- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Documentation
- Getting Started
- Comparison with Related Libraries
- References
- Citing TSAD
TSAD is a powerful Python module designed to simplify the work of researchers utilizing machine learning techniques, specifically tailored for addressing key challenges in industrial domains.
The primary objective of TSAD is to empower researchers with effective tools for solving complex problems related to:
-
Fault Detection in Industrial Equipment:
- Identify and address faults in industrial machinery with precision, ensuring optimal equipment performance and reliability.
-
Improvement of Technological Processes:
- Boost overall performance to enhance operational efficiency.
- Implement cost-effective measures to reduce operational expenses.
- Strengthen quality control and management practices for superior outcomes.
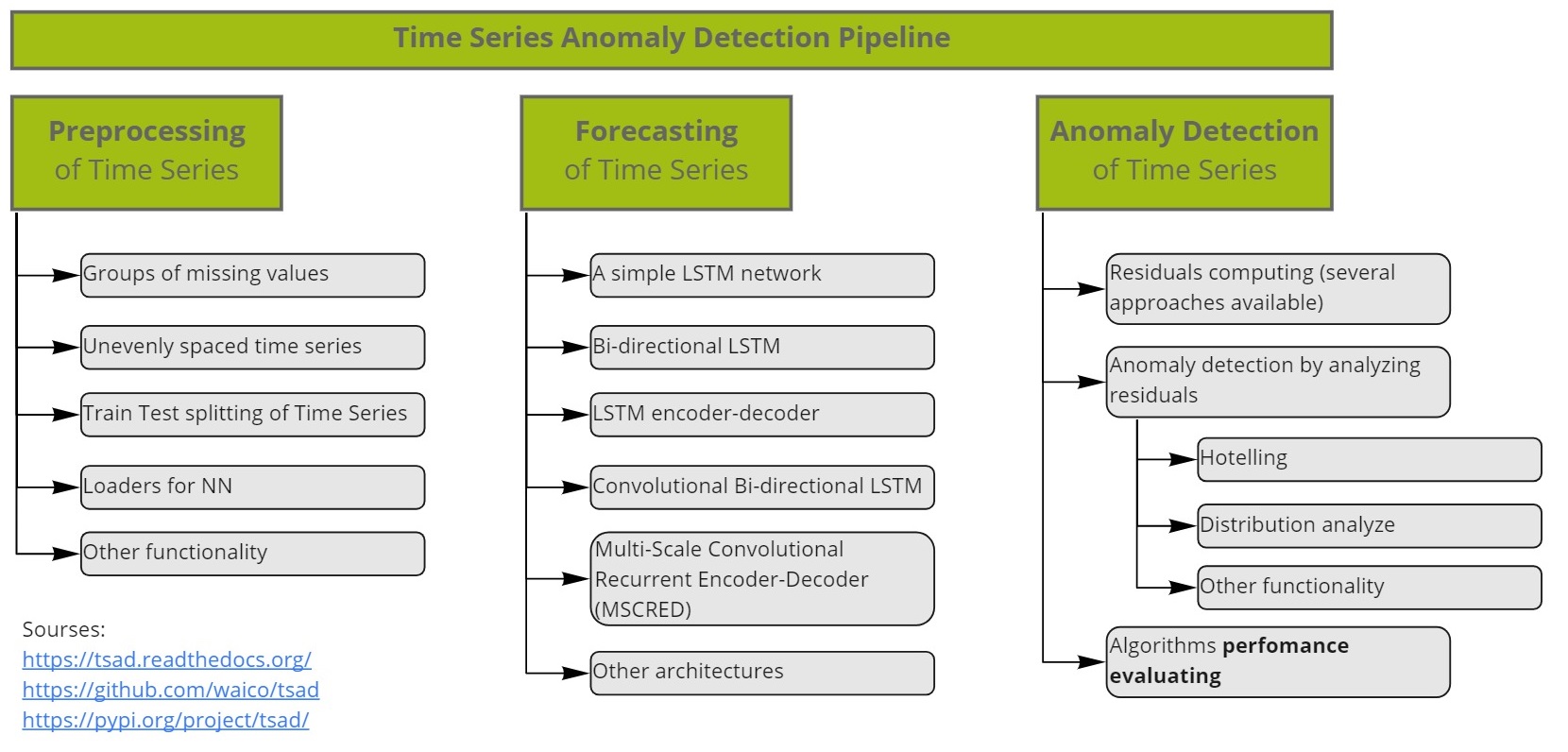
In TSAD, the problem of fault detection is reduced to the problem of detecting time series anomalies using a well-known technique:
- Forecast a multivariate Time Series (TS) one point ahead (Also works for univariate TS)
- Compute residuals between forecast and true values
- Apply analysis of residuals and thus find anomalies
-
Predictive and Prescriptive Analysis:
- Predict the development of situations based on data analysis.
- Automate decision-making for equipment diagnostics and repairs.
-
Predictive Equipment Maintenance:
- Utilize mathematical modeling methods, including machine learning.
- Reduce equipment breakdown frequency and associated damages.
- Decrease costs for diagnostics and maintenance of machinery and industrial equipment.
- Create artificial intelligence systems for predictive maintenance.
-
Ultra-Short-Term Forecasting:
- Analyze real-time data streams.
- Forecast abnormal situations.
- Implement artificial intelligence systems for real-time monitoring.
-
Detection of Anomalies in Production Processes:
- Identify anomalies in manufacturing processes.
- Investigate the root causes of anomalies.
- Develop artificial intelligence systems based on mathematical modeling algorithms, machine learning, and historical data.
-
Wide-Scope Time Series Forecasting:
- Forecast time series broadly, beyond technical system diagnostics.
-
Anomaly Detection in a Broad Context:
- Detect anomalies in various contexts, not limited to technical system diagnostics.
-
Sensor Failure Detection:
- Detect malfunctioning sensors.
-
Creation of Virtual Sensors:
- Develop virtual sensors.
-
Quality Production Forecasting:
- Forecast the quality of production.
These applied use cases showcase the versatility of TSAD in addressing a wide range of scenarios within industrial data analysis. Whether it's predicting equipment failures, monitoring real-time data streams, or forecasting production quality, TSAD provides powerful solutions for enhancing decision-making and optimizing operational processes.
Explore the powerful features offered by TSAD for comprehensive testing, evaluation, and data analysis refinement:
- Evaluate TSAD with your own dataset.
- Test custom anomaly detection and forecasting algorithms.
- Analyze distributions, missing data, and patterns.
- Identify and resolve data problems with measurable metrics.
- Utilize machine learning for anomaly detection and forecasting tasks.
- Assess the quality of anomaly detection algorithms.
The TSAD Documentation covers a wide range of topics, including:
-
Getting Started:
- A step-by-step guide on installing TSAD and setting up your environment.
- Quick start examples to get you up and running with minimal effort.
-
Library Overview:
- In-depth explanations of the core components and concepts within the TSAD library.
- Understanding the structure and design philosophy for effective utilization.
-
Usage Guides and Tutorials:
- Detailed guides on utilizing specific functionalities of the library.
- Practical examples and use cases to demonstrate real-world applications.
-
API Reference:
- Comprehensive documentation of the TSAD API.
- Detailed descriptions of classes, methods, and parameters for advanced users.
This section will guide you through the process of getting started with the TSAD library.
Ensure that your system meets the following hardware specifications for optimal performance of TSAD:
- Minimum Number of Processors (Intel): 2
- Minimum Processor Frequency (GHz): 2.0
- Minimum RAM Size (GB): 4.0
- Minimum Video Memory Size (for an external video adapter) (MB): 512
- RAID Configuration Type and Minimum HDD Space (GB): RAID 5; 500
These requirements are intended to provide a guideline for the minimum hardware specifications that should be available on the system where TSAD is deployed. Adjustments may be needed based on the size and complexity of the time series data being processed.
Keep in mind that these specifications are recommended for optimal performance, and deviations may impact the efficiency of the library.
Install the latest stable version of tsad using pip for Python 3.10:
pip install -U tsadAlternatively, you can install the latest development version directly from the GitHub repository:
pip install git+https://github.com/waico/tsad.gitTo quickly see TSAD in action, consider using a simple example in your Python script. Below is a basic example:
# Import necessary modules
import sys
sys.path.insert(1, '../')
from tsad.base.pipeline import Pipeline
from tsad.base.datasets import load_skab
from tsad.pipelines import ResidualAnomalyDetectionTaskSet
# Loading data
dataset = load_skab()
targets = dataset.target_names
data = dataset.frame.drop(columns=targets).droplevel(level=0)
# Create a pipeline and fit/predict
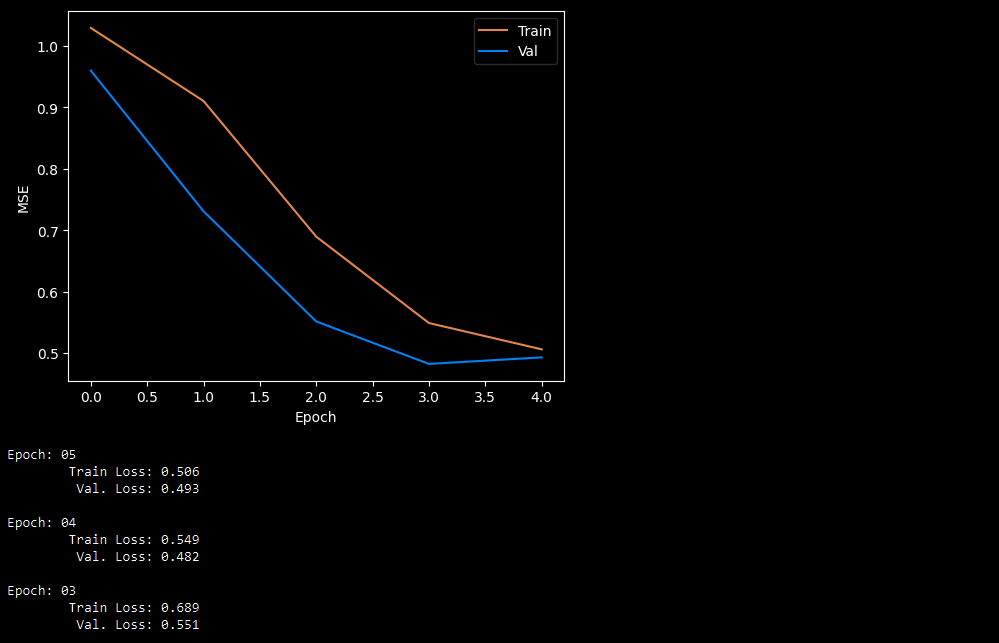
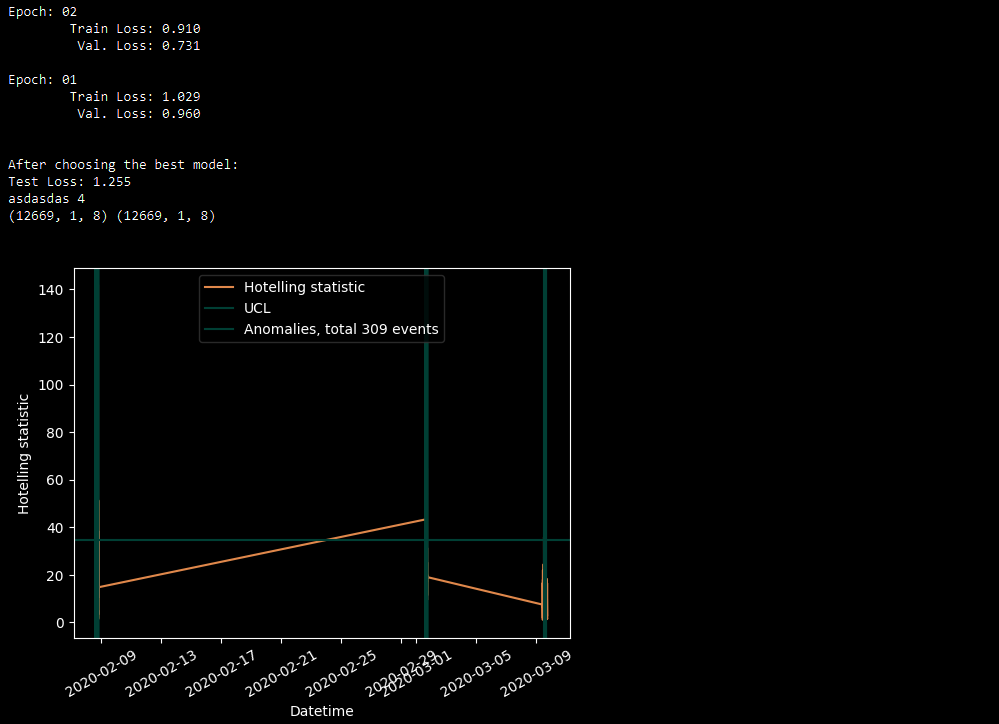
pipeline = Pipeline(ResidualAnomalyDetectionTaskSet)
pred = pipeline.fit_predict(data,n_epochs=5)After that, you can see:
Visit the Tutorials section in the TSAD GitHub repository for hands-on examples and practical insights.
We welcome active participation from the community and value your feedback on the desired functionalities of TSAD. Our ongoing development plans include:
-
Advanced Time Series Preprocessing:
- Exploring more sophisticated preprocessing techniques, particularly addressing challenges related to the reduction of time series to a single sampling rate, especially in cases of unevenly spaced time series.
-
Incorporation of State-of-the-Art (SOTA) Algorithms:
- Continuous efforts to integrate additional state-of-the-art algorithms into TSAD, ensuring that the library remains at the forefront of time series analysis.
-
Flexible Model Implementation:
- Introducing a feature that allows users to seamlessly implement and integrate their models into our pipeline by providing a straightforward link to their GitHub repositories. This feature aims to facilitate collaboration among researchers who often seek to validate and compare their models with others.
-
Benchmark Integration:
- Working towards the integration of TSAD with various forecasting and anomaly detection benchmarks. This integration will enable users to assess the performance of TSAD against established standards, fostering transparency and reliability in time series analysis.
Your input and collaboration are vital in shaping the future development of TSAD. We encourage you to share your thoughts, suggestions, and contributions to enhance the functionality and versatility of the library. Together, we can continue to advance time series analysis within the TSAD community.
Explore how TSAD compares with other libraries in various aspects:
| Merlion | Alibi Detect | Kats | pyod | GluonTS | RRCF | STUMPY | Greykite | Prophet | pmdarima | deepad | TSAD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forecasting (Прогнозирование) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||||
| Anomaly Detection (Поиск аномалий) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| Metrics (Алгоритмы оценки) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |||||||
| Ensembles (Ансамбли) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||||||||
| Benchmarking (Бенчмарки и датасеты) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||||||||
| Visualization (Визуализация результатов) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||||||
| Data preprocessing (Предварительная обработка данных) | ✅ | ✅ | ||||||||||
| Automated EDA (Автоматизированный разведочный анализ данных) | ✅ |
Explore related libraries and resources:
- https://github.com/salesforce/Merlion
- https://github.com/fastforwardlabs/deepad
- https://github.com/HendrikStrobelt/LSTMVis
- https://github.com/TezRomacH/python-package-template
- https://github.com/khundman/telemanom
- https://github.com/signals-dev/Orion
- https://github.com/NetManAIOps/OmniAnomaly
- https://github.com/unit8co/darts
- https://github.com/tinkoff-ai/etna-ts
- https://github.com/yzhao062/pyod
- https://www.radiativetransfer.org/misc/typhon/doc/modules.html#datasets
- https://github.com/AutoViML/Auto_TS
- https://nuancesprog.ru/p/15161/
- https://www.sktime.org/en/stable/
- https://github.com/zalandoresearch/pytorch-ts
- https://github.com/qdata/spacetimeformer
- https://joaquinamatrodrigo.github.io/skforecast/0.6.0/index.html
If you're using TSAD in your research or applications, please cite using this BibTeX:
@misc{TSAD2013,
author = {Viacheslav Kozitsin and Oleg Berezin and Iurii Katser and Ivan Maksimov},
title = {Time Series Analysis for Simulation of Technological Processes - TSAD},
year = {2023},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/waico/tsad}},
}