- Link URL Expressions: @{...}
- Fragment Expressions: ~{...}
Literals(字面值)
- Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…
- Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…
- Boolean literals: true , false
- Null literal: null
- Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,…
Text operations:(文本操作)
- String concatenation: +
- Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|
Arithmetic operations:(算数运算)
- Binary operators: + , - , * , / , %
- Minus sign (unary operator): -
Boolean operations:(布尔运算)
- Binary operators: and , or
- Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not
Comparisons and equality:(比较运算)
- Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
- Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )
Conditional operators:(条件运算)
- If-then: (if) ? (then)
- If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
- Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
Special tokens:
- No-Operation:
补充:
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;
配合 th:object="${session.user}:
<div th:object="${session.user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p>
<p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p>
<p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p>
</div>
Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容
Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL;
@{/order/process(execId=${execId},execType='FAST')}
Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式
<div th:insert="~{commons :: main}">...</div>简单使用测试:
相关代码:
Controller:
@Controller
public class MyController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
@RequestMapping("/success")
public String success(Map<String, Object> map){
map.put("hello", "<h1>你好</<h1>");
map.put("users", Arrays.asList("zhangsan", "lisi", "wangwu"));
return "success"; //跳转到template/success.html视图
}
}success.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!--suppress ALL--> <!--解决thymeleaf红线问题-->
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>成功!</h1>
<!--th:text将div里面的内容设置成-->
<div th:text="${hello}">这是显示欢迎信息</div>
<hr/>
<div th:text="${hello}"></div> <!--转义-->
<div th:utext="${hello}"></div>
<hr/>
<!--th:each每次遍历都会生成当前这个标签, 3个h4-->
<h4 th:text="${user}" th:each="user:${users}"></h4>
<hr/>
<h4>
<span th:each="user:${users}">[[${user}]]</span>
</h4>
</body>
</html>在线文档参考,org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web:web的所有自动场景。
Spring MVC auto-configuration,即SpringBoot自动配置好了SpringMVC,
-
Inclusion of
ContentNegotiatingViewResolverandBeanNameViewResolverbeans.- 自动配置了
ViewResolver(视图解析器:根据方法的返回值得到视图对象(View),视图对象决定如何渲染(转发?重定向?)) ContentNegotiatingViewResolver:组合所有的视图解析器的;- 如何定制:我们可以自己给容器中添加一个视图解析器;自动的将其组合进来;比如
MyViewResolver;
- 自动配置了
-
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (see below).静态资源文件夹路径,webjars等;
-
Static
index.htmlsupport. 静态首页访问 -
Custom
Faviconsupport (see below).favicon.ico图标; -
自动注册了 of
Converter,GenericConverter,Formatterbeans.Converter:类型转换器; public String hello(User user):类型转换使用ConverterFormatter格式化器(例如日期格式化(和SpringMVC息息相关)); 2017.12.17===Date;
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "spring.mvc",
name = {"date-format"}//在配置文件中配置日期格式化规则
)
public Formatter<Date> dateFormatter() {
return new DateFormatter(this.mvcProperties.getDateFormat());//日期格式化组件
}自己添加的格式化器转换器,我们只需要放在容器中即可。
-
Support for
HttpMessageConverters(see below).-
HttpMessageConverter:SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的,例如想将User以Json方法写出去User---Json; -
HttpMessageConverters是从容器中确定;获取所有的HttpMessageConverter;自己给容器中添加HttpMessageConverter,只需要将自己的组件注册容器中(@Bean,@Component)
-
-
Automatic registration of
MessageCodesResolver(see below).定义错误代码生成规则; -
Automatic use of a
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializerbean (see below).我们可以配置一个ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer来替换默认的;(添加到容器)--> 数据初始化绑定初始化
WebDataBinder;
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features, and you just want to add additional MVC configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers etc.) you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurerAdapter, but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance providing such components.
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
以前的配置,视图解析viewController,以及拦截器(interceptor)。
<mvc:view-controller path="/hello" view-name="success"/>
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/hello"/>
<bean></bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>编写一个配置类(@Configuration),是WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类型;不能标注@EnableWebMvc;
既保留了所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置,下面是SpringBoot1.0以上的,但是现在过时了
//使用WebMvcConfigurerAdapter可以来扩展SpringMVC的功能
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// super.addViewControllers(registry);
//浏览器发送 /zxin 请求来到 success
registry.addViewController("/zxin").setViewName("success");
}
}SpringBoot2.0以上的替代方案:
// 以前是使用 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter扩展SpringMVC的功能
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
//浏览器发送 /zxin请求,来到 success.html页面
registry.addViewController("/zxin").setViewName("success");
}
}原理:
1)、WebMvcAutoConfiguration是SpringMVC的自动配置类;
2)、在做其他自动配置时会导入;@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@Configuration
public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
//下面的代码是 DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration(父类)中的, 从容器中获取所有的WebMvcConfigurer
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
//一个参考实现;将所有的WebMvcConfigurer相关配置都来一起调用;
//@Override
// public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) {
// delegate.addViewControllers(registry);
// }
}
}
} 3)、容器中所有的WebMvcConfigurer都会一起起作用;
4)、我们的配置类也会被调用;
效果:SpringMVC的自动配置和我们的扩展配置都会起作用;
这个就是当你标注了
@EnableWebMvc注解,就可以完全的控制SpringMVC了(SpringBoot对SpringMVC不会起作用了)。
SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们自己配置;所有的SpringMVC(web场景)的自动配置都失效了。
我们需要在配置类中添加@EnableWebMvc即可;
@EnableWebMvc // 全面接管SpringMVC,静态资源都不能访问了
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/zxin").setViewName("success");
}
}原理:
为什么@EnableWebMvc自动配置就失效了;
1)、@EnableWebMvc的核心
@Import({DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class}) //核心
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}2)、导入的DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration类:
@Configuration
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
}3)、而WebMvcAutoConfiguration类的开始是这样写的: 关键就在这一行@ConditionalOnMissingBean({WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class})
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class})
//容器中没有这个组件的时候,这个自动配置类才生效,但是如果上面有了,就不生效了,所以这就是原因
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class})
@AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483638)
@AutoConfigureAfter({DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class})
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
}4)、@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来;
5)、而导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是SpringMVC最基本的功能;
模式:
1)、SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(@Bean、@Component)如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有,才自动配置;如果有些组件可以有多个(ViewResolver)将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来;
2)、在SpringBoot中会有非常多的xxxConfigurer帮助我们进行扩展配置;
3)、在SpringBoot中会有很多的xxxCustomizer帮助我们进行定制配置;
如果我们在静态资源文件夹(public、META-INF/resources、resources、static)中放了index.html页面,就不会默认访问到我们在template下面的首页,有两种方法可以解决这个问题。
方法一:
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping({"/", "/index.html"})
public String index(){
return "login";// 跳转到template/login.html
}
}方法二:
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("login");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("login");
}
}另外,可以用Thymeleaf来替换login.html中的一些代码。这样,当改变项目名称时不会受影响。
以前SpringMVC的配置步骤:
1)、编写国际化配置文件;
2)、使用ResourceBundleMessageSource管理国际化资源文件;
3)、在页面使用fmt:message取出国际化内容;
现在SpringBoot帮我们做好了后面的两项。我们只需要编写配置文件即可。
步骤:
1)、编写国际化配置文件,抽取页面需要显示的国际化消息;
2)、SpringBoot自动配置好了管理国际化资源文件的组件MessageSourceAutoConfiguration;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages")
public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Comma-separated list of basenames (essentially a fully-qualified classpath
* location), each following the ResourceBundle convention with relaxed support for
* slash based locations. If it doesn't contain a package qualifier (such as
* "org.mypackage"), it will be resolved from the classpath root.
*/
private String basename = "messages";
//我们的配置文件可以直接放在类路径下叫messages.properties;
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.basename)) {
//设置国际化资源文件的基础名(去掉语言国家代码的en_US) 默认是message
messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(this.basename)));
}
if (this.encoding != null) {
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(this.encoding.name());
}
messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(this.fallbackToSystemLocale);
messageSource.setCacheSeconds(this.cacheSeconds);
messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(this.alwaysUseMessageFormat);
return messageSource;
}
}3)、编写配置基础名的配置文件代码;
spring.messages.basename=i18n.login4)、去页面获取国际化的值;
login.html完整代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<meta name="description" content="">
<meta name="author" content="">
<title>Signin Template for Bootstrap</title>
<!-- Bootstrap core CSS -->
<link href="asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css" th:href="@{/webjars/bootstrap/4.0.0/css/bootstrap.css}" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- Custom styles for this template -->
<link href="asserts/css/signin.css" th:href="@{/asserts/css/signin.css}" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body class="text-center">
<form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html">
<img class="mb-4" th:src="@{asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}" src="asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg" alt="" width="72" height="72">
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1>
<label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.username}">Username</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Username" th:placeholder="#{login.username}" required="" autofocus="">
<label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.password}">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" placeholder="Password" th:placeholder="#{login.password}" required="">
<div class="checkbox mb-3">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"/> [[#{login.remember}]]
</label>
</div>
<button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit" th:text="#{login.btn}">Sign in</button>
<p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">© 2017-2018</p>
<a class="btn btn-sm">中文</a>
<a class="btn btn-sm">English</a>
</form>
</body>
</html>效果:根据浏览器语言设置的信息切换了国际化;
原理:
国际化Locale(区域信息对象);LocaleResolver(获取区域信息对象);
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "spring.mvc",
name = {"locale"}
)
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
if (this.mvcProperties.getLocaleResolver() == org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcProperties.LocaleResolver.FIXED) {
return new FixedLocaleResolver(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
} else {
AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver localeResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver();
localeResolver.setDefaultLocale(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
return localeResolver;
}
}
// 默认的就是根据 请求头 带来的区域信息获取Locale进行国际化4)、可以配置自己的LocaleResolver点击链接切换国际化
login.html更改:
/**
* 可以在链接上携带区域信息
*/
public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver{
// 解析区域信息
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
String l = request.getParameter("l");
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(l)){
String[] split = l.split("_");
locale = new Locale(split[0], split[1]);// public Locale(String language, String country)
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, @Nullable HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, @Nullable Locale locale) {
}
}最后记得要注册这个组件。
// 注册组件
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}开发期间模板引擎页面修改以后,要实时生效:
1)、禁用模板引擎的缓存;
# 禁用模板引擎的缓存 (这样就不会在更改html代码的时候没有立即显示改变),然后IDEA CTRL + F9重新编译一下
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false2)、页面修改完成以后ctrl+f9:重新编译;
实现登录的前端代码,在form表单添加action:
具体代码:
<body class="text-center">
<form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html" th:action="@{/user/login}" method="post">
<!--注意下面的th:src的路径前面带了一个/ 不然到了/user/login页面,图片不会显示-->
<img class="mb-4" th:src="@{/asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}" src="asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg" alt="" width="72" height="72">
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1>
<p style="color: red" th:text="${msg}" th:if="${not #strings.isEmpty(msg)}"></p>
<label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.username}">Username</label>
<input type="text" name="username" class="form-control" placeholder="Username" th:placeholder="#{login.username}" required="" autofocus="">
<label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.password}">Password</label>
<input type="password" name="password" class="form-control" placeholder="Password" th:placeholder="#{login.password}" required="">
<div class="checkbox mb-3">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"/> [[#{login.remember}]]
</label>
</div>
<button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit" th:text="#{login.btn}">Sign in</button>
<p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">© 2017-2018</p>
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='zh_CN')}">中文</a>
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='en_US')}">English</a>
</form>
</body>登陆错误消息的显示
<p style="color: red" th:text="${msg}" th:if="${not #strings.isEmpty(msg)}"></p>后台Java代码:
@Controller
public class LoginController {
// @GetMapping
// @PutMapping
// @DeleteMapping
// @RequestMapping(value = "/user/login", method = RequestMethod.POST) //太长
@PostMapping(value = "/user/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestParam("password") String password,
Map<String, Object>map){
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(username) && "123456".equals(password)){
return "dashboard";
}else {
// 登录失败
map.put("msg", "用户名密码错误");
return "login";
}
}
}防止表单的重复提交
如果按照上面的处理(对重复提交表单的处理)会发生你登录之后在另一个浏览器中不需要登录可以直接访问dashboard.html(main.html)的情况,所以要使用拦截器interceptor进行拦截器检查。
自已定义一个LoginHandlerInterceptor
/**
* 登录检查
*/
public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//目标方法执行之前
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
Object user = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser");
if(user == null){
// 未登录,返回登录页面
request.setAttribute("msg", "没有权限,请先登录");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request, response);
return false;
}else {
//已登录, 放行请求
return true;
}
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}在MVC的配置类MyMvcConfig注册拦截器:
// 注册拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
// 除了 "/index.html", "/", "/user/login" 都要拦截
// 以前SpringMVC还需要配置: 不能拦截静态资源,
// 现在SpringBoot已经做好了不拦截静态资源的配置
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**")
.excludePathPatterns("/index.html", "/", "/user/login"
);
}
}效果:
实验要求:
1)、RestfulCRUD:CRUD满足Rest风格;
URI: /资源名称/资源标识 : HTTP请求方式区分对资源CRUD操作
| 普通CRUD(uri来区分操作) | RestfulCRUD | |
|---|---|---|
| 查询 | getEmp | emp---GET |
| 添加 | addEmp?xxx | emp---POST |
| 修改 | updateEmp?id=xxx&ooo=xx | emp/{id}---PUT |
| 删除 | deleteEmp?id=1 | emp/{id}---DELETE |
2)、实验的请求架构;
| 实验功能 | 请求URI | 请求方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 查询所有员工 | emps |
GET |
| 查询某个员工(来到修改页面) | emp/1(emp/{id}) |
GET |
| 来到添加页面 | emp | GET |
| 添加员工 | emp | POST |
| 来到修改页面(查出员工进行信息回显) | emp/1 | GET |
| 修改员工 | emp | PUT |
| 删除员工 | emp/1 | DELETE |
3)、员工列表:
thymeleaf公共页面元素抽取(因为员工列表页面list.html的顶部和左边都是和dashboard.html相同,所以可以将公共部分抽取出来)
1、抽取公共片段
<div th:fragment="copy">
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
</div>
2、引入公共片段
<div th:insert="~{footer :: copy}"></div>
~{templatename::selector}:模板名::选择器
~{templatename::fragmentname}:模板名::片段名
3、默认效果:
insert的公共片段在div标签中
如果使用th:insert等属性进行引入,可以不用写~{}:
行内写法可以(必须)加上:[[~{}]];[(~{})];三种引入公共片段的th属性:
th:insert:将公共片段整个插入到声明引入的元素中
th:replace:将声明引入的元素替换为公共片段
th:include:将被引入的片段的内容包含进这个标签中
<footer th:fragment="copy">
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
</footer>
引入方式
<div th:insert="footer :: copy"></div>
<div th:replace="footer :: copy"></div>
<div th:include="footer :: copy"></div>
效果
1. insert
<div>
<footer>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
</footer>
</div>
2. replace
<footer>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
</footer>
3. th:include
<div>
© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery
</div>dashboard.html顶部公共元素抽取:
在list.html中引入:
dashboard.html侧栏公共元素抽取:
在list.html中引入:
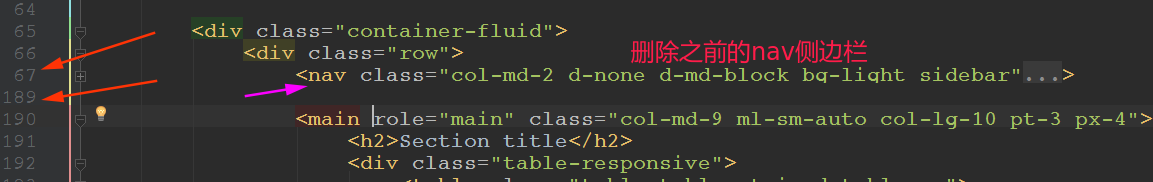
先删除原来的nav标签(侧栏):
引入新的:
引入片段的时候传入参数: (这个解决的就是侧栏的点击高亮问题(当前选项高亮))
此时将公共部分抽取出来bar.html(不是将公共部分继续放在dashboard.html中):
(1).bar.html中添加th:class属性判断(带参数)
DashBoard部分
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link active"
th:class="${activeUri=='main.html'?'nav-link active':'nav-link'}"<!--重要-->
href="#" th:href="@{/main.html}">
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="24" height="24" viewBox="0 0 24 24" fill="none" stroke="currentColor" stroke-width="2" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-linejoin="round" class="feather feather-home">
<path d="M3 9l9-7 9 7v11a2 2 0 0 1-2 2H5a2 2 0 0 1-2-2z"></path>
<polyline points="9 22 9 12 15 12 15 22"></polyline>
</svg>
Dashboard <span class="sr-only">(current)</span>
</a>
</li>
员工管理部分
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#" th:href="@{/emps}"
th:class="${activeUri=='emps'?'nav-link active':'nav-link'}"> <!--发送restful式的请求,查看所有的员工-->
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="24" height="24" viewBox="0 0 24 24" fill="none" stroke="currentColor" stroke-width="2" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-linejoin="round" class="feather feather-users">
<path d="M17 21v-2a4 4 0 0 0-4-4H5a4 4 0 0 0-4 4v2"></path>
<circle cx="9" cy="7" r="4"></circle>
<path d="M23 21v-2a4 4 0 0 0-3-3.87"></path>
<path d="M16 3.13a4 4 0 0 1 0 7.75"></path>
</svg>
员工管理
</a>
</li>(2). list.html和dashboard.html引入更改:
list.html
<!--引入公共部分topbar-->
<div th:replace="commons/bar::topbar"></div>
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<!--引入侧边栏-->
<!--<div th:replace="~{dashboard::#sidebar}"></div>-->
<div th:replace="commons/bar::#sidebar(activeUri='emps')"></div>
dashboard.html
<!--引入公共部分topbar-->
<div th:replace="commons/bar::topbar"></div>
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<!--引入公共部分sidebar-->
<div th:replace="commons/bar::#sidebar(activeUri='main.html')"></div> list.html页面员工展示:
<div class="table-responsive">
<table class="table table-striped table-sm">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>lastName</th>
<th>email</th>
<th>gender</th>
<th>department</th>
<th>birth</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="emp:${emps}">
<td th:text="${emp.id}"></td>
<td>[[${emp.lastName}]]</td>
<td th:text="${emp.email}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.gender}==0?'女':'男'"</td>
<td th:text="${emp.department.departmentName}"></td>
<!--<td th:text="${emp.birth}"></td>-->
<!--日期格式化-->
<td th:text="${#dates.format(emp.birth, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm')}"></td>
<td>
<!--小号的蓝颜色的bootstrap的按钮-->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-primary">编辑</button>
<!--小号的红颜色的bootstrap的按钮-->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-danger">删除</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>效果:
list页面添加按钮:
<h2><a class="btn btn-sm btn-success" href="emp" th:href="@{/emp}">员工添加</a></h2>controlloer:
//来到员工添加页面
@GetMapping("/emp")
public String toAddPage(Model model){
//来到添加页面, 需要所有的部门,在页面显示
Collection<Department> departments = departmentDao.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("depts", departments);
return "emp/add";
}add.html页面中的表单添加页面
<main role="main" class="col-md-9 ml-sm-auto col-lg-10 pt-3 px-4">
<!--不是之前的list.html的内容,而是一个表单添加员工-->
<!--表单在bootstrap中有-->
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label>LastName</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="zhangsan">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Email</label>
<input type="email" class="form-control" placeholder="[email protected]">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Gender</label><br/>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="1">
<label class="form-check-label">男</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="0">
<label class="form-check-label">女</label>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>department</label>
<select class="form-control">
<!--提交的是部门的id-->
<option th:value="dept.id" th:each="dept:${depts}" th:text="${dept.departmentName}">1</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Birth</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="2001-01-01">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">添加</button>
</form>
</main>提交的数据格式不对:生日:日期;
2017-12-12;2017/12/12;2017.12.12;
配置(application.properties中配置)
# 日期格式化
spring.mvc.date-format=yyyy-MM-dd日期的格式化;SpringMVC将页面提交的值需要转换为指定的类型;
2017-12-12---Date; 类型转换,格式化;
默认日期是按照/的方式;
修改添加二合一表单
<!--需要区分是员工修改还是添加;-->
<form th:action="@{/emp}" method="post">
<!--发送put请求修改员工数据-->
<!--
1、SpringMVC中配置HiddenHttpMethodFilter;(SpringBoot自动配置好的)
2、页面创建一个post表单
3、创建一个input项,name="_method";值就是我们指定的请求方式
-->
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="put" th:if="${emp!=null}"/>
<input type="hidden" name="id" th:if="${emp!=null}" th:value="${emp.id}">
<div class="form-group">
<label>LastName</label>
<input name="lastName" type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="zhangsan" th:value="${emp!=null}?${emp.lastName}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Email</label>
<input name="email" type="email" class="form-control" placeholder="[email protected]" th:value="${emp!=null}?${emp.email}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Gender</label><br/>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="1" th:checked="${emp!=null}?${emp.gender==1}">
<label class="form-check-label">男</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gender" value="0" th:checked="${emp!=null}?${emp.gender==0}">
<label class="form-check-label">女</label>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>department</label>
<!--提交的是部门的id-->
<select class="form-control" name="department.id">
<option th:selected="${emp!=null}?${dept.id == emp.department.id}" th:value="${dept.id}" th:each="dept:${depts}" th:text="${dept.departmentName}">1</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Birth</label>
<input name="birth" type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="zhangsan" th:value="${emp!=null}?${#dates.format(emp.birth, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm')}">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" th:text="${emp!=null}?'修改':'添加'">添加</button>
</form>后台java代码:
来到修改页面代码:
//来到修改页面,查出当前员工,在页面回显
@GetMapping("/emp/{id}")
public String toEditPage(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, Model model){
Employee employee = employeeDao.get(id);
model.addAttribute("emp",employee);
//页面要显示所有的部门列表
Collection<Department> departments = departmentDao.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("depts",departments);
//回到修改页面(add是一个修改添加二合一的页面);
return "emp/add";
}真正修改:
//员工修改;需要提交员工id;
@PutMapping("/emp")
public String updateEmployee(Employee employee){
System.out.println("修改的员工数据:"+employee);
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/emps";
}<tr th:each="emp:${emps}">
<td th:text="${emp.id}"></td>
<td>[[${emp.lastName}]]</td>
<td th:text="${emp.email}"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.gender}==0?'女':'男'"></td>
<td th:text="${emp.department.departmentName}"></td>
<td th:text="${#dates.format(emp.birth, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm')}"></td>
<td>
<a class="btn btn-sm btn-primary" th:href="@{/emp/}+${emp.id}">编辑</a>
<button th:attr="del_uri=@{/emp/}+${emp.id}" class="btn btn-sm btn-danger deleteBtn">删除</button>
</td>
</tr>
<script>
$(".deleteBtn").click(function(){
//删除当前员工的
$("#deleteEmpForm").attr("action",$(this).attr("del_uri")).submit();
return false;
});
</script>后台java代码:
//员工删除
@DeleteMapping("/emp/{id}")
public String deleteEmployee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
employeeDao.delete(id);
return "redirect:/emps";
}默认效果,浏览器返回一个默认的错误页面
浏览器发送请求的请求头():
如果是其他客户端,默认响应一个json数据(Postman客户端查看):
{
"timestamp": "2019-02-10T05:04:15.852+0000",
"status": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"message": "No message available",
"path": "/crud/aaa"
}原理:
可以参照ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration;错误处理的自动配置;
给容器中添加了以下组件:
1、DefaultErrorAttributes:
帮我们在页面共享信息;页面能获取的信息getErrorAttributes
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(RequestAttributes requestAttributes,
boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
addStatus(errorAttributes, requestAttributes);
addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, requestAttributes, includeStackTrace);
addPath(errorAttributes, requestAttributes);
return errorAttributes;
}2、BasicErrorController:处理默认/error请求(可以在配置文件中配置)
这个就是上面那两种的html错误页面和json的效果。
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
@RequestMapping(produces = "text/html")//产生html类型的数据;浏览器发送的请求来到这个方法处理
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(
request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
//去哪个页面作为错误页面;包含页面地址和页面内容 resolveErrorView方法
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView == null ? new ModelAndView("error", model) : modelAndView);
}
@RequestMapping
@ResponseBody //产生json数据,其他客户端来到这个方法处理;
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request,
isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>>(body, status);
}
}比如默认网页错误页面发送的请求头:
客户端的:
3、ErrorPageCustomizer:
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error"; 系统出现错误以后来到error请求进行处理;(web.xml注册的错误页面规则)4、DefaultErrorViewResolver:
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status,
Map<String, Object> model) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
//默认SpringBoot可以去找到一个页面? error/404
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
//模板引擎可以解析这个页面地址就用模板引擎解析
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders
.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext);
if (provider != null) {
//模板引擎可用的情况下返回到errorViewName指定的视图地址
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
//模板引擎不可用,就在静态资源文件夹下找errorViewName对应的页面 error/404.html
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}步骤:
一但系统出现4xx或者5xx之类的错误;ErrorPageCustomizer就会生效(定制错误的响应规则);就会来到/error请求;就会被**BasicErrorController**处理;
1)响应页面: 去哪个页面是由**DefaultErrorViewResolver**解析得到的;
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
//所有的ErrorViewResolver得到ModelAndView
for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
if (modelAndView != null) {
return modelAndView;
}
}
return null;
} 2)响应json数据的处理:
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> body = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity(body, status);
}a、如何定制错误的页面;
1)、有模板引擎的情况下;error/状态码;【将错误页面命名为 错误状态码.html 放在模板引擎文件夹里面的 error文件夹下】,发生此状态码的错误就会来到对应的页面;
我们可以使用4xx和5xx作为错误页面的文件名来匹配这种类型的所有错误,精确优先(优先寻找精确的状态码.html);
页面能获取的信息;
timestamp:时间戳
status:状态码
error:错误提示
exception:异常对象
message:异常消息
errors:JSR303数据校验的错误都在这里
2)、没有模板引擎(模板引擎找不到这个错误页面),静态资源文件夹下找;
3)、以上都没有错误页面,就是默认来到SpringBoot默认的错误提示页面;
b、如何定制错误的json数据;
开始测试:
客户端方式:
1)、自定义异常处理 & 返回定制json数据:
效果:
代码:
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public Map<String, Object> handleException(Exception e){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", "user.not exist");
map.put("message", e.getMessage());
return map;
}
}
//没有自适应效果... 2)、转发到/error进行自适应响应效果处理
效果:
来源: BasicErrorController中errorHtml方法中的getStatus方法里面:
protected HttpStatus getStatus(HttpServletRequest request) {
Integer statusCode = (Integer)request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
if (statusCode == null) {
return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
} else {
try {
return HttpStatus.valueOf(statusCode.intValue());
} catch (Exception var4) {
return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
}
}具体的设置代码(有自适应效果):
// 有自适应效果的json处理
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public String handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//传入我们自己的错误状态码 4xx 5xx,否则就不会进入定制错误页面的解析流程
/**
*
* Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
*/
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500);
map.put("code","user.not exist");
map.put("message",e.getMessage());
//转发到/error
return "forward:/error";
} 3)、将我们的定制数据携带出去;
出现错误以后,会来到/error请求,会被BasicErrorController处理,响应出去可以获取的数据是由getErrorAttributes得到的(是AbstractErrorController(ErrorController)规定的方法);
1、完全来编写一个ErrorController(就不会用默认的)的实现类【或者是编写AbstractErrorController的子类】,放在容器中;(比较复杂 )
2、页面上能用的数据,或者是json返回能用的数据都是通过errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes得到; 容器中DefaultErrorAttributes.getErrorAttributes();默认进行数据处理的;
自定义ErrorAttributes
// 给容器中加入我们自己定义的ErrorAttributes
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes{
// 返回值的map就是页面和json能获取的所有字段
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace);
map.put("company", "zxzxin"); //加上自己的字段 // 改变默认行为
// 我们的异常处理器携带的数据
Map<String, Object>extMap = (Map<String, Object>) webRequest.getAttribute("extMap", 0); // int SCOPE_REQUEST = 0; SCOPE_SESSION = 1;
map.put("extMap", extMap);
return map;
}
}最终的效果:响应是自适应的,可以通过定制ErrorAttributes改变需要返回的内容。
SpringBoot默认使用Tomcat作为嵌入式的Servlet容器;
问题?
1、方法一: 修改和server有关的配置(ServerProperties【也是EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer】);
server.port=8081
server.servlet.context-path=/servlet
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8
//通用的Servlet容器设置
server.xxx
//Tomcat的设置
server.tomcat.xxx2、方法二: 编写一个**EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer**:嵌入式的Servlet容器的定制器;来修改Servlet容器的配置
这是SpringBoot1.0的废弃方案:
@Bean //一定要将这个定制器加入到容器中
public EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer embeddedServletContainerCustomizer(){
return new EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer() {
//定制嵌入式的Servlet容器相关的规则
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer container) {
container.setPort(8083);
}
};
}SpringBoot2.0的新方案:
// 替代方案
// 博客 : https://blog.csdn.net/Hard__ball/article/details/81281898
@Bean
public WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableWebServerFactory> webServerFactoryCustomizer(){
// 定制嵌入式的Servlet容器相关的规则
return new WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableWebServerFactory>() {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableWebServerFactory factory) {
factory.setPort(8081);
}
};
// 使用lambda表达式
// return factory -> factory.setPort(8081);
}由于SpringBoot默认是以jar包的方式启动嵌入式的Servlet容器来启动SpringBoot的web应用,没有web.xml文件。(以前是在webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml下注册)
注册三大组件用以下方式
ServletRegistrationBean
//注册三大组件 - Servlet
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet(){
return new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(), "/myServlet");
}FilterRegistrationBean
// 注册Filter
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(new MyFilter());
filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/hello", "/myServlet"));
return filterRegistrationBean;
}ServletListenerRegistrationBean
// 注册Listener
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener(){
return new ServletListenerRegistrationBean<>(new MyListener());
}SpringBoot帮我们自动SpringMVC的时候,自动的注册SpringMVC的前端控制器;DispatcherServlet;
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration中:
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public ServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet) {
ServletRegistrationBean registration = new ServletRegistrationBean(
dispatcherServlet, this.serverProperties.getServletMapping());
//默认拦截: / 所有请求;包静态资源,但是不拦截jsp请求; /*会拦截jsp
//可以通过server.servletPath来修改SpringMVC前端控制器默认拦截的请求路径
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(
this.webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
if (this.multipartConfig != null) {
registration.setMultipartConfig(this.multipartConfig);
}
return registration;
}默认支持:
Tomcat(默认使用)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
引入web模块默认就是使用嵌入式的Tomcat作为Servlet容器;
</dependency>Jetty
<!-- 引入web模块 排除了默认的tomcat-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--引入其他的Servlet容器-->
<dependency>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</dependency>Undertow
<!-- 引入web模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--引入其他的Servlet容器-->
<dependency>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</dependency>EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration:嵌入式的Servlet容器自动配置?
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@Import(BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class)
//导入BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar:Spring注解版;给容器中导入一些组件
//导入了EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor:
//后置处理器:bean初始化前后(创建完对象,还没赋值赋值)执行初始化工作
public class EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration {
// 下面三个内部类,导入了哪个就用哪个容器
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Tomcat.class })//判断当前是否引入了Tomcat依赖;
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) //判断当前容器没有用户自己定义EmbeddedServletContainerFactory:嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂;作用:创建嵌入式的Servlet容器
public static class EmbeddedTomcat {
@Bean
public TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory tomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory() {
return new TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Server.class, Loader.class,
WebAppContext.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public static class EmbeddedJetty {
@Bean
public JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory jettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory() {
return new JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Undertow.class, SslClientAuthMode.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public static class EmbeddedUndertow {
@Bean
public UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory undertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory() {
return new UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
}
}1)、EmbeddedServletContainerFactory(嵌入式Servlet容器工厂)
public interface EmbeddedServletContainerFactory {
//获取嵌入式的Servlet容器
EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer(
ServletContextInitializer... initializers);
}2)、EmbeddedServletContainer:(嵌入式的Servlet容器)
3)、以TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory为例
@Override
public EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer(
ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
//创建一个Tomcat
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
//配置Tomcat的基本环节
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat"));
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//将配置好的Tomcat传入进去,返回一个EmbeddedServletContainer;并且启动Tomcat服务器
return getTomcatEmbeddedServletContainer(tomcat);
}4)、我们对嵌入式容器的配置修改是怎么生效?
ServerProperties、EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer
EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer:定制器帮我们修改了Servlet容器的配置?
怎么修改的原理?
5)、容器中导入了EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor
//初始化之前
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
//如果当前初始化的是一个ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer类型的组件
if (bean instanceof ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer) {
//
postProcessBeforeInitialization((ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer) bean);
}
return bean;
}
//上面调用的方法
private void postProcessBeforeInitialization(
ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer bean) {
//获取所有的定制器,调用每一个定制器的customize方法来给Servlet容器进行属性赋值;
for (EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer customizer : getCustomizers()) {
customizer.customize(bean);
}
}
private Collection<EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer> getCustomizers() {
if (this.customizers == null) {
// Look up does not include the parent context
this.customizers = new ArrayList<EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer>(
this.beanFactory
//从容器中获取所有这葛类型的组件:EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer
//定制Servlet容器,给容器中可以添加一个EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer类型的组件
.getBeansOfType(EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer.class,
false, false)
.values());
Collections.sort(this.customizers, AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
this.customizers = Collections.unmodifiableList(this.customizers);
}
return this.customizers;
}
ServerProperties也是定制器 (实现了EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer接口)原理步骤:
1)、SpringBoot根据导入的依赖情况,给容器中添加相应的EmbeddedServletContainerFactory【如TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory】
2)、容器中某个组件要创建对象就会惊动后置处理器;EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor;
只要是嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂,后置处理器就工作;
3)、后置处理器,从容器中获取所有的**EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer**,调用定制器的定制方法
什么时候创建嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂?什么时候获取嵌入式的Servlet容器并启动Tomcat;
获取嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂:
1)、SpringBoot应用启动运行run方法;
2)、refreshContext(context);SpringBoot刷新IOC容器【创建IOC容器对象,并初始化容器,创建容器中的每一个组件】;如果是web应用创建AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext,否则:AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
3)、 refresh(context);**刷新刚才创建好的ioc容器;**代码如下:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}4)、onRefresh(); web的IOC容器重写了onRefresh方法
5)、webIOC容器会创建嵌入式的Servlet容器;createEmbeddedServletContainer();
6)、获取嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂:
// 从ioc容器中获取EmbeddedServletContainerFactory 组件;
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory containerFactory = getEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory创建对象,后置处理器BeanPostProcesser一看是这个对象,就获取所有的定制器来先定制Servlet容器的相关配置;
7)、使用容器工厂获取嵌入式的Servlet容器:
this.embeddedServletContainer = containerFactory.getEmbeddedServletContainer(getSelfInitializer());8)、嵌入式的Servlet容器创建对象并启动Servlet容器;
先启动嵌入式的Servlet容器,再将ioc容器中剩下没有创建出的对象获取出来;
IOC容器启动创建嵌入式的Servlet容器
嵌入式Servlet容器:应用打成可执行的jar
-
优点:简单、便携;
-
缺点:默认不支持JSP、优化定制比较复杂(使用定制器【
ServerProperties、自定义EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer】,自己编写嵌入式Servlet容器的创建工厂【EmbeddedServletContainerFactory】);
可以使用外置的Servlet容器:外面安装Tomcat---应用war包的方式打包;
1)、必须创建一个war项目;(利用idea创建好目录结构)
可以将应用打成war包,也可以将IDE整合外部服务器tomcat:
2)、将嵌入式的Tomcat指定为provided;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>3)、必须编写一个SpringBootServletInitializer的子类,并调用configure方法
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
// 传入SpringBoot的主程序
return application.sources(SpringBoot04WebWithServletContainerExternalApplication.class);
}
}4)、启动服务器就可以使用;
两种方式的不同原理:
jar包:执行SpringBoot主类的main方法,启动IOC容器,创建嵌入式的Servlet容器;war包:启动服务器,服务器启动SpringBoot应用【SpringBootServletInitializer】,启动IOC容器;
servlet3.0(Spring注解版):章节: 8.2.4 Shared libraries / runtimes pluggability;
规则:
1)、服务器启动(web应用启动)会创建当前web应用里面每一个jar包里面ServletContainerInitializer实例:
2)、ServletContainerInitializer的实现放在jar包的META-INF/services文件夹下,有一个名为javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的文件,内容就是ServletContainerInitializer的实现类的全类名
3)、还可以使用@HandlesTypes,在应用启动的时候加载我们感兴趣的类;
流程:
1)、启动Tomcat;
2)、org\springframework\spring-web\4.3.14.RELEASE\spring-web-4.3.14.RELEASE.jar!\META-INF\services\javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer:
Spring的web模块里面有这个文件:org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
3)、SpringServletContainerInitializer将@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)标注的所有这个类型的类都传入到onStartup方法的Set<Class<?>>;为这些WebApplicationInitializer类型的类创建实例;
4)、每一个WebApplicationInitializer都调用自己的onStartup;
5)、相当于我们的SpringBootServletInitializer的类会被创建对象,并执行onStartup方法;
6)、SpringBootServletInitializer实例执行onStartup的时候会createRootApplicationContext;创建容器
下面是SpringBootServletInitializer的createRootApplicationContext方法:
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(
ServletContext servletContext) {
//1、创建SpringApplicationBuilder
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = createSpringApplicationBuilder();
StandardServletEnvironment environment = new StandardServletEnvironment();
environment.initPropertySources(servletContext, null);
builder.environment(environment);
builder.main(getClass());
ApplicationContext parent = getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (parent != null) {
this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent).");
servletContext.setAttribute(
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, null);
builder.initializers(new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent));
}
builder.initializers(
new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext));
builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext.class);
//调用configure方法,子类重写了这个方法,将SpringBoot的主程序类传入了进来
builder = configure(builder);
//使用builder创建一个Spring应用
SpringApplication application = builder.build();
if (application.getSources().isEmpty() && AnnotationUtils
.findAnnotation(getClass(), Configuration.class) != null) {
application.getSources().add(getClass());
}
Assert.state(!application.getSources().isEmpty(),
"No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the "
+ "configure method or add an @Configuration annotation");
// Ensure error pages are registered
if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) {
application.getSources().add(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class);
}
//启动Spring应用
return run(application);
}7)、Spring的应用就启动并且创建IOC容器(run方法)
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
//刷新IOC容器
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
listeners.finished(context, null);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}即先启动Servlet容器,再启动SpringBoot应用
Docker是一个开源的应用容器引擎;是一个轻量级容器技术;
Docker支持将软件编译成一个镜像;然后在镜像中各种软件做好配置,将镜像发布出去,其他使用者可以直接使用这个镜像;
运行中的这个镜像称为容器,容器启动是非常快速的。
Docker的思想和虚拟机类似,但是实际还是有区别的。
- docker主机(Host):安装了Docker程序的机器(Docker直接安装在操作系统之上);
- docker客户端(Client):连接docker主机进行操作;
- docker仓库(Registry):用来保存各种打包好的软件镜像;
- docker镜像(Images):软件打包好的镜像,放在docker仓库中;
- docker容器(Container):镜像启动后的实例称为一个容器;容器是独立运行的一个或一组应用;
使用Docker的步骤:
1)、安装Docker
2)、去Docker仓库找到这个软件对应的镜像;
3)、使用Docker运行这个镜像,这个镜像就会生成一个Docker容器;
4)、对容器的启动停止就是对软件的启动停止;
1)、VMWare、VirtualBox(安装);
2)、导入虚拟机文件centos7.ova文件;
3)、双击启动linux虚拟机;使用 root/ 123456登陆;
4)、使用客户端(smarTTy或者xshell)连接linux服务器进行命令操作;
5)、设置虚拟机网络;
桥接网络===选好网卡===接入网线;
6)、设置好网络以后使用命令重启虚拟机的网络
service network restart 7)、查看linux的ip地址
ip addr 8)、使用客户端连接linux;
几个关键命令:
systemctl start docker,启动;systemctl stop docker,停止;
1、检查内核版本,必须是3.10及以上
uname -r
2、安装docker
yum install docker
3、输入y确认安装
4、启动docker
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start docker
[root@localhost ~]# docker -v
Docker version 1.12.6, build 3e8e77d/1.12.6
5、开机启动docker
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable docker
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service.
6、停止docker
systemctl stop docker具体安装教程网络上有,我的是
Deepin环境,找到一篇不错的教程:
| 操作 | 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 检索 | docker search 关键字 eg:docker search redis | 我们经常去docker hub上检索镜像的详细信息,如镜像的TAG。 |
| 拉取 | docker pull 镜像名:tag | :tag是可选的,tag表示标签,多为软件的版本,默认是latest |
| 列表 | docker images | 查看所有本地镜像 |
| 删除 | docker rmi image-id | 删除指定的本地镜像 |
官方仓库: https://hub.docker.com/
软件镜像(QQ安装程序)----运行镜像----产生一个容器(正在运行的软件,运行的QQ);
步骤:
1、搜索镜像
[root@localhost ~]# docker search tomcat
2、拉取镜像
[root@localhost ~]# docker pull tomcat
3、根据镜像启动容器
docker run --name mytomcat -d tomcat:latest
4、docker ps
查看运行中的容器
5、 停止运行中的容器
docker stop 容器的id
6、查看所有的容器
docker ps -a
7、启动容器
docker start 容器id
8、删除一个容器
docker rm 容器id
9、启动一个做了端口映射的tomcat
[root@localhost ~]# docker run -d -p 8888:8080 tomcat
-d:后台运行
-p: 将主机的端口映射到容器的一个端口 主机端口:容器内部的端口
10、注意有时候需要关闭防火墙, s为了演示简单关闭了linux的防火墙
service firewalld status ;查看防火墙状态
service firewalld stop:关闭防火墙
11、查看容器的日志
docker logs container-name/container-id| 操作 | 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 运行 | docker run --name container-name -d image-nameeg:docker run ––name myredis –d redis |
--name:自定义容器名-d:后台运行image-name : 指定镜像模板 |
| 列表 | docker ps(查看运行中的容器); |
加上-a;可以查看所有容器 |
| 停止 | docker stop container-name/container-id |
停止当前你运行的容器 |
| 启动 | docker start container-name/container-id |
启动容器 |
| 删除 | docker rm container-id |
删除指定容器 |
| 端口映射 | -p 6379:6379eg:docker run -d -p 6379:6379 --name myredis docker.io/redis |
-p: 主机端口(映射到)容器内部的端口 |
| 容器日志 | docker logs container-name/container-id |
其中
container-name表示容器的名字,container-id表示容器的id;
更多命令: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/docker/
docker pull mysql错误的启动
[root@localhost ~]# docker run --name mysql01 -d mysql
42f09819908bb72dd99ae19e792e0a5d03c48638421fa64cce5f8ba0f40f5846
mysql退出了(出现异常)
[root@localhost ~]# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
42f09819908b mysql "docker-entrypoint.sh" 34 seconds ago Exited (1) 33 seconds ago mysql01
538bde63e500 tomcat "catalina.sh run" About an hour ago Exited (143) About an hour ago compassionate_
goldstine
c4f1ac60b3fc tomcat "catalina.sh run" About an hour ago Exited (143) About an hour ago lonely_fermi
81ec743a5271 tomcat "catalina.sh run" About an hour ago Exited (143) About an hour ago sick_ramanujan
//错误日志
[root@localhost ~]# docker logs 42f09819908b
error: database is uninitialized and password option is not specified
You need to specify one of MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD, MYSQL_ALLOW_EMPTY_PASSWORD and MYSQL_RANDOM_ROOT_PASSWORD;这个三个参数必须指定一个正确的启动(还是不能使用,没有做映射)
[root@localhost ~]# docker run --name mysql01 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 -d mysql
b874c56bec49fb43024b3805ab51e9097da779f2f572c22c695305dedd684c5f
[root@localhost ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
b874c56bec49 mysql "docker-entrypoint.sh" 4 seconds ago Up 3 seconds 3306/tcp mysql01做了端口映射 -p 3306:3306
[root@localhost ~]# docker run -p 3306:3306 --name mysql02 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 -d mysql
ad10e4bc5c6a0f61cbad43898de71d366117d120e39db651844c0e73863b9434
[root@localhost ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
ad10e4bc5c6a mysql "docker-entrypoint.sh" 4 seconds ago Up 2 seconds 0.0.0.0:3306->3306/tcp mysql02几个其他的高级操作(详细参考官方文档)
docker run --name mysql03 -v /conf/mysql:/etc/mysql/conf.d -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw -d mysql:tag
把主机的/conf/mysql文件夹挂载到 mysqldocker容器的/etc/mysql/conf.d文件夹里面
改mysql的配置文件就只需要把mysql配置文件放在自定义的文件夹下(/conf/mysql)
docker run --name some-mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw -d mysql:tag --character-set-server=utf8mb4 --collation-server=utf8mb4_unicode_ci
指定mysql的一些配置参数pom.xml基本配置:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>application.yml简单配置:
spring:
datasource:
password: root
username: root
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_jdbc
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver效果:
-
SpringBoot1.XX默认是用org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource作为数据源;SpringBoot2.XX默认使用com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource(很快)作为数据源; -
数据源的相关配置都在
DataSourceProperties里面;
自动配置原理都在这个包下:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc
1、参考DataSourceConfiguration,根据配置创建数据源,SpringBoot1.0X默认使用Tomcat连接池、SpringBoot2.0X默认使用HikariDataSource数据源。
2、可以使用spring.datasource.type指定自定义的数据源类型;
3、SpringBoot默认可以支持
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource、HikariDataSource、BasicDataSource.
4、自定义数据源类型
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({DataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"spring.datasource.type"}
)
static class Generic {
Generic() {
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
//使用DataSourceBuilder创建数据源,利用反射创建响应type的数据源,并且绑定相关属性
return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
}
}5、DataSourceAutoConfiguration中的DataSourceInitializer(是一个ApplicationListener)
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({DataSource.class, EmbeddedDatabaseType.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({DataSourceProperties.class})
@Import({Registrar.class, DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration.class})
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class);
public DataSourceAutoConfiguration() {
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
//
public DataSourceInitializer dataSourceInitializer(DataSourceProperties properties, ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
return new DataSourceInitializer(properties, applicationContext);
}
}作用:
-
runSchemaScripts();运行建表语句; -
runDataScripts();运行插入数据的sql语句;
默认只需要将文件命名为下面的方式,启动项目就会自动根据SQL文件创建表。(一定要是SpringBoot.10XX)
schema-*.sql、data-*.sql
1、默认规则:schema.sql,schema-all.sql;
2、可以使用下面的方式指定位置
schema:
- classpath:department.sql
# springBoot2.0以上要加上下面才会起作用
initialization-mode: always # 程序启动时会默认执行sql脚本注意如果是SpringBoot2.0X在启动的时候如果要创建数据表,要添加一句:initialization-mode: always #
默认配置的相关源码:
private List<Resource> getScripts(String propertyName, List<String> resources, String fallback) {
if (resources != null) {
return this.getResources(propertyName, resources, true);
} else {
String platform = this.properties.getPlatform();
List<String> fallbackResources = new ArrayList();
// fallback 就是 "schema"
fallbackResources.add("classpath*:" + fallback + "-" + platform + ".sql");
fallbackResources.add("classpath*:" + fallback + ".sql");
return this.getResources(propertyName, fallbackResources, false);
}
}6、操作数据库:自动配置了JdbcTemplate操作数据库;
JDBCTemplate简单测试:
编写的Controller:
@Controller
public class QueryDBTestController {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/query")
public Map<String, Object> queryDB(){
List<Map<String,Object>> list = jdbcTemplate.queryForList("select * from student");
return list.get(0);
}
}项目:springboot_06_data_druid
启动报错问题解决博客:
博客: https://blog.csdn.net/xingkongtianma01/article/details/81624313
改变默认的数据源需要配置type属性:
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: root
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 改变默认的数据源
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# Druid的一些默认配置,可以发现下面这些是黄色的,需要在配置类中配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
# 配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,'wall'用于防火墙
filters: stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500Druid的相关配置:
- 一定需要编写一个
Configuration配置类,并且绑定spring.datasources,不然配置不会生效; - 配置Druid的监控功能需要编写Servlet和Filter,指定访问路径以及相关用户名和密码,具体配置如下;
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") // 必须要配置这个,不能单单在配置文件中配置
@Bean
public DataSource druid(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
// 配置Druid的监控
// 1、配置一个管理后台的Servlet
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("loginUsername", "admin");
initParams.put("loginPassword", "root");
initParams.put("allow", "");// 默认就是允许所有访问
initParams.put("deny", "192.168.43.100");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
return bean;
}
// 2、配置web监控的filter
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("exclusions", "*.js,*.css,/druid/*");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));
return bean;
}
}效果:
pom.xml导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>mybatis-starter的依赖图:
步骤:
1)、配置数据源相关属性;(见上一节Druid)
2)、给数据库建表;
3)、创建JavaBean;
项目: springboot_06_data_mybatis
只需要编写Mapper即可。
// 指定这是一个操作数据库的mapper
@Mapper
public interface DepartmentMapper {
@Select("select * from department where id=#{id}")
public Department getDeptById(Integer id);
@Delete("delete from department where id=#{id}")
public int deleteDeptById(Integer id);
//因为id是自增的
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = "id")
@Insert("insert into department(departmentName) values(#{departmentName})")
public int insertDept(Department department);
@Update("update department set departmentName=#{departmentName} where id=#{id}")
public int updateDept(Department department);
}Controller:
@RestController // 包括了
public class DeptController {
@Autowired
DepartmentMapper departmentMapper;
@GetMapping("/dept/{id}")
public Department getDepartMent(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return departmentMapper.getDeptById(id);
}
@GetMapping("/dept")
public Department insertDept(Department department){
departmentMapper.insertDept(department);
return department;
}
}测试:
自定义的规则:在Configuration中编写ConfigurationCustomizer即可(自定义Mybatis的配置规则)。
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public ConfigurationCustomizer configurationCustomizer() {
return new ConfigurationCustomizer() {
@Override
public void customize(org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration configuration) {
// 开启驼峰命名 department_name和departName映射
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true);
}
};
}
}可以将@MapperScan标注在主配置类中,这样就不需要在所有的Mapper接口上都标注@Mapper注解了。
@MapperScan(value = "com.zxin.springboot.mapper") //这个包下都是Mapper,不需要标注Mapper注解EmployeeMapper.xml配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.zxin.springboot.mapper.EmployeeMapper">
<!--public Employee getEmpById(Integer id);-->
<!--public void insertEmp(Employee employee);-->
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.zxin.springboot.bean.Employee">
SELECT * FROM employee WHERE id=#{id}
</select>
<insert id="insertEmp">
INSERT INTO employee(lastName, email, gender, d_id) VALUES (#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{dId})
</insert>
</mapper>mybatis-config主配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
</configuration>application.yml配置:
mybatis:
config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml # 指定全局配置文件位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml # 指定SQL映射文件的位置
type-aliases-package: com.zxin.springboot.beans编写Controller测试:
@RestController
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@GetMapping("/emp/{id}")
public Employee getEmp(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
return employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
}
}测试结果:
JPA:ORM(Object Relational Mapping), 操作步骤如下:
1)、编写一个实体类(bean)和数据表进行映射,并且配置好映射关系;
这里的表不需要自己手动创建,JPA会自动创建。
//使用JPA注解配置映射关系
@Entity //告诉JPA这是一个实体类(和数据表映射的类)
@Table(name = "tbl_user") //@Table来指定和哪个数据表对应;如果省略默认表名就是user;
public class User {
@Id //这是一个主键
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)//自增主键
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "last_name",length = 50) //这是和数据表对应的一个列
private String lastName;
@Column //省略默认列名就是属性名
private String email;
}2)、编写一个Dao接口来操作实体类对应的数据表(Repository)(有一些自动的方法,所以这里啥也不需要写)
//继承JpaRepository来完成对数据库的操作, 第一个参数是要操作的实体,第二个参数是实体的主键的类型
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> {
}3)、基本的配置JpaProperties
jpa:
hibernate:
# 更新或者创建数据表结构(第一次是创建,后面是更新)
ddl-auto: update
# 控制台显示SQL
show-sql: true
测试代码:
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
// User user = userRepository.getOne(id); // 不是findOne()(SpringBoot1.0的)
User user = userRepository.findAll().get(0); // 不是findOne()(SpringBoot1.0的)
return user;
}
@GetMapping("/user")
public User insertUser(User user){
User save = userRepository.save(user);
return save;
}
}测试结果: