-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 56
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
82 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,82 @@ | ||
|
|
||
| >- 原文链接:[medium.com/@nufailismat...](https://medium.com/@nufailismath15/time-complexity-in-solidity-61460958cda6) | ||
| >- 译者:[AI翻译官](https://learnblockchain.cn/people/19584),校对:[翻译小组](https://learnblockchain.cn/people/412) | ||
| >- 本文链接:[learnblockchain.cn/article…](https://learnblockchain.cn/article/10509) | ||
| # Solidity 中的时间复杂度 | ||
|
|
||
| 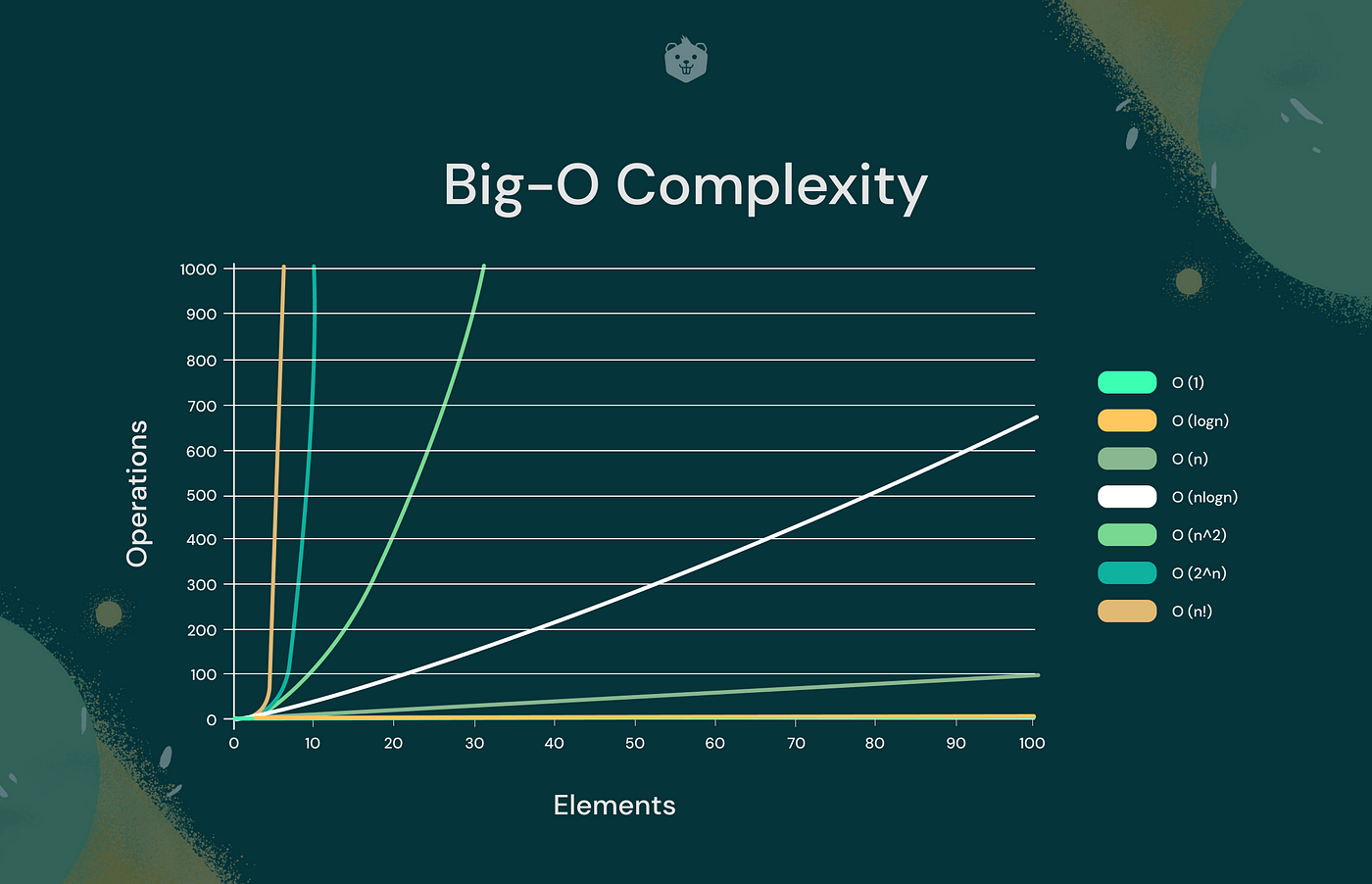 | ||
|
|
||
| [https://www.crio.do/blog/content/images/2022/02/BIG-O-COMPLEXITY.png](https://www.crio.do/blog/content/images/2022/02/BIG-O-COMPLEXITY.png) | ||
|
|
||
| # 什么是时间复杂度?它在智能合约开发中为什么重要? | ||
|
|
||
| ## 时间复杂度是什么? | ||
|
|
||
| 时间复杂度是运行算法所需的计算时间,取决于输入。它概述了相对于输入大小增长的过程数量。这些时间复杂度使用**大 O 符号(O)**表示: | ||
|
|
||
| * O(1):常数时间 | ||
| * O(n):线性时间 | ||
| * O(n²):平方时间 | ||
| * O(log n):对数时间 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 为什么? | ||
|
|
||
| 在智能合约开发中,总是需要编写节省 gas 的代码。要理解每个函数的 gas 是如何工作的,你需要对每个**OPCODES**的 gas 使用有一些基本了解。你可以参考 [evm.codes](https://www.evm.codes/)。在开发智能合约时,考虑时间复杂度的两个最重要的优点是: | ||
|
|
||
| * **Gas 效率**:每个更新存储布局的操作都会消耗 gas。高时间消耗的函数可能会消耗更多的 gas。优化时间复杂度将确保函数具有成本效益,并且不会超过 gas 限制。 | ||
| * **可扩展性**:优化时间复杂度使智能合约能够高效处理更大的数据集,确保更好的性能和可靠性。 | ||
|
|
||
| # Solidity 中的时间复杂度示例: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. **高效函数 O(1):** | ||
|
|
||
| 访问映射是一个常数时间操作,使其非常高效。 | ||
|
|
||
| mapping(address => uint256) balances; | ||
|
|
||
| function getBalance(address user) public view returns (uint256) { | ||
| return balances[user]; // O(1) - 常数时间 | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| 2. **低效函数 O(n):** | ||
|
|
||
| 遍历数组的时间复杂度与用户数量线性增长,随着数组的增长效率降低。 | ||
|
|
||
| uint256[] public users; | ||
|
|
||
| function findUser(uint256 id) public view returns (bool) { | ||
| for (uint256 i = 0; i < users.length; i++) { // O(n) - 线性时间 | ||
| if (users[i] == id) { | ||
| return true; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return false; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| 3. **潜在危险函数 O(n²)**: | ||
|
|
||
| 嵌套循环导致平方时间复杂度,这在处理大数组时代价高昂,可能超过 gas 限制。 | ||
|
|
||
| uint256[] public users; | ||
|
|
||
| function compareUsers() public view { | ||
| for (uint256 i = 0; i < users.length; i++) { // 外层循环 | ||
| for (uint256 j = 0; j < users.length; j++) { // 内层循环 | ||
| if (users[i] == users[j]) { | ||
| // 做一些事情 | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| # Solidity 中时间复杂度类别的总结: | ||
|
|
||
| * **O(1)**:常数时间操作(简单赋值、访问存储/内存)。 | ||
| * **O(n)**:线性时间操作(例如,遍历数组或列表)。 | ||
| * **O(n²)**:平方时间操作(嵌套循环)。 | ||
| * **O(log n)**:对数时间操作(例如,二分查找或基于树的结构)。 | ||
|
|
||
| 时间复杂度在智能合约开发中起着至关重要的作用,影响着 gas 效率和可扩展性。这个概述只是一个开始——还有大量的技术和见解可以探索,以优化你的合约并提供高性能的区块链解决方案。无论你是新兴开发者、经验丰富的工程师,还是行业中的决策者,掌握这些概念都能为你在构建创新和高效的去中心化应用程序中提供显著优势。 | ||
|
|
||
| > 我是 [AI 翻译官](https://learnblockchain.cn/people/19584),为大家转译优秀英文文章,如有翻译不通的地方,在[这里](https://github.com/lbc-team/Pioneer/blob/master/translations/10509.md)修改,还请包涵~ |