This guide provides steps to set up and secure a Spring Boot Redis connection using SSL/TLS with self-signed certificates. The instructions include generating certificates, configuring Redis and Java keystore, and setting up the Spring Boot configuration.
Run the following commands to generate the private key, certificate signing request (CSR), and self-signed certificate:
# Generate a private key
openssl genrsa -out redis.key 2048
# Generate a certificate signing request (CSR)
openssl req -new -key redis.key -out redis.csr -subj "/CN=localhost/OU=IT/O=OWN/L=PUNGGOL/ST=SINGAPORE/C=US"
# Generate a self-signed certificate
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in redis.csr -signkey redis.key -out redis.pemThis generates:
redis.key: The private key for Redis.redis.csr: The certificate signing request.redis.pem: The self-signed certificate.
Java's keytool requires the certificate in DER format to import into the Java keystore (cacerts). Convert redis.pem to redis.der:
openssl x509 -outform der -in redis.pem -out redis.derTo allow Java to trust the self-signed certificate, import redis.der into the Java keystore:
sudo keytool -import -alias redisCert -file redis.der -keystore /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-17.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/security/cacertsProvide the keystore password (default is usually changeit), and confirm the trust for this certificate.
Move the redis.key and redis.pem files to the Redis directory, e.g., /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis.
In the Redis configuration file (redis.conf), add the following lines:
tls-port 6379
port 0
tls-cert-file /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis/redis.pem
tls-key-file /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis/redis.key
tls-ca-cert-file /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis/redis.pem
tls-auth-clients optional # No Mutual TLS is optional
user admin on >madhukar ~* +@all
Define a Redis user with permissions and credentials. Start the Redis CLI:
redis-cliRun the following commands to create a user with required permissions:
ACL SETUSER admin ON >password ~* +@allReplace password with your desired password.
redis-server /path/to/redis.confStart the Spring Boot application. It should now connect securely to the Redis server over TLS.
To debug SSL issues in your Java application, you can add the following JVM option to enable debugging for SSL and TLS connections:
-Djavax.net.debug=ssl:handshake:verbose
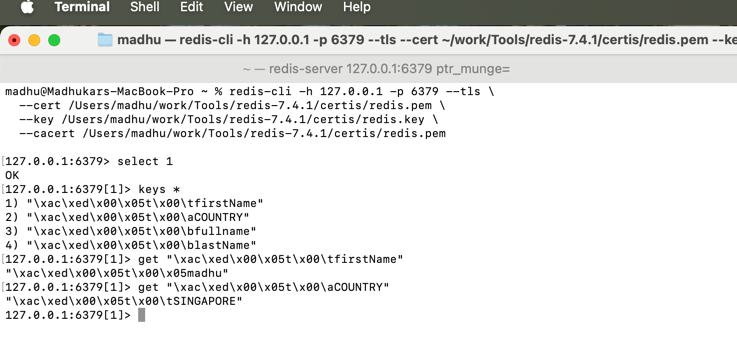
redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379 --tls --cert /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis/redis.pem --key /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis/redis.key --cacert /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis/redis.pem
This configuration enables a secure, SSL/TLS-protected connection between your Spring Boot application and Redis server using self-signed certificates.
openssl x509 -in /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis/redis.pem -text -noout
openssl s_client -connect 127.0.0.1:6379 -cert /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis/redis.pem -key /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis/redis.key -CAfile /Users/madhu/work/Tools/redis-7.4.1/certis/redis.pem
1.Redis allowing us to store the data into logical partitions with in the Redis database server instance. 2.These daabases are numbered from 0 to 15 by default, give 16 database names. 3.Each Database is independent of the other database. 4.One database keys are not visible to other databases. 5.This is one of the way where we can keep the data separate with out having multiple redis instances. 6.By Default , Redis Client connect to database 0. 7.Using SELECT redis command we can switch database.
SELECT 0