Based on OpenAI-DotNet
A OpenAI package for the Unity Game Engine to use chat-gpt, GPT-4, GPT-3.5-Turbo and Dall-E though their RESTful API (currently in beta). Independently developed, this is not an official library and I am not affiliated with OpenAI. An OpenAI API account is required.
All copyrights, trademarks, logos, and assets are the property of their respective owners.
This repository is available to transfer to the OpenAI organization if they so choose to accept it.
Requires Unity 2021.3 LTS or higher.
The recommended installation method is though the unity package manager and OpenUPM.
- Open your Unity project settings
- Add the OpenUPM package registry:
- Name:
OpenUPM - URL:
https://package.openupm.com - Scope(s):
com.openaicom.utilities
- Name:
- Open the Unity Package Manager window
- Change the Registry from Unity to
My Registries - Add the
OpenAIpackage
- Open your Unity Package Manager
- Add package from git url:
https://github.com/RageAgainstThePixel/com.openai.unity.git#upmNote: this repo has dependencies on other repositories! You are responsible for adding these on your own.
- Authentication
- Azure OpenAI
- OpenAI API Proxy
- Models
- Completions
- Chat
- Edits
- Embeddings
- Audio
- Images
- Files
- Fine Tuning
- Moderations
There are 4 ways to provide your API keys, in order of precedence:
- Pass keys directly with constructor
- Unity Scriptable Object
- Load key from configuration file
- Use System Environment Variables
var api = new OpenAIClient("sk-apiKey");Or create a OpenAIAuthentication object manually
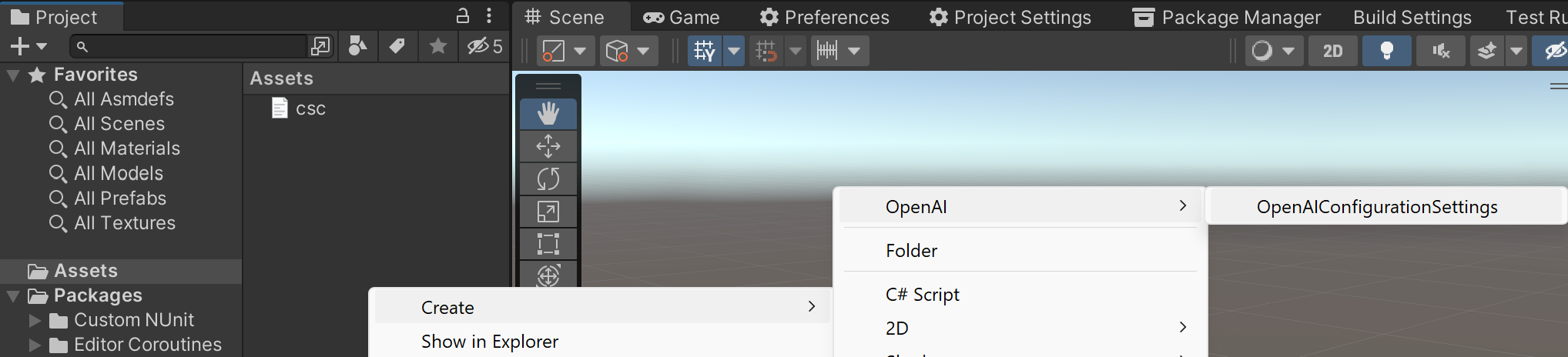
var api = new OpenAIClient(new OpenAIAuthentication("sk-apiKey", "org-yourOrganizationId"));You can save the key directly into a scriptable object that is located in the Assets/Resources folder.
You can create a new one by using the context menu of the project pane and creating a new OpenAIConfiguration scriptable object.
Attempts to load api keys from a configuration file, by default .openai in the current directory, optionally traversing up the directory tree or in the user's home directory.
To create a configuration file, create a new text file named .openai and containing the line:
Organization entry is optional.
{
"apiKey": "sk-aaaabbbbbccccddddd",
"organization": "org-yourOrganizationId"
}OPENAI_KEY=sk-aaaabbbbbccccddddd
ORGANIZATION=org-yourOrganizationIdYou can also load the configuration file directly with known path by calling static methods in OpenAIAuthentication:
- Loads the default
.openaiconfig in the specified directory:
var api = new OpenAIClient(OpenAIAuthentication.Default.LoadFromDirectory("path/to/your/directory"));- Loads the configuration file from a specific path. File does not need to be named
.openaias long as it conforms to the json format:
var api = new OpenAIClient(OpenAIAuthentication.Default.LoadFromPath("path/to/your/file.json"));Use your system's environment variables specify an api key and organization to use.
- Use
OPENAI_API_KEYfor your api key. - Use
OPENAI_ORGANIZATION_IDto specify an organization.
var api = new OpenAIClient(OpenAIAuthentication.Default.LoadFromEnvironment());You can also choose to use Microsoft's Azure OpenAI deployments as well.
You can find the required information in the Azure Playground by clicking the View Code button and view a URL like this:
https://{your-resource-name}.openai.azure.com/openai/deployments/{deployment-id}/chat/completions?api-version={api-version}your-resource-nameThe name of your Azure OpenAI Resource.deployment-idThe deployment name you chose when you deployed the model.api-versionThe API version to use for this operation. This follows the YYYY-MM-DD format.
To setup the client to use your deployment, you'll need to pass in OpenAISettings into the client constructor.
var auth = new OpenAIAuthentication("sk-apiKey");
var settings = new OpenAISettings(resourceName: "your-resource-name", deploymentId: "deployment-id", apiVersion: "api-version");
var api = new OpenAIClient(auth, settings);Authenticate with MSAL as usual and get access token, then use the access token when creating your OpenAIAuthentication. Then be sure to set useAzureActiveDirectory to true when creating your OpenAISettings.
Tutorial: Desktop app that calls web APIs: Acquire a token
// get your access token using any of the MSAL methods
var accessToken = result.AccessToken;
var auth = new OpenAIAuthentication(accessToken);
var settings = new OpenAISettings(resourceName: "your-resource", deploymentId: "deployment-id", apiVersion: "api-version", useActiveDirectoryAuthentication: true);
var api = new OpenAIClient(auth, settings);Using either the OpenAI-DotNet or com.openai.unity packages directly in your front-end app may expose your API keys and other sensitive information. To mitigate this risk, it is recommended to set up an intermediate API that makes requests to OpenAI on behalf of your front-end app. This library can be utilized for both front-end and intermediary host configurations, ensuring secure communication with the OpenAI API.
In the front end example, you will need to securely authenticate your users using your preferred OAuth provider. Once the user is authenticated, exchange your custom auth token with your API key on the backend.
Follow these steps:
- Setup a new project using either the OpenAI-DotNet or com.openai.unity packages.
- Authenticate users with your OAuth provider.
- After successful authentication, create a new
OpenAIAuthenticationobject and pass in the custom token with the prefixsess-. - Create a new
OpenAISettingsobject and specify the domain where your intermediate API is located. - Pass your new
authandsettingsobjects to theOpenAIClientconstructor when you create the client instance.
Here's an example of how to set up the front end:
var authToken = await LoginAsync();
var auth = new OpenAIAuthentication($"sess-{authToken}");
var settings = new OpenAISettings(domain: "api.your-custom-domain.com");
var api = new OpenAIClient(auth, settings);This setup allows your front end application to securely communicate with your backend that will be using the OpenAI-DotNet-Proxy, which then forwards requests to the OpenAI API. This ensures that your OpenAI API keys and other sensitive information remain secure throughout the process.
In this example, we demonstrate how to set up and use OpenAIProxyStartup in a new ASP.NET Core web app. The proxy server will handle authentication and forward requests to the OpenAI API, ensuring that your API keys and other sensitive information remain secure.
- Create a new ASP.NET Core minimal web API project.
- Add the OpenAI-DotNet nuget package to your project.
- Powershell install:
Install-Package OpenAI-DotNet-Proxy - Manually editing .csproj:
<PackageReference Include="OpenAI-DotNet-Proxy" />
- Powershell install:
- Create a new class that inherits from
AbstractAuthenticationFilterand override theValidateAuthenticationmethod. This will implement theIAuthenticationFilterthat you will use to check user session token against your internal server. - In
Program.cs, create a new proxy web application by callingOpenAIProxyStartup.CreateDefaultHostmethod, passing your customAuthenticationFilteras a type argument. - Create
OpenAIAuthenticationandOpenAIClientSettingsas you would normally with your API keys, org id, or Azure settings.
public partial class Program
{
private class AuthenticationFilter : AbstractAuthenticationFilter
{
public override void ValidateAuthentication(IHeaderDictionary request)
{
// You will need to implement your own class to properly test
// custom issued tokens you've setup for your end users.
if (!request.Authorization.ToString().Contains(userToken))
{
throw new AuthenticationException("User is not authorized");
}
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var auth = OpenAIAuthentication.LoadFromEnv();
var settings = new OpenAIClientSettings(/* your custom settings if using Azure OpenAI */);
var openAIClient = new OpenAIClient(auth, settings);
var proxy = OpenAIProxyStartup.CreateDefaultHost<AuthenticationFilter>(args, openAIClient);
proxy.Run();
}
}Once you have set up your proxy server, your end users can now make authenticated requests to your proxy api instead of directly to the OpenAI API. The proxy server will handle authentication and forward requests to the OpenAI API, ensuring that your API keys and other sensitive information remain secure.
List and describe the various models available in the API. You can refer to the Models documentation to understand what models are available and the differences between them.
Also checkout model endpoint compatibility to understand which models work with which endpoints.
To specify a custom model not pre-defined in this library:
var model = new Model("model-id");The Models API is accessed via OpenAIClient.ModelsEndpoint
Lists the currently available models, and provides basic information about each one such as the owner and availability.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var models = await api.ModelsEndpoint.GetModelsAsync();
foreach (var model in models)
{
Debug.Log(model.ToString());
}Retrieves a model instance, providing basic information about the model such as the owner and permissions.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var model = await api.ModelsEndpoint.GetModelDetailsAsync("text-davinci-003");
Debug.Log(model.ToString());Delete a fine-tuned model. You must have the Owner role in your organization.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var result = await api.ModelsEndpoint.DeleteFineTuneModelAsync("your-fine-tuned-model");
Assert.IsTrue(result);Given a prompt, the model will return one or more predicted completions, and can also return the probabilities of alternative tokens at each position.
The Completions API is accessed via OpenAIClient.CompletionsEndpoint
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var result = await api.CompletionsEndpoint.CreateCompletionAsync("One Two Three One Two", temperature: 0.1, model: Model.Davinci);
Debug.Log(result);To get the
CompletionResult(which is mostly metadata), use its implicit string operator to get the text if all you want is the completion choice.
Streaming allows you to get results are they are generated, which can help your application feel more responsive, especially on slow models like Davinci.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
await api.CompletionsEndpoint.StreamCompletionAsync(result =>
{
foreach (var choice in result.Completions)
{
Debug.Log(choice);
}
}, "My name is Roger and I am a principal software engineer at Salesforce. This is my resume:", maxTokens: 200, temperature: 0.5, presencePenalty: 0.1, frequencyPenalty: 0.1, model: Model.Davinci);Given a chat conversation, the model will return a chat completion response.
The Chat API is accessed via OpenAIClient.ChatEndpoint
Creates a completion for the chat message
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var messages = new List<Message>
{
new Message(Role.System, "You are a helpful assistant."),
new Message(Role.User, "Who won the world series in 2020?"),
new Message(Role.Assistant, "The Los Angeles Dodgers won the World Series in 2020."),
new Message(Role.User, "Where was it played?"),
};
var chatRequest = new ChatRequest(messages, Model.GPT3_5_Turbo);
var result = await api.ChatEndpoint.GetCompletionAsync(chatRequest);
Debug.Log($"{result.FirstChoice.Message.Role}: {result.FirstChoice.Message.Content}");var api = new OpenAIClient();
var messages = new List<Message>
{
new Message(Role.System, "You are a helpful assistant."),
new Message(Role.User, "Who won the world series in 2020?"),
new Message(Role.Assistant, "The Los Angeles Dodgers won the World Series in 2020."),
new Message(Role.User, "Where was it played?"),
};
var chatRequest = new ChatRequest(messages, Model.GPT3_5_Turbo, number: 2);
await api.ChatEndpoint.StreamCompletionAsync(chatRequest, result =>
{
foreach (var choice in result.Choices.Where(choice => !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(choice.Delta?.Content)))
{
// Partial response content
Debug.Log(choice.Delta.Content);
}
foreach (var choice in result.Choices.Where(choice => !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(choice.Message?.Content)))
{
// Completed response content
Debug.Log($"{choice.Message.Role}: {choice.Message.Content}");
}
});Only available with the latest 0613 model series!
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var messages = new List<Message>
{
new Message(Role.System, "You are a helpful weather assistant."),
new Message(Role.User, "What's the weather like today?"),
};
foreach (var message in messages)
{
Debug.Log($"{message.Role}: {message.Content}");
}
// Define the functions that the assistant is able to use:
var functions = new List<Function>
{
new Function(
nameof(WeatherService.GetCurrentWeather),
"Get the current weather in a given location",
new JObject
{
["type"] = "object",
["properties"] = new JObject
{
["location"] = new JObject
{
["type"] = "string",
["description"] = "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA"
},
["unit"] = new JObject
{
["type"] = "string",
["enum"] = new JArray {"celsius", "fahrenheit"}
}
},
["required"] = new JArray { "location", "unit" }
})
};
var chatRequest = new ChatRequest(messages, functions: functions, functionCall: "auto", model: "gpt-3.5-turbo-0613");
var result = await api.ChatEndpoint.GetCompletionAsync(chatRequest);
messages.Add(result.FirstChoice.Message);
Debug.Log($"{result.FirstChoice.Message.Role}: {result.FirstChoice.Message.Content} | Finish Reason: {result.FirstChoice.FinishReason}");
var locationMessage = new Message(Role.User, "I'm in Glasgow, Scotland");
messages.Add(locationMessage);
Debug.Log($"{locationMessage.Role}: {locationMessage.Content}");
chatRequest = new ChatRequest(messages, functions: functions, functionCall: "auto", model: "gpt-3.5-turbo-0613");
result = await api.ChatEndpoint.GetCompletionAsync(chatRequest);
messages.Add(result.FirstChoice.Message);
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(result.FirstChoice.Message.Content))
{
// It's possible that the assistant will also ask you which units you want the temperature in.
Debug.Log($"{result.FirstChoice.Message.Role}: {result.FirstChoice.Message.Content} | Finish Reason: {result.FirstChoice.FinishReason}");
var unitMessage = new Message(Role.User, "celsius");
messages.Add(unitMessage);
Debug.Log($"{unitMessage.Role}: {unitMessage.Content}");
chatRequest = new ChatRequest(messages, functions: functions, functionCall: "auto", model: "gpt-3.5-turbo-0613");
result = await api.ChatEndpoint.GetCompletionAsync(chatRequest);
}
Debug.Log($"{result.FirstChoice.Message.Role}: {result.FirstChoice.Message.Function.Name} | Finish Reason: {result.FirstChoice.FinishReason}");
Debug.Log($"{result.FirstChoice.Message.Function.Arguments}");
var functionArgs = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<WeatherArgs>(result.FirstChoice.Message.Function.Arguments.ToString());
var functionResult = WeatherService.GetCurrentWeather(functionArgs);
messages.Add(new Message(Role.Function, functionResult));
Debug.Log($"{Role.Function}: {functionResult}");
// System: You are a helpful weather assistant.
// User: What's the weather like today?
// Assistant: Sure, may I know your current location? | Finish Reason: stop
// User: I'm in Glasgow, Scotland
// Assistant: GetCurrentWeather | Finish Reason: function_call
// {
// "location": "Glasgow, Scotland",
// "unit": "celsius"
// }
// Function: The current weather in Glasgow, Scotland is 20 celsiusGiven a prompt and an instruction, the model will return an edited version of the prompt.
The Edits API is accessed via OpenAIClient.EditsEndpoint
Creates a new edit for the provided input, instruction, and parameters using the provided input and instruction.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var request = new EditRequest("What day of the wek is it?", "Fix the spelling mistakes");
var result = await api.EditsEndpoint.CreateEditAsync(request);
Debug.Log(result);Get a vector representation of a given input that can be easily consumed by machine learning models and algorithms.
Related guide: Embeddings
The Edits API is accessed via OpenAIClient.EmbeddingsEndpoint
Creates an embedding vector representing the input text.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var result = await api.EmbeddingsEndpoint.CreateEmbeddingAsync("The food was delicious and the waiter...", Models.Embedding_Ada_002);
Debug.Log(result);Converts audio into text.
The Audio API is accessed via OpenAIClient.AudioEndpoint
Transcribes audio into the input language.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var request = new AudioTranscriptionRequest(audioClip, language: "en");
var result = await api.AudioEndpoint.CreateTranscriptionAsync(request);
Debug.Log(result);Translates audio into into English.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var request = new AudioTranslationRequest(audioClip);
var result = await api.AudioEndpoint.CreateTranslationAsync(request);
Debug.Log(result);Given a prompt and/or an input image, the model will generate a new image.
The Images API is accessed via OpenAIClient.ImagesEndpoint
Creates an image given a prompt.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var results = await api.ImagesEndPoint.GenerateImageAsync("A house riding a velociraptor", 1, ImageSize.Small);
foreach (var (path, texture) in results)
{
Debug.Log(path);
// path == file://path/to/image.png
Assert.IsNotNull(texture);
// texture == The preloaded Texture2D
}Creates an edited or extended image given an original image and a prompt.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var results = await api.ImagesEndPoint.CreateImageEditAsync(Path.GetFullPath(imageAssetPath), Path.GetFullPath(maskAssetPath), "A sunlit indoor lounge area with a pool containing a flamingo", 1, ImageSize.Small);
foreach (var (path, texture) in results)
{
Debug.Log(path);
// path == file://path/to/image.png
Assert.IsNotNull(texture);
// texture == The preloaded Texture2D
}Creates a variation of a given image.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var results = await api.ImagesEndPoint.CreateImageVariationAsync(Path.GetFullPath(imageAssetPath), 1, ImageSize.Small);
foreach (var (path, texture) in results)
{
Debug.Log(path);
// path == file://path/to/image.png
Assert.IsNotNull(texture);
// texture == The preloaded Texture2D
}Alternatively, the endpoint can directly take a Texture2D with Read/Write enabled and Compression set to None.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var results = await api.ImagesEndPoint.CreateImageVariationAsync(imageTexture, 1, ImageSize.Small);
// imageTexture is of type Texture2D
foreach (var (path, texture) in results)
{
Debug.Log(path);
// path == file://path/to/image.png
Assert.IsNotNull(texture);
// texture == The preloaded Texture2D
}Files are used to upload documents that can be used with features like Fine-tuning.
The Files API is accessed via OpenAIClient.FilesEndpoint
Returns a list of files that belong to the user's organization.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var files = await api.FilesEndpoint.ListFilesAsync();
foreach (var file in files)
{
Debug.Log($"{file.Id} -> {file.Object}: {file.FileName} | {file.Size} bytes");
}Upload a file that contains document(s) to be used across various endpoints/features. Currently, the size of all the files uploaded by one organization can be up to 1 GB. Please contact us if you need to increase the storage limit.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var fileData = await api.FilesEndpoint.UploadFileAsync("path/to/your/file.jsonl", "fine-tune");
Debug.Log(fileData.Id);Delete a file.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var result = await api.FilesEndpoint.DeleteFileAsync(fileData);
Assert.IsTrue(result);Returns information about a specific file.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var fileData = await GetFileInfoAsync(fileId);
Debug.Log($"{fileData.Id} -> {fileData.Object}: {fileData.FileName} | {fileData.Size} bytes");Downloads the specified file.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var downloadedFilePath = await api.FilesEndpoint.DownloadFileAsync(fileId);
Debug.Log(downloadedFilePath);
Assert.IsTrue(File.Exists(downloadedFilePath));Manage fine-tuning jobs to tailor a model to your specific training data.
Related guide: Fine-tune models
The Files API is accessed via OpenAIClient.FineTuningEndpoint
Creates a job that fine-tunes a specified model from a given dataset.
Response includes details of the enqueued job including job status and the name of the fine-tuned models once complete.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var request = new CreateFineTuneRequest(fileData);
var fineTuneJob = await api.FineTuningEndpoint.CreateFineTuneJobAsync(request);
Debug.Log(fineTuneJob.Id);List your organization's fine-tuning jobs.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var fineTuneJobs = await api.FineTuningEndpoint.ListFineTuneJobsAsync();
foreach (var job in fineTuneJobs)
{
Debug.Log($"{job.Id} -> {job.Status}");
}Gets info about the fine-tune job.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var result = await api.FineTuningEndpoint.RetrieveFineTuneJobInfoAsync(fineTuneJob);
Debug.Log($"{result.Id} -> {result.Status}");Immediately cancel a fine-tune job.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var result = await api.FineTuningEndpoint.CancelFineTuneJobAsync(fineTuneJob);
Assert.IsTrue(result);Get fine-grained status updates for a fine-tune job.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var fineTuneEvents = await api.FineTuningEndpoint.ListFineTuneEventsAsync(fineTuneJob);
Debug.Log($"{fineTuneJob.Id} -> status: {fineTuneJob.Status} | event count: {fineTuneEvents.Count}");var api = new OpenAIClient();
await api.FineTuningEndpoint.StreamFineTuneEventsAsync(fineTuneJob, fineTuneEvent =>
{
Debug.Log($" {fineTuneEvent.CreatedAt} [{fineTuneEvent.Level}] {fineTuneEvent.Message}");
});Given a input text, outputs if the model classifies it as violating OpenAI's content policy.
Related guide: Moderations
The Moderations API can be accessed via OpenAIClient.ModerationsEndpoint
Classifies if text violates OpenAI's Content Policy.
var api = new OpenAIClient();
var response = await api.ModerationsEndpoint.GetModerationAsync("I want to kill them.");
Assert.IsTrue(response);