PyTorch implementation of Gaussian YOLOv3
The benchmark results below have been obtained by training models for 500k iterations on the COCO 2017 train dataset using darknet repo and our repo.
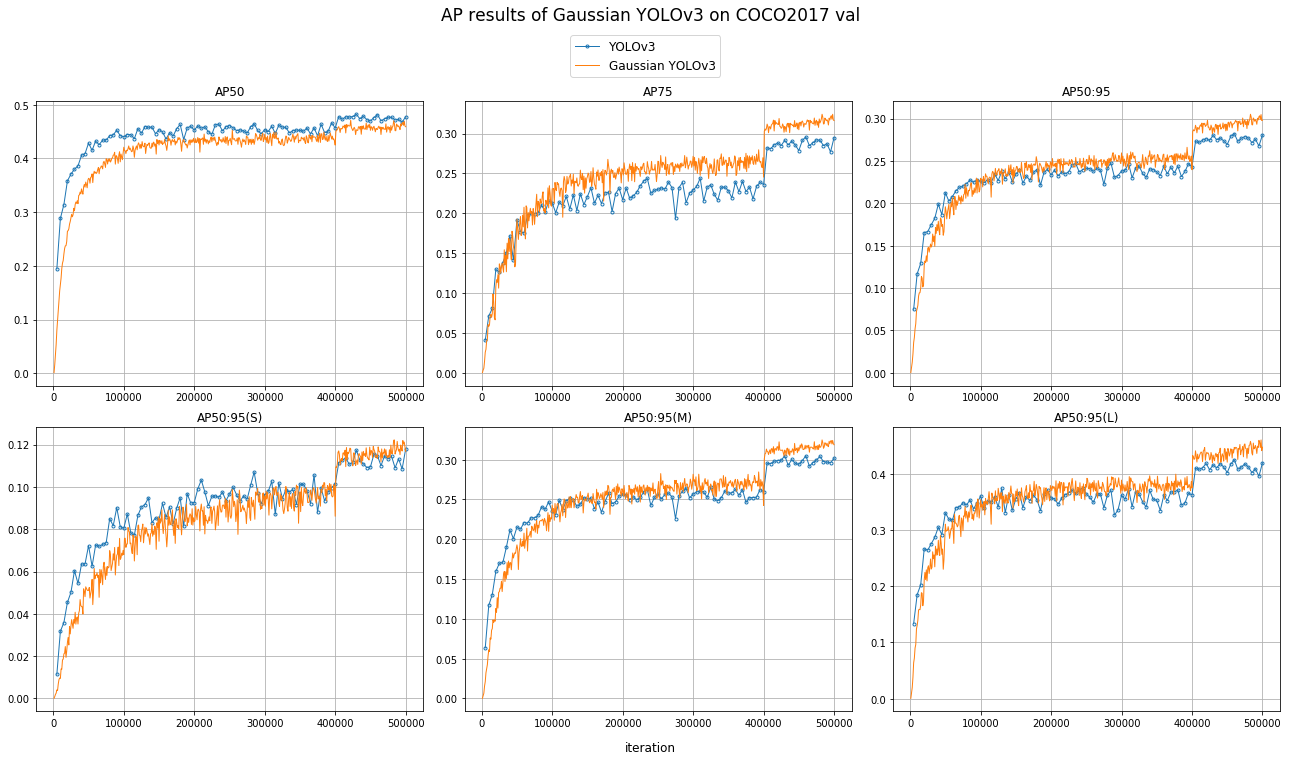
Gaussian YOLOv3 implemented in our repo achieved 30.4% in COCO AP[IoU=0.50:0.95], which is 2.6 ~ 2.7 point higher than the score of YOLOv3 implemented in darknet and our repo.
This gain is smaller than 3.1, the one reported in the Gaussian YOLOv3 paper. This may come from:
- absence of
sigma_constparameter: Gaussian YOLOv3 official repo uses a hyper parametersigma_constas an offset for predicted uncertainties but we do not use it - use of gradient clipping: we use gradient clipping technique to avoid divergence during training
- difference of hyper parameters: official repo does not contain hyper parameters for training with COCO dataset
| YOLOv3 (darknet repo) | YOLOv3 (our repo) | Gaussian YOLOv3 (our repo) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COCO AP [IoU=0.50:0.95] | 0.278 | 0.277 | 0.304 |
| COCO AP [IoU=0.50] | 0.476 | 0.478 | 0.467 |
Training configurations used in our repo can be found under config dir.
- Python 3.6.3+
- Numpy (verified as operable: 1.15.2)
- OpenCV
- Matplotlib
- Pytorch 1.0.0+ (verified as operable: v0.4.0, v1.0.0)
- Cython (verified as operable: v0.29.1)
- pycocotools (verified as operable: v2.0.0)
- seaborn (verified as operable: v0.9.0)
- Cuda (verified as operable: v9.0)
optional:
- tensorboard (>1.7.0)
- tensorboardX
- CuDNN (verified as operable: v7.0)
we provide a Dockerfile to build an environment that meets the above requirements.
# build docker image
$ nvidia-docker build -t yolov3-in-pytorch-image --build-arg UID=`id -u` -f docker/Dockerfile .
# create docker container and login bash
$ nvidia-docker run -it -v `pwd`:/work --name yolov3-in-pytorch-container yolov3-in-pytorch-image
docker@4d69df209f4a:/work$ python train.py --helpdownload Gaussian YOLOv3 pretrained weight from our GoogleDrive.
see demo.ipynb.
Make sure you specify the path to the pretrained weight correctly in the notebook.
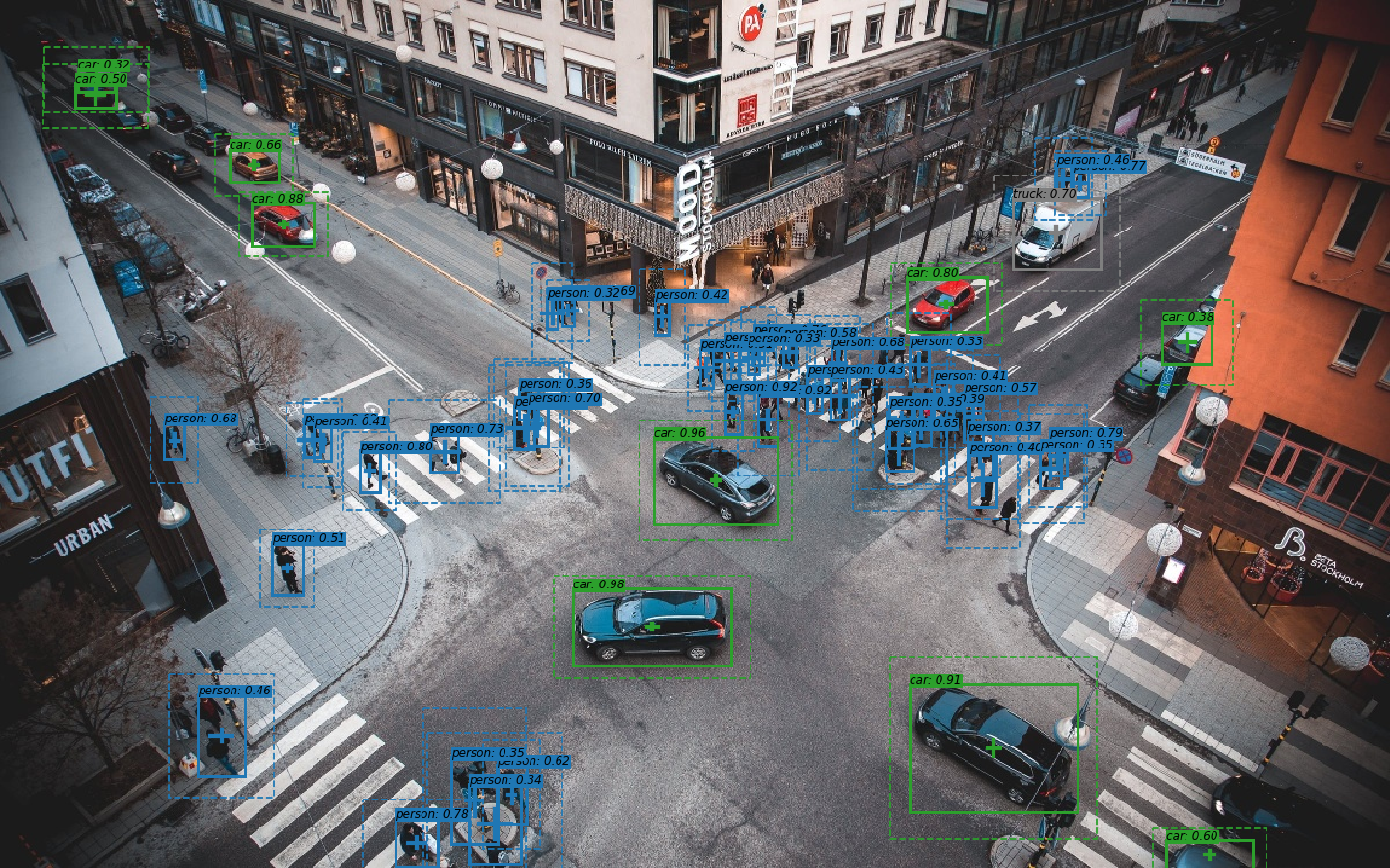
In this notebook, predicted uncertainties of box size are represented by dashed lines around the boxes, and uncertainties of box center coordinates are visualized by crossed lines inside the boxes:
The more occlusions are added, predicted uncertainties get higher as you can see below:
In examples above, 2-sigma confidence intervals are visualized.
COCO dataset is downloaded and unzipped by:
$ bash requirements/getcoco.shdownload Darknet53 pretrained weights from the author's project page:
$ mkdir weights
$ cd weights/
$ bash ../requirements/download_weights.sh$ python train.py --help
usage: train.py [-h] [--cfg CFG] [--weights_path WEIGHTS_PATH] [--n_cpu N_CPU]
[--checkpoint_interval CHECKPOINT_INTERVAL]
[--eval_interval EVAL_INTERVAL] [--checkpoint CHECKPOINT]
[--checkpoint_dir CHECKPOINT_DIR] [--use_cuda USE_CUDA]
[--debug] [--tfboard TFBOARD]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--cfg CFG config file. see readme
--weights_path WEIGHTS_PATH
darknet weights file
--n_cpu N_CPU number of workers
--checkpoint_interval CHECKPOINT_INTERVAL
interval between saving checkpoints
--eval_interval EVAL_INTERVAL
interval between evaluations
--checkpoint CHECKPOINT
pytorch checkpoint file path
--checkpoint_dir CHECKPOINT_DIR
directory where checkpoint files are saved
--use_cuda USE_CUDA
--debug debug mode where only one image is trained
--tfboard TFBOARD tensorboard path for loggingexample:
$ python train.py --cfg config/gaussian_yolov3_default.cfg --weights_path weights/darknet53.conv.74 --tfboard logThe train configuration is written in yaml files located in config folder. We use the following format:
MODEL:
TYPE: YOLOv3
BACKBONE: darknet53
ANCHORS: [[10, 13], [16, 30], [33, 23],
[30, 61], [62, 45], [59, 119],
[116, 90], [156, 198], [373, 326]]
ANCH_MASK: [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
N_CLASSES: 80
GAUSSIAN: True
TRAIN:
LR: 0.001
MOMENTUM: 0.9
DECAY: 0.0005
BURN_IN: 1000
MAXITER: 500000
STEPS: (400000, 450000)
BATCHSIZE: 4
SUBDIVISION: 16
IMGSIZE: 608
LOSSTYPE: l2
IGNORETHRE: 0.7
GRADIENT_CLIP: 2000.0
AUGMENTATION:
RANDRESIZE: True
JITTER: 0.3
RANDOM_PLACING: True
HUE: 0.1
SATURATION: 1.5
EXPOSURE: 1.5
LRFLIP: True
RANDOM_DISTORT: True
TEST:
CONFTHRE: 0.8
NMSTHRE: 0.45
IMGSIZE: 416
NUM_GPUS: 1$ python train.py --cfg config/gaussian_yolov3_eval.cfg --eval_interval 1 [--checkpoint ckpt_path] [--weights_path weights_path]Gaussian YOLOv3: An Accurate and Fast Object Detector Using Localization Uncertainty for Autonomous Driving
Jiwoong Choi, Dayoung Chun, Hyun Kim, Hyuk-Jae Lee
[Paper] [Author's Implementation]
@InProceedings{Choi_2019_ICCV,
author = {Choi, Jiwoong and Chun, Dayoung and Kim, Hyun and Lee, Hyuk-Jae},
title = {Gaussian YOLOv3: An Accurate and Fast Object Detector Using Localization Uncertainty for Autonomous Driving},
booktitle = {The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
month = {October},
year = {2019}
}