Hi there!
This is a self optimized personal study notes for AWS Certificated Cloud Practitioner training whitepaper summarized by Matthew WANG.
The contents are mostly noted down from the source pages as below. Should you have any enquires, please get in touch with me at matthewwang dot my at gmail dot com.
Online course
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3hLmDS179YE&t=26s
Official Whitepaper
https://d0.awsstatic.com/whitepapers/aws-overview.pdf
Other website:
https://digitalcloud.training/certification-training/aws-certified-cloud-practitioner/
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of computing power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources through a cloud services platform via the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing.
On premise (私有部署):
- Users own the servers
- Users hire the IT people
- Users pay or rent the real estate
- Users take all the risk
With Cloud Provider:
- Users are only responsible for configuring the cloud services and code.
- Trade capital expense for variable expense. No upfront cost
- Benefit from massive economies of scale.
- Stop guessing capacity.
- Increase speed and agility.
- Stop spending money running and maintaining data centers.
- Go global in minutes.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), For Admins
- Platform as a Service (PaaS), For developer
- Software as a Servcie (SaaS), For users
- Cloud A cloud-based application is fully deployed in the cloud and all parts of the application run in the cloud. Fully utilize cloud computing. For Start-Ups, offering SaaS
- Hybrid A hybrid deployment is a way to connect infrastructure and applications between cloud-based resources and existing resources that are not located in the cloud. Banks, Fintechs
- On-premises: The deployment of resources on-premises, using virtualization and resource management tools, is sometimes called the “private cloud.” Public sectors, like Gov Sensitive Data, like hospital A large enterprise with regulations
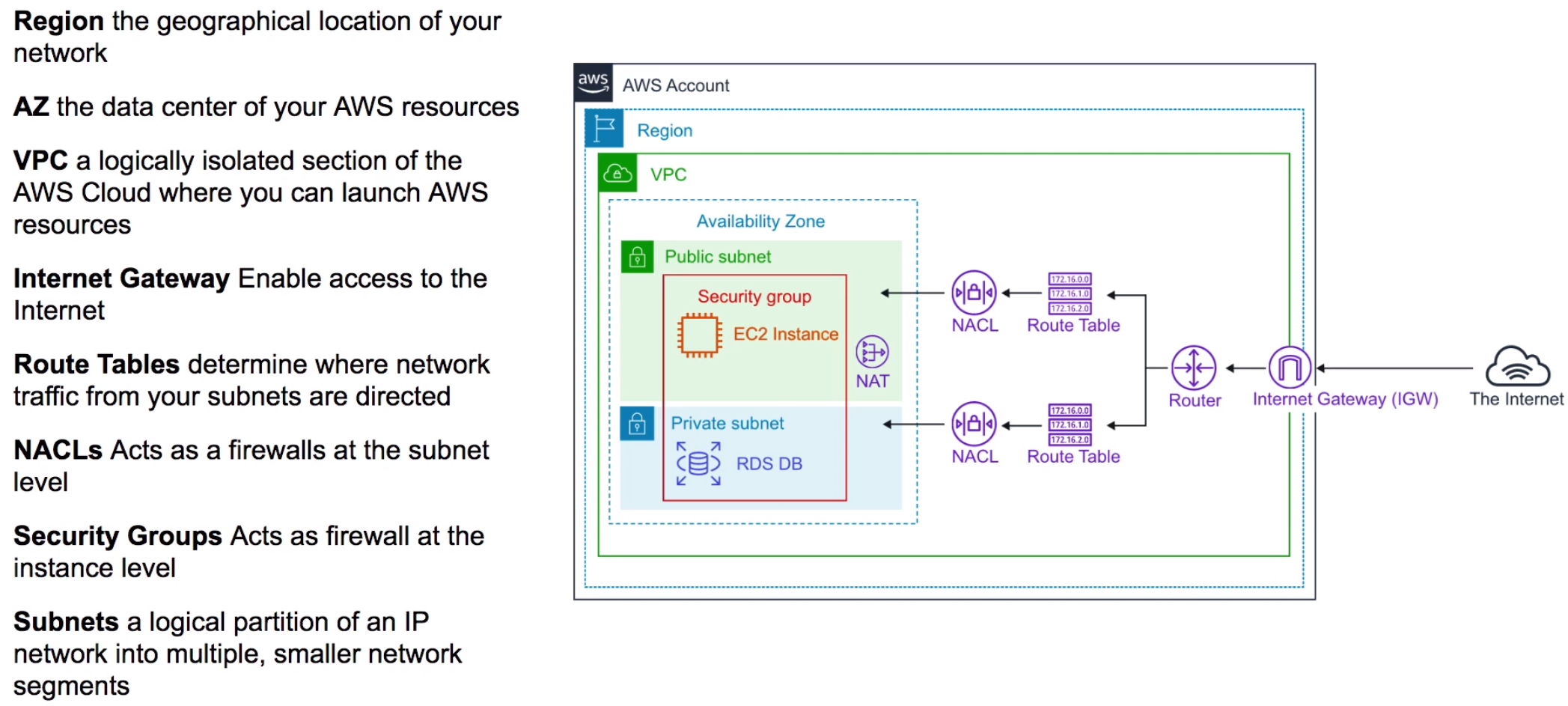
AWS Cloud operates in over 60 Availability Zones within over 20 geographic Regions around the world.
- A physical location in the world where we have multiple Availability Zones.
- Geographically distinct.
- US-EAST: edging one
- One or more physically discrete data centers, each with redundant power, networking, and connectivity, housed in separate facilities.
- Each Availability Zone is designed as an independent failure zone.
- ****Availability Zones are all redundantly connected to multiple tier-1 transit providers.
- letter identifier like us-east-1a (a refers to AZ number)
- <10ms latency between AZs
- Data centers owned by AWS trusted partners.
- Direct connection to AWS network
- Low latency
- A web service that provides secure, resizable compute capacity in the cloud.
- quickly scale capacity, both up and down, as your computing requirements change.
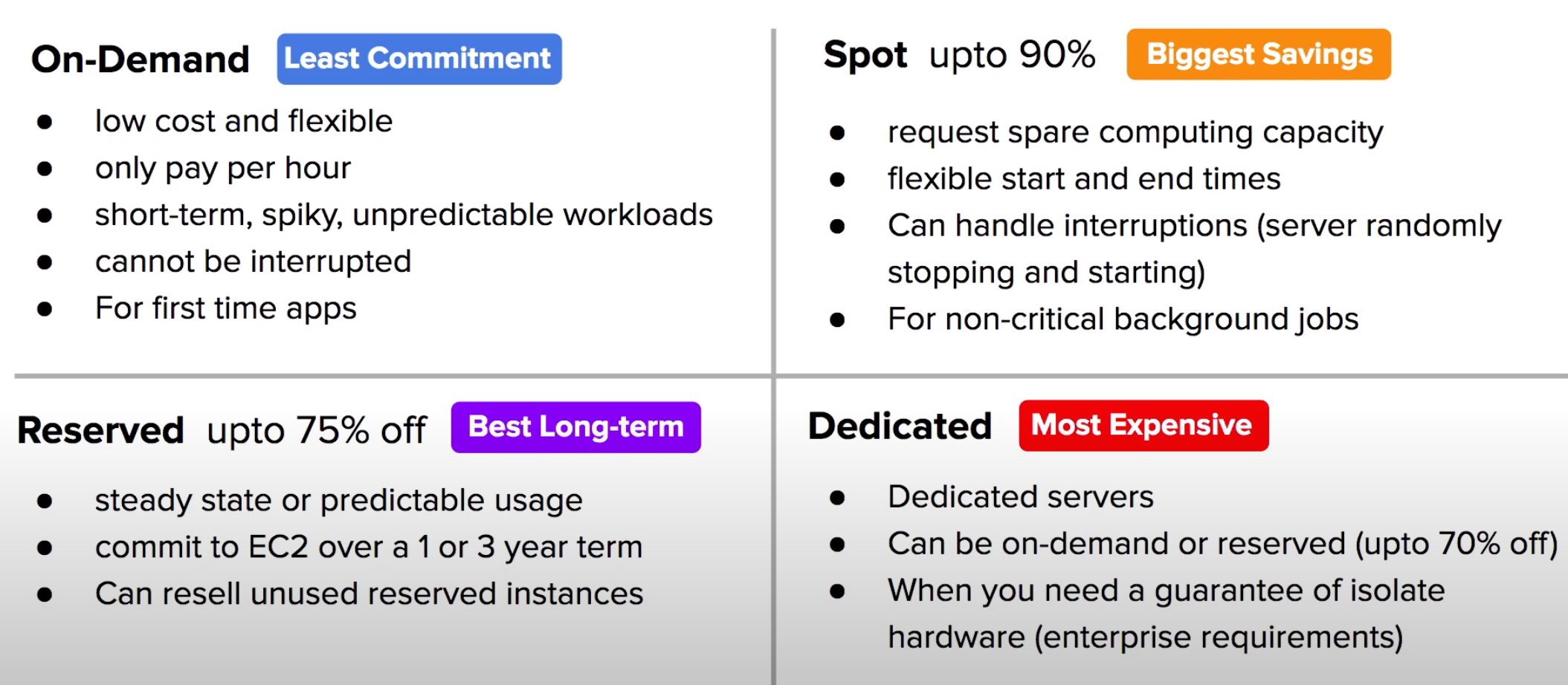
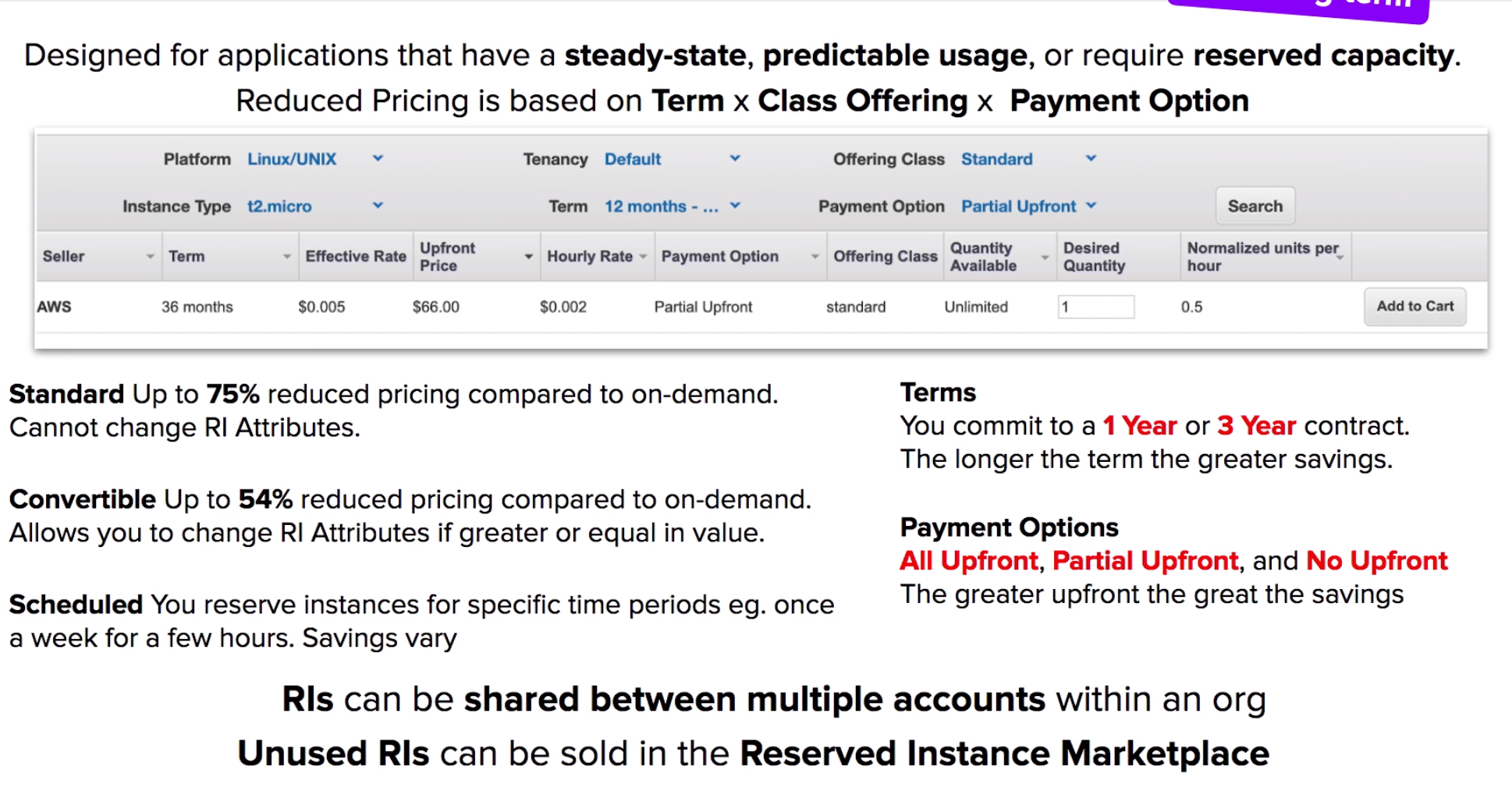
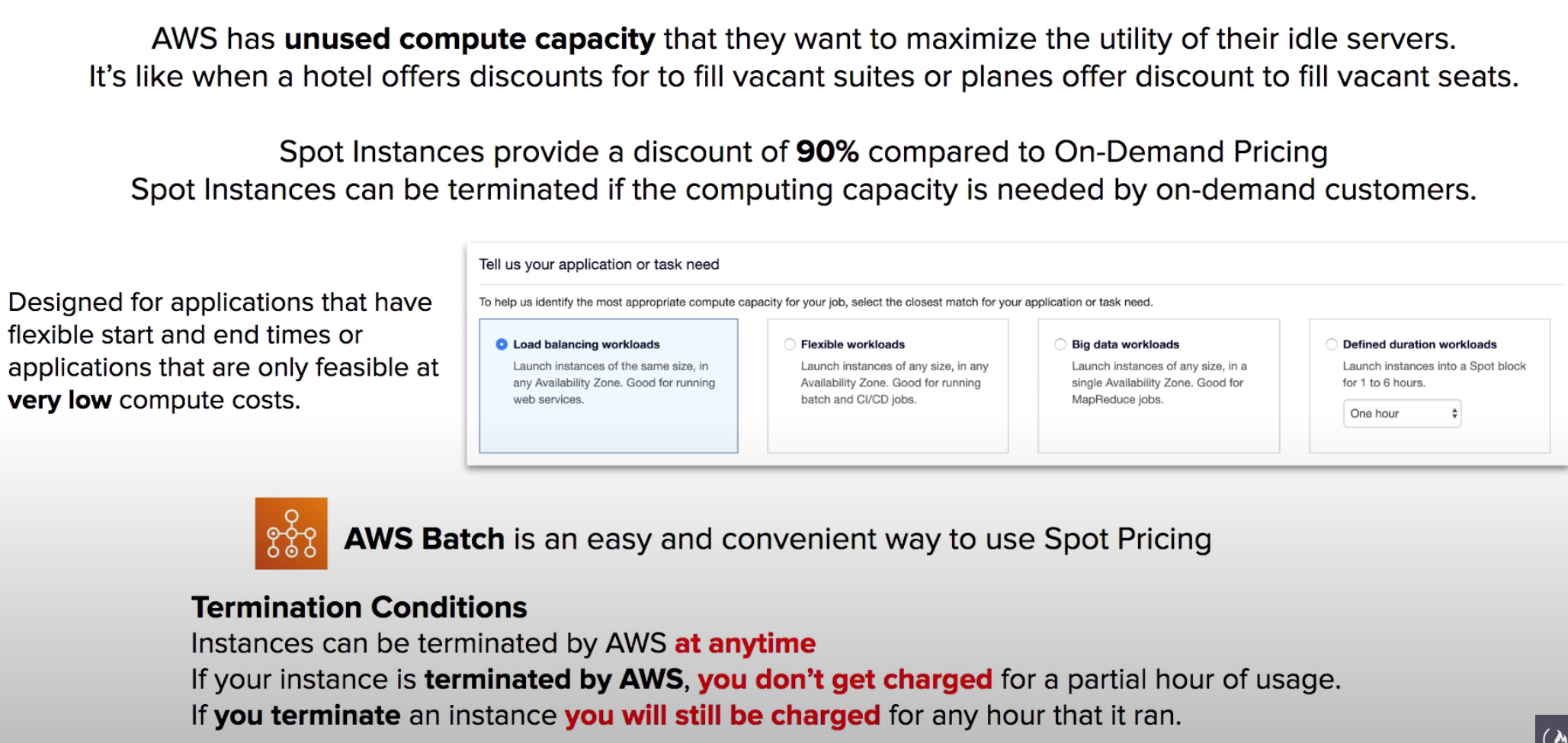
- Instance types: On-Demand Instances Reserved Instances Spot Instances, bid on spare Amazon EC2 computing capacity.
- Session manager: Provides a browser-based interactive shell and CLI for managing Windows and Linux EC2 instances, without the need to open inbound ports, manage SSH keys, or use bastion hosts.
Maintain application availability and allows you to automatically add or remove EC2 instances according to conditions you define.
Automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as Amazon EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses.
It can handle the varying load of your application traffic in a single Availability Zone or across multiple Availability Zones
- Application Load Balancer: HTTP & HTTPS
- Network Load Balancer: TCP
- Classic Load Balancer: basic load balancing across multiple Amazon EC2 instances
An object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance.
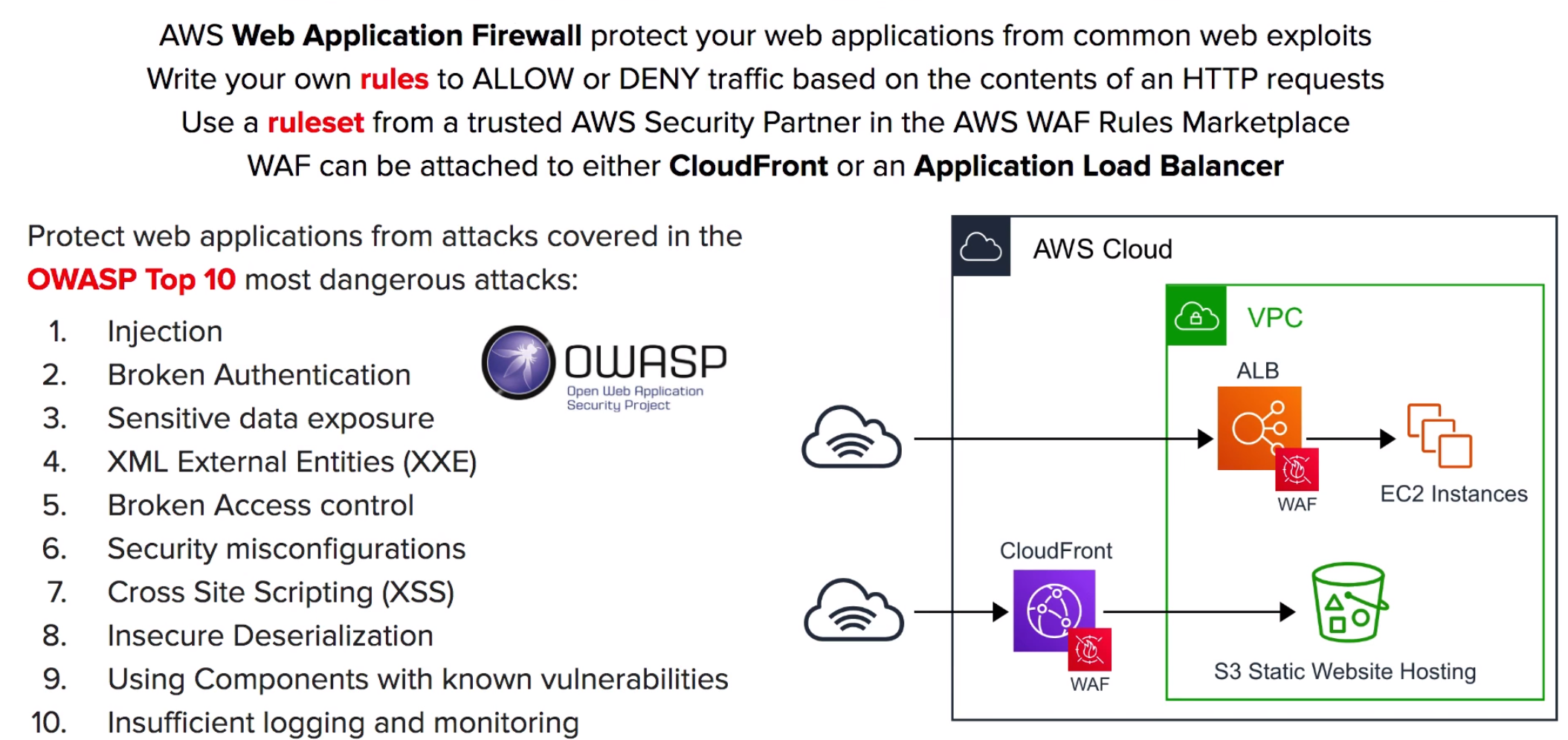
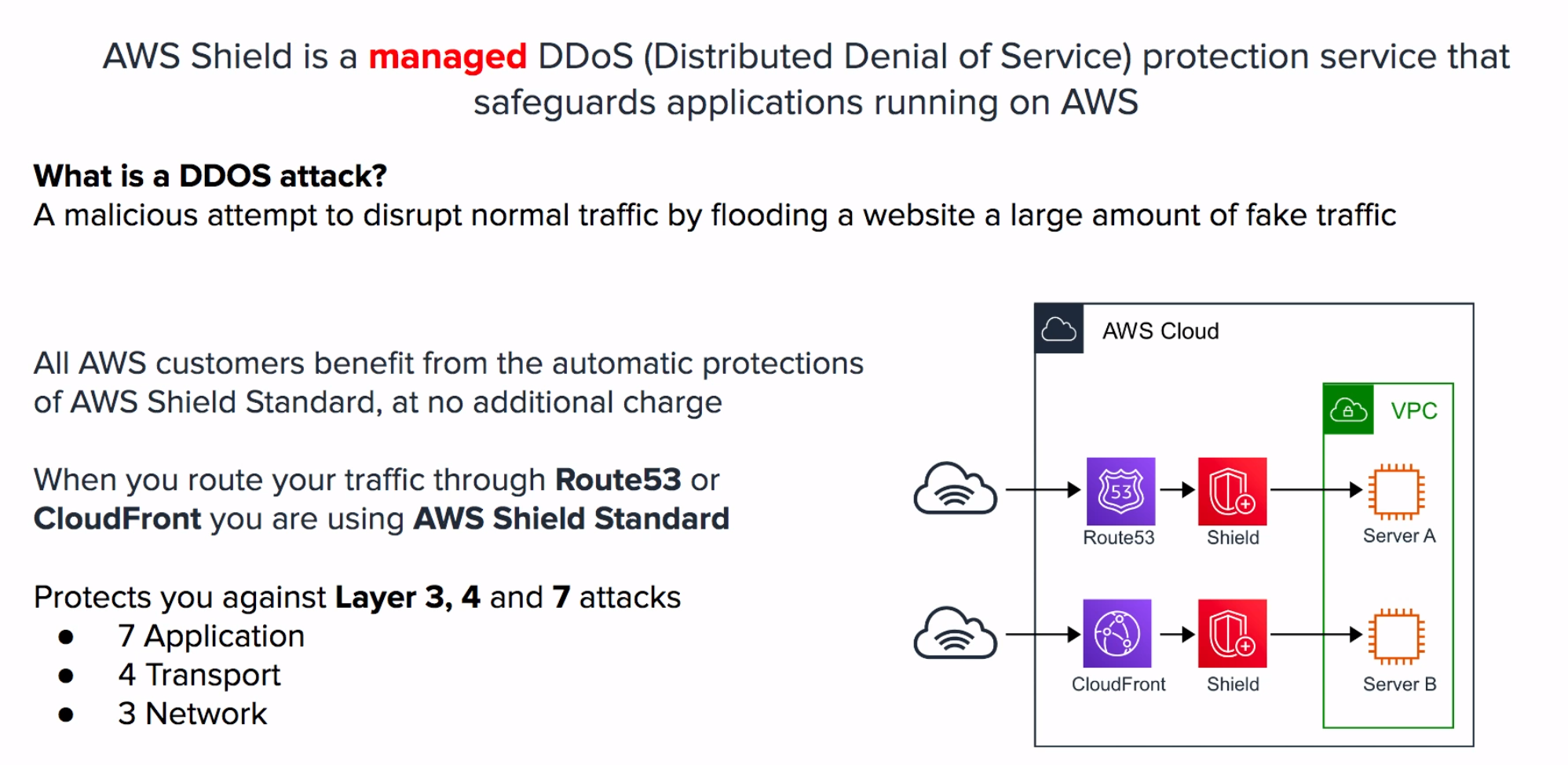
A fast content delivery network (CDN) service that securely delivers data, videos, applications, and APIs to customers.
- integrated with AWS –both physical locations that are directly connected to the AWS global infrastructure, as well as other AWS services.
- works seamlessly with services including AWS Shield for DDoS mitigation, Amazon S3, Elastic Load Balancing or Amazon EC2.
- has a domain name, will redirect the traffic to this domain name.
- Amazon Aurora is fully managed by Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS), which automates time-consuming administration tasks like hardware provisioning, database setup, patching, and backups.
- makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud.
- provides you with six familiar database engines to choose from, including Amazon Aurora, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, oracle database, and SQL Server. You can use the AWS Database Migration Service to easily migrate or replicate your existing databases to Amazon RDS.
- Run code without provisioning or managing servers.
- Only run small amount of time.
- Being able to see the configuration and logs.
- no up front payment
- no long term commitment
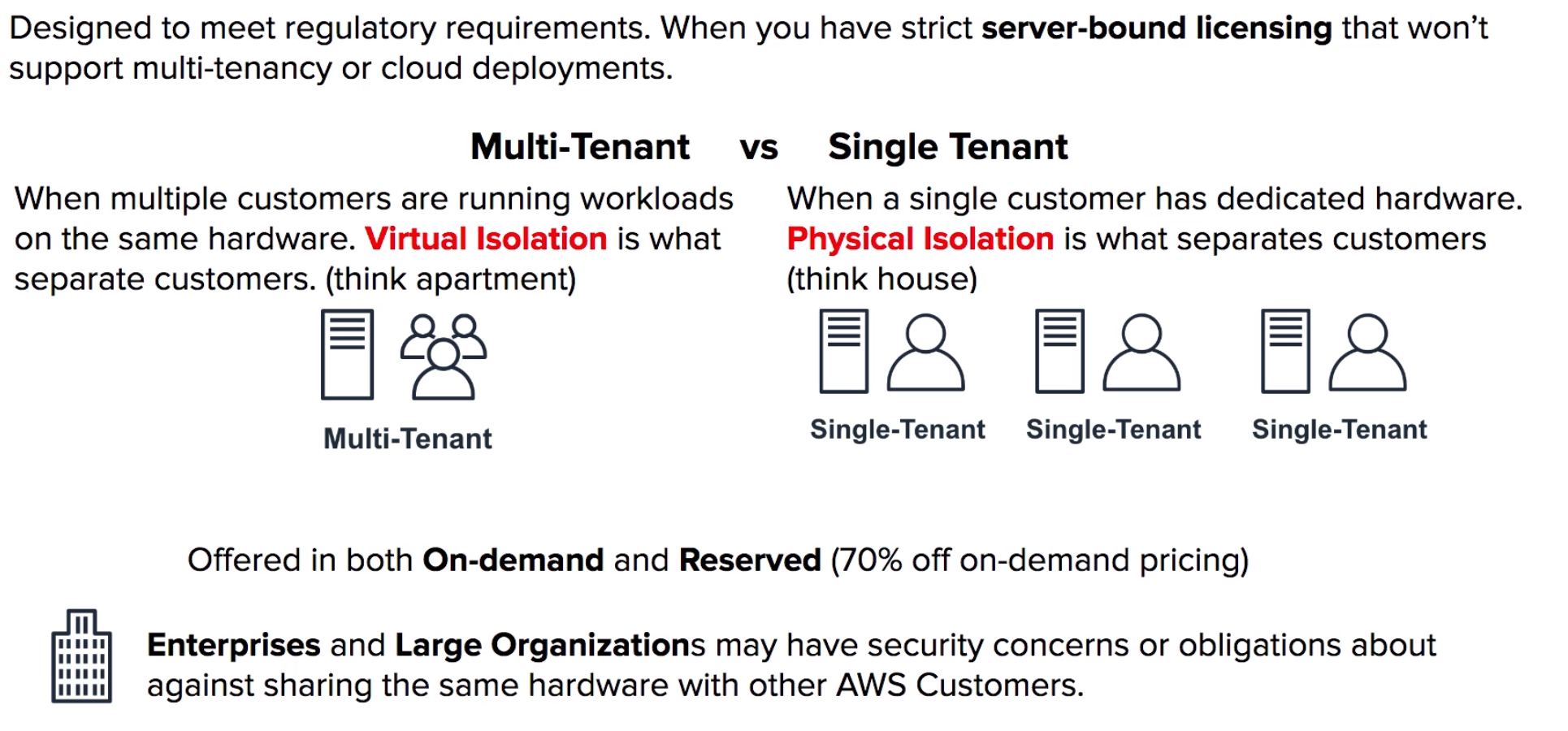
Isolated hardware
concierge: 看门人
TAM: Technical Account Manager
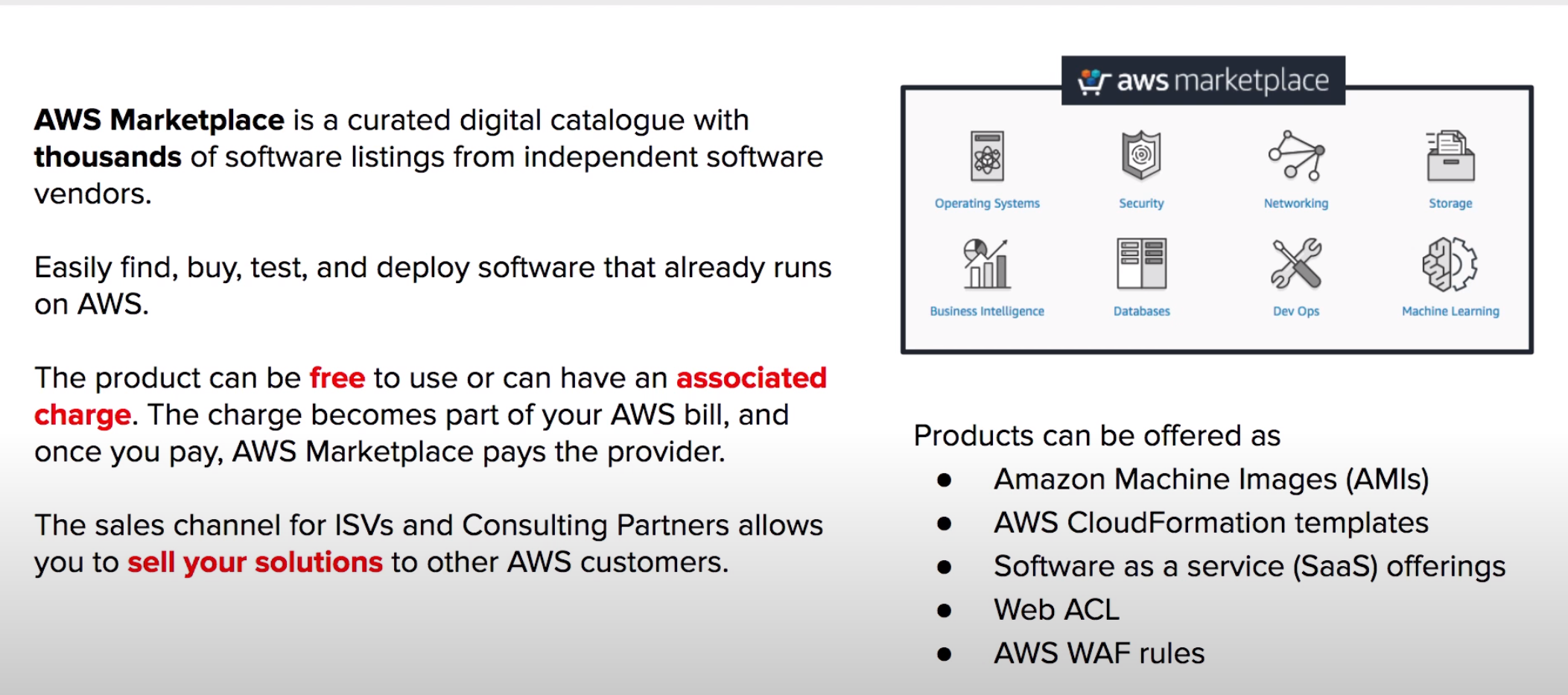
Find Buy Deploy
- Advises you on security, saving money, performance, service limits and fault tolerance.
- A automated checklist.
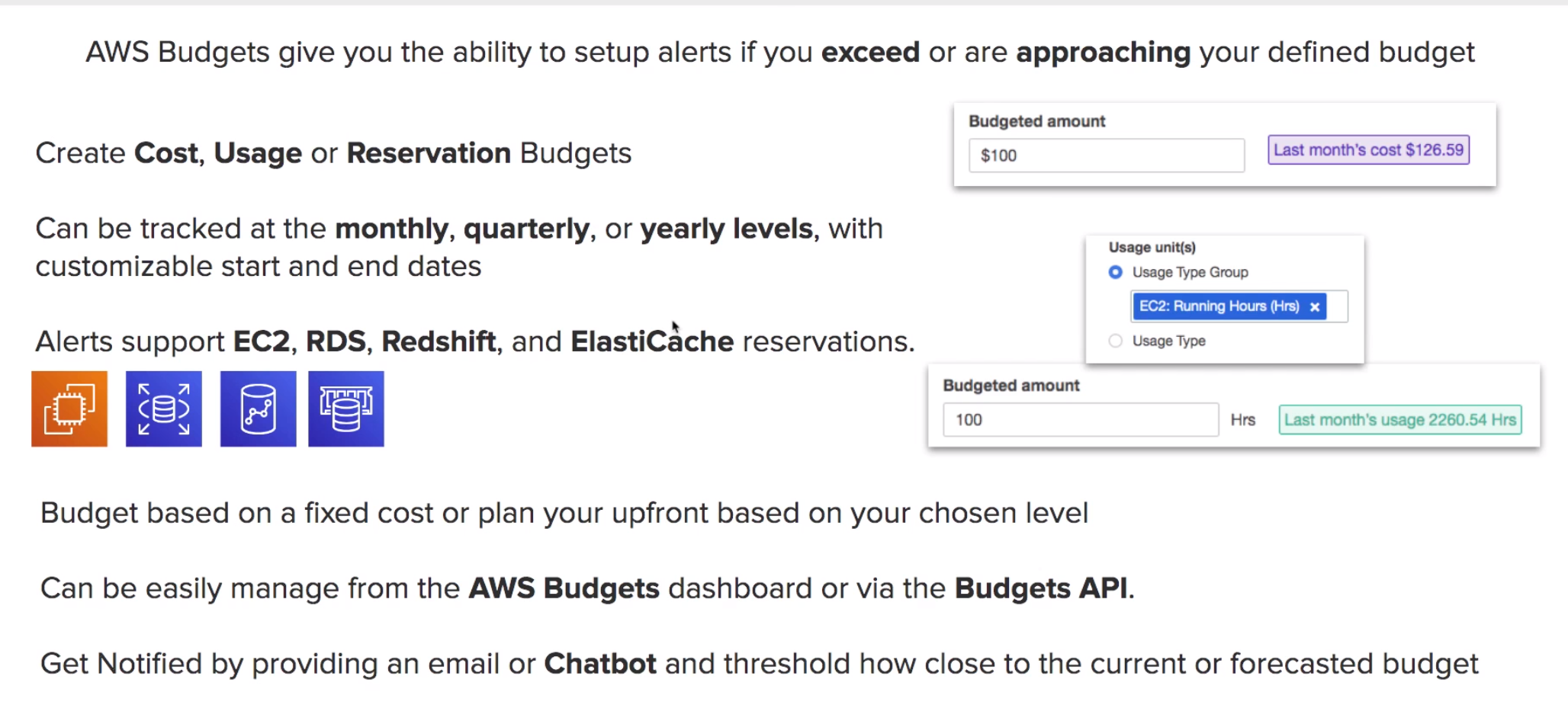
- Being able to know the forecast cost.
- Breakdown cost
Resource groups:
Lets you create a logical group of resources associated with a particular workload such as different layers of an application stack, or production versus development environments.
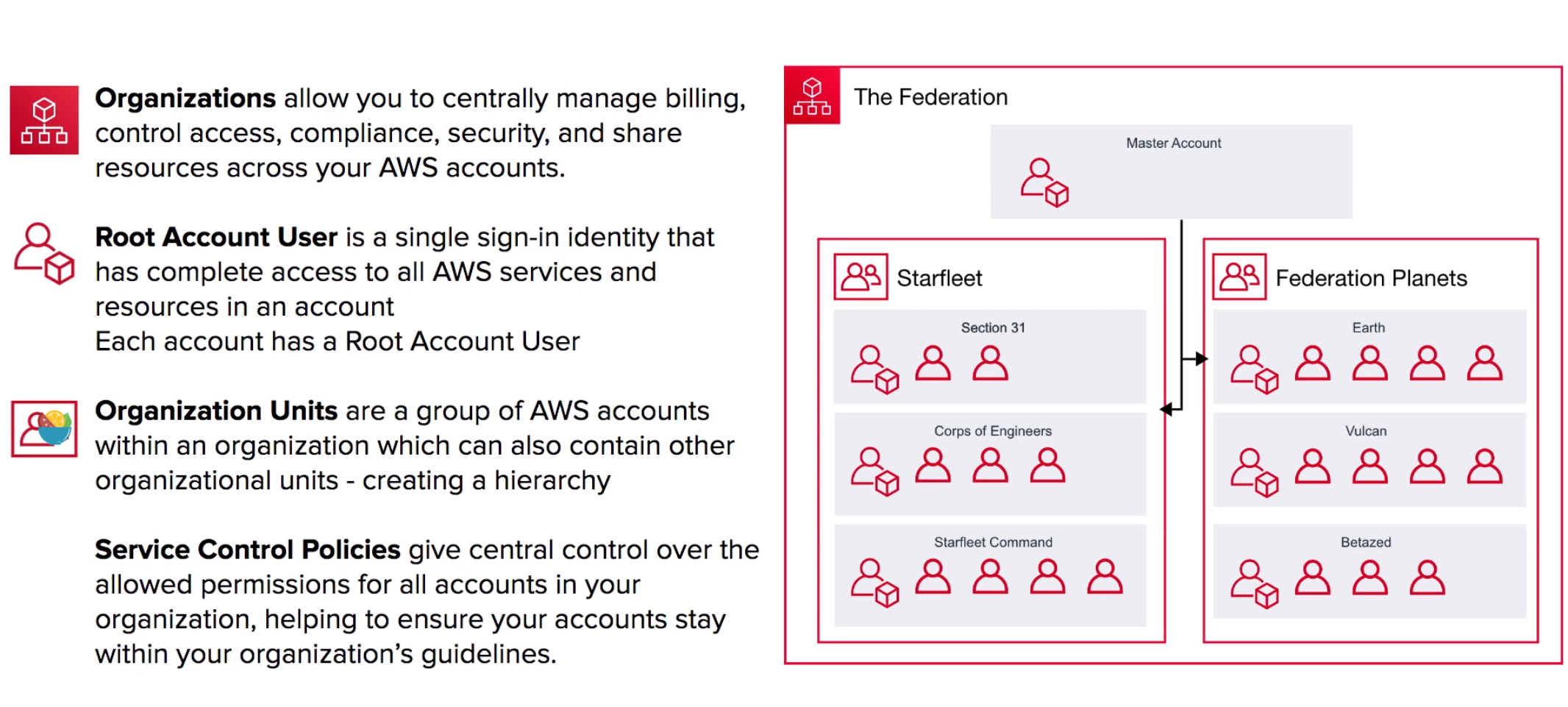
Where the root user is the master account.
VPC: Virtual Private Cloud
DynamoDB: key-value and document database that delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale.
Redshift: handle a huge amount of data.
Elastic Beanstalk: simply upload your code, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk automatically handles the deployment, from capacity provisioning, load balancing, and auto-scaling to application health monitoring.
Chef and Puppet: are automation platforms that allow you to use code to automate the configurations of your servers.
Amazon ECS eliminates the need for you to install and operate your own container orchestration software, manage and scale a cluster of virtual machines, or schedule containers on those virtual machines. Only pay for the run time and CPU used.
Fargate: a compute engine for Amazon ECS that allows you to run containers without having to manage servers or clusters.
Storage Gateway: a hybrid storage service that enables your on-premises applications to seamlessly use AWS cloud storage. You can use the service for backup and archiving, disaster recovery, cloud data processing, storage tiering, and migration.
EBS: provides persistent block storage volumes for use with Amazon EC2 instances in the AWS Cloud. Each Amazon EBS volume is automatically replicated within its Availability Zone to protect you from component failure, offering high availability and durability.
EFS: Similar to EBS, while multiple EC2 can access the storage.
Snowball: a petabyte-scale data transport solution that uses secure appliances to transfer large amounts of data into and out of AWS.
You can deny a particular IP address using NACLs.
SNS: like billing emails
SQS: for delay test
Inspector: only EC2 instance
Trusted advisor: multiple aspects
Load Banlancer
Layer 7 is the application layer.
Layer 4 is transprt layer
SNS: internal and practical purposes. No HTML emails.
SES: Professional and marketing purposes. Optimized for emails.
- Amazon Cognito: lets you add user sign-up, sign-in, and access control to your web and mobile apps quickly and easily. Amazon Cognito scales to millions of users and supports sign-in with social identity providers, such as Facebook, Google, and Amazon, and enterprise identity providers via SAML 2.0
- APN Consulting Partners: are professional services firms that help customers of all sizes design, architect, build, migrate, and manage their workloads and applications on AWS. Consulting Partners include System Integrators (SIs), Strategic Consultancies, Agencies, Managed Service Providers (MSPs), and Value-Added Resellers (VARs).
- Shared Controls: Controls which apply to both the infrastructure layer and customer layers, but in completely separate contexts or perspectives
- Patch Management– AWS is responsible for patching and fixing flaws within the infrastructure, but customers are responsible for patching their guest OS and applications
- Configuration Management– AWS maintains the configuration of its infrastructure devices, but a customer is responsible for configuring their own guest operating systems, databases, and applications
- Service and Communications Protection- It is an example of a customer-specific control
- Amazon Elastic Map Reduce (EMR)- provides a managed Hadoop framework that makes it easy, fast, and cost-effective to process vast amounts of data across dynamically scalable Amazon EC2 instance. (For data analysis)
- Amazon Athena: It is an interactive query service that makes it easy to analyze data in Amazon S3 using standard SQL.
- AWS Systems Manager gives you visibility and control of your infrastructure on AWS. Systems Manager provides a unified user interface so you can view operational data from multiple AWS services and allows you to automate operational tasks across your AWS resources.
- AWS OpsWorks: It is a configuration management service that provides managed instances of Chef and Puppet.
- AWS Config: it is a fully-managed service that provides you with an AWS resource inventory, configuration history, and configuration change notifications to enable security and regulatory compliance.
- Amazon CloudWatch: is a monitoring service for AWS cloud resources and the applications you run on AWS. You use CloudWatch for performance monitoring, not automating operational tasks.
- 5 Pillars of the AWS Well-Architected Framework Operational Excellence Security Reliability Performance Efficiency Cost Optimization Detailer may see below:
The 5 Pillars of the AWS Well-Architected Framework | Amazon Web Services