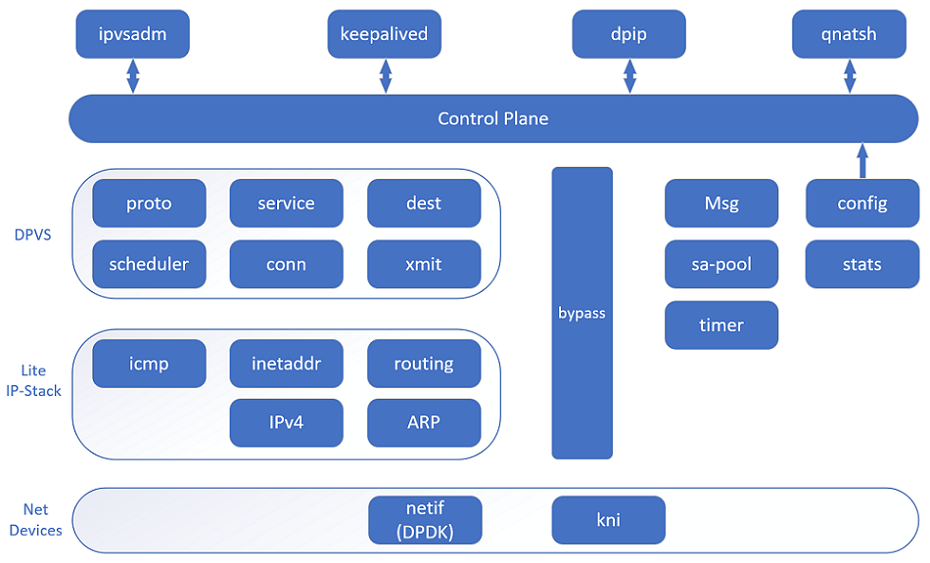
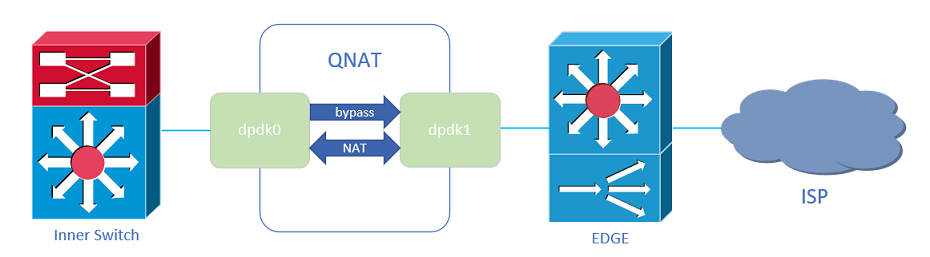
QNAT is a high-performance NAT (Network Address Translation) project base on DPVS and DPDK , mainly used in IDC (data center) or office network outlet. Support NAT44 , traffic bypass, multiple address pool selection, single IP session limit, NAT session logging, etc. We also added acommand-line interface function, allowing you to manage QNAT just like managing network devices.
Linux Kernel version >= 2.6.34 (Need to support UIO and HUGETLBFS)DPDK version = 17.05.2GCC version >= 4.8.5
Linux Distribution: CentOS 7.2Kernel: 3.10.0-327.36.3.el7.x86_64CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2630 v2 @ 2.60GHzNIC: Intel Corporation 82599ES 10-Gigabit SFI/SFP+ Network Connection (rev 01)Memory: 64G with two NUMA nodeGCC: gcc version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-4)DPDK: dpdk-stable-17.05.2
$ yum install -y popt-devel.x86_64
$ yum install -y openssl-devel.x86_64$ wget https://fast.dpdk.org/rel/dpdk-17.05.2.tar.xz
$ tar vxf dpdk-17.05.2.tar.xz$ cd {path-of-dpdk}
$ make config T=x86_64-native-linuxapp-gcc
$ make -j12
$ echo export RTE_SDK=$PWD >> ~/.bashrc
$ source ~/.bashrc$ echo 12288 > /sys/devices/system/node/node0/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages
$ echo 12288 > /sys/devices/system/node/node1/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages
$ mkdir /mnt/huge
$ mount -t hugetlbfs nodev /mnt/huge$ modprobe uio
$ insmod {path-of-dpdk}/build/kmod/igb_uio.ko
$ insmod {path-of-dpdk}/build/kmod/rte_kni.ko
$ {path-of-dpdk}/usertools/dpdk-devbind.py -s
#get the UIO numbers of the network cards that need to be bound to the dpdk
#assume that the UIO numbers of eth0 is 0000:84:00.0, the UIO numbers of eth2 is 0000:84:00.1
$ ifconfig eth0 down ; ifconfig eth1 down
$ {path-of-dpdk}/usertools/dpdk-devbind.py -b igb_uio 0000:84:00.0
$ {path-of-dpdk}/usertools/dpdk-devbind.py -b igb_uio 0000:84:00.1$ git clone https://github.com/Qihoo360/qnat.git$ cd QNAT
$ make -j12
$ make installConfiguration example(Assume that the IP of the server's eth0 is 10.10.10.3/27, the IP of the server's eth1 is 110.110.110.2/28; eth0 is configured as dpdk0, eth1 is configured as dpdk1)
$ qnatsh #Start the command line tool of QNAT
______ ______ ______ ______ _______ ______
/ \ / \ / \ / \ | \ / \
| ######\| ######\| ######\ | ######\| #######\| ######\
\##__| ##| ##___\##| ###\| ## | ## | ##| ##__/ ##| ##___\##
| ##| ## \ | ####\ ## | ## | ##| ## ## \## \
__\#####\| #######\| ##\##\## | ## | ##| ####### _\######\
| \__| ##| ##__/ ##| ##_\#### | ##__/ ##| ## | \__| ##
\## ## \## ## \## \### \## ##| ## \## ##
\###### \###### \###### \###### \## \######
nathost# ip nat start #start QNAT service
nathost# configure terminal #enter the config node
nathost(config)# hostname nattest #mdify username
nattest(config)#local ip 10.10.10.2/27 #add ip for intranet
nattest(config)#ip addr 10.10.10.3/27 dev dpdk0.kni #add ip for dpdk0.kni
nattest(config)#ip addr 110.110.110.2/28 dev dpdk1.kni #add ip for dpdk1.kni
nattest(config)#ip route 10.10.10.3/32 dev inside kni_host #add route to kni device
nattest(config)#ip route 110.110.110.2/32 dev outside kni_host #add route to kni device
nattest(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0/8 via 10.10.10.1 dev inside #add route for back to intranet
nattest(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0/0 via 110.110.110.1 dev outside #add defaut route
nattest(config)# ip nat pool default #create a nat address pool named default
nattest(config-nat-pool)# member ip 110.110.110.5/28 #add ip member to the nat address pool
nattest(config-nat-pool)# exit
nattest(config)# ip nat source 10.0.0.0 10.255.255.255 #create a nat rule
nattest(config-nat-service)# dest pool default
nattest(config-nat-service)# end
nattest# write file #save configurationConfiguration example(Assume that the IP of the server's eth0 is 10.10.10.3/27, the IP of the server's eth1 is 110.110.110.2/28; eth0 is configured as dpdk0, eth1 is configured as dpdk1)
$ cat /etc/qnatcft.conf
local ip 10.10.10.2/27
ip addr 10.10.10.3/27 dev dpdk0.kni
ip addr 110.110.110.2/28 dev dpdk1.kni
ip route 10.10.10.3/32 dev inside kni_host
ip route 110.110.110.2/32 dev outside kni_host
ip route 10.0.0.0/8 via 10.10.10.1 dev inside
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 via 110.110.110.1 dev outside
hostname nattest
ip nat pool default
member ip 110.110.110.5/28
exit
ip nat source 10.0.0.0 10.255.255.255
dest pool default
exit
$ qnatsh #Start the command line tool of QNAT
______ ______ ______ ______ _______ ______
/ \ / \ / \ / \ | \ / \
| ######\| ######\| ######\ | ######\| #######\| ######\
\##__| ##| ##___\##| ###\| ## | ## | ##| ##__/ ##| ##___\##
| ##| ## \ | ####\ ## | ## | ##| ## ## \## \
__\#####\| #######\| ##\##\## | ## | ##| ####### _\######\
| \__| ##| ##__/ ##| ##_\#### | ##__/ ##| ## | \__| ##
\## ## \## ## \## \### \## ##| ## \## ##
\###### \###### \###### \###### \## \######
nathost# ip nat start #start QNAT service
nathost# load config #load saved configuration
nattest# write file #save configurationQNATSH uses node level control to execute executable configuration commands, the node level includes enable node, config node, pool node, and service node.
qnatsh (start without parameters)do not start the QNAT service, nor load saved configuration, enter enable node.
qnatsh -b (start with parameters '-b')start the QNAT service and load saved configuration, enter enable node.
ip nat start start QNAT service without loading the configuration
ip nat stop stop QNAT service
load config load saved configuration
| Command Line | Own node | Features |
|---|---|---|
end |
all nodes | return enable node |
exit |
all nodes | exit from current mode |
write file |
all nodes | save current configuration |
list |
all nodes | show current node executable commands |
config terminal |
enable node | enter config node |
show ip nat pool |
enable node | show all nat address pool configurations |
show link stats |
enable node | show nat link statistics |
show local-ip |
enable node | show local ip address |
show nat |
enable node | show nat service configuration information |
show ospf interface |
enable node | show information of the interface that can run ospf |
show route |
enable node | show qnat routing table |
show running-config |
enable node | show the currently running configuration |
show startup-config |
enable node | show the saved configuration |
hostname WORD |
config node | configure hostname |
ip addr A.B.C.D/M dev (dpdk0.kni|dpdk1.kni) |
config node | configure the IP address of the kni interface |
ip nat pool NAME |
config node | configure nat address pool and enter pool node |
ip nat source A.B.C.D A.B.C.D |
config node | configure nat service and enter service node |
ip route A.B.C.D/M dev (inside|outside) [kni_host] |
config node | configure route for kni device |
ip route A.B.C.D/M via A.B.C.D dev (inside|outside) |
config node | configure route for qnat service |
local ip A.B.C.D/M |
config node | configure local ip (intranet ip) |
no hostname |
config node | cancel hostname setting |
no ip addr A.B.C.D/M dev (dpdk0.kni|dpdk1.kni) |
config node | cancel kni interface IP address setting |
no ip nat pool NAME |
config node | cancel nat address pool setting and enter pool node |
no ip nat source A.B.C.D A.B.C.D |
config node | cancel mat service setting and enter service node |
no ip route A.B.C.D/M dev (inside|outside) [kni_host] |
config node | cancel kni device route setting |
no ip route A.B.C.D/M via A.B.C.D dev (inside|outside) |
config node | cancel qnat service route setting |
no local ip A.B.C.D/M |
config node | cancel local ip (intranet ip) setting |
member ip A.B.C.D/M |
pool node | configure nat address pool single IP member |
member range A.B.C.D A.B.C.D masklen <0-32> |
pool node | configure nat addrdss pool continuous IP address member |
no member ip A.B.C.D/M |
pool node | cancel nat address pool single IP member setting |
no member range A.B.C.D A.B.C.D |
pool node | cancel nat addrdss pool continuous IP address member |
dest A.B.C.D/M |
service node | configure the translation address of the NAT service |
dest pool NAME |
service node | configure the translation pool of the NAT service |
no dest A.B.C.D/M |
service node | cancel the NAT service translation address setting |
no dest pool NAME |
service node | cancel the NAT pool translation address setting |
-
Need to use static/dynamic (default) routing or PBR (Policy Based Routing) to direct NAT traffic to the intranet NIC of the QNAT server.
$ cat /etc/qnat/qnat_blk.conf
255.255.255.255=10000
$ tail -f /var/log/qnat_blk.log$ tail -f /var/log/qnat.log$ echo 8192 > /sys/devices/system/node/node0/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages
$ echo 8192 > /sys/devices/system/node/node1/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages
$ modprobe uio
$ insmod {path-of-dpdk}/build/kmod/igb_uio.ko
$ insmod {path-of-dpdk}/build/kmod/rte_kni.ko
$ ifdown eth0; ifdown eth1
$ {path-of-dpdk}/usertools/dpdk-devbind.py -b igb_uio 0000:84:00.0
$ {path-of-dpdk}/usertools/dpdk-devbind.py -b igb_uio 0000:84:00.1Main code of QNAT is GNU General Public License, version 2 (GPLv2) licensed.
DPVS is a high performance Layer-4 load balancer based on DPDK. It's derived from Linux Virtual Server LVS and its modification alibaba/LVS.
Keepalived is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
Linux Virtual Server kernel patches and related programs, released under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
Main code of DPDK is BSD licensed and Linux kernel related parts are naturally licensed under the GPL.
Linux Virtual Server kernel patches and related programs, released under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
Linux Kernel is available under GPL, see this document for details.
Alibaba/LVS is based on LVS kernel components and related programs.
Quagga Routing Software Suite, GPL licensed.
Consistent hashing library is BSD licensed.
- QQ Group: 914897475