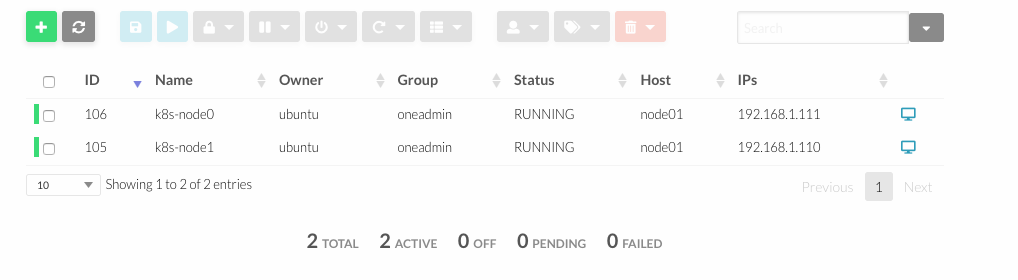
Terraform files for deploying a Rancher HA cluster in OpenNebula
Important: RKE add-on install is only supported up to Rancher v2.0.8.
To install Terraform, find the appropriate package for your system and download it
$ curl -O https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.11.12/terraform_0.11.12_linux_amd64.zip
After downloading Terraform, unzip the package
$ sudo unzip terraform_0.11.12_linux_amd64.zip -d /usr/local/bin
After installing Terraform, verify the installation worked by opening a new terminal session and checking that terraform is available.
$ terraform --version
You need to install go first: https://golang.org/doc/install
Install Prerequisites
$ sudo apt install bzr
$ sudo yum install -y bzr
Use the wget command and the link from Go to download the tarball:
$ curl -O https://dl.google.com/go/go1.12.linux-amd64.tar.gz
The installation of Go consists of extracting the tarball into the /usr/local
$ sudo tar -C /usr/local -xvzf go1.12.linux-amd64.tar.gz
We will call our workspace directory projects, but you can name it anything you would like. The -p flag for the mkdir command will create the appropriate directory tree
$ mkdir -p ~/projects/{bin,pkg,src}
To execute Go like any other command, we need to append its install location to the $PATH variable.
$ export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
$ echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin' >> ~/.bashrc
Additionally, define the GOPATH and GOBIN Go environment variables:
$ export GOBIN=$HOME/projects/bin
$ export GOPATH=$HOME/projects/src
$ echo 'export GOBIN=$HOME/projects/bin' >> ~/.bashrc
$ echo 'export GOPATH=$HOME/projects/src' >> ~/.bashrc
After go is installed and set up, just type:
$ go get github.com/blackberry/terraform-provider-opennebula
$ go install github.com/blackberry/terraform-provider-opennebula
Copy your terraform-provider-opennebula binary in a folder, like /usr/local/bin, and write this in ~/.terraformrc:
$ sudo cp ~/projects/bin/terraform-provider-opennebula /usr/local/bin/terraform-provider-opennebula
For RKE provider, download the binary and copy in the same folder:
$ wget https://github.com/yamamoto-febc/terraform-provider-rke/releases/download/0.9.0/terraform-provider-rke_0.9.0_linux-amd64.zip
$ sudo unzip terraform-provider-rke_0.9.0_linux-amd64.zip -d /usr/local/bin/terraform-provider-rke
cat <<EOF >> ~/.terraformrc
providers {
opennebula = "/usr/local/bin/terraform-provider-opennebula"
}
providers {
rke = "/usr/local/bin/terraform-provider-rke"
}
EOF
This repository provide a TF file to install Rancher in a high-availability configuration. The goal is easily install a Rancher on machines running CentOS 7.
Clone this repo:
$ git clone https://github.com/mangelft/terraform-rke-paas.git
First we have to initialize terraform simply with:
$ terraform init
This will read your configuration files and install the plugins for your provider.
We let terraform create a plan, which we can review:
$ terraform plan
The plan command lets you see what Terraform will do before actually doing it.
Now we execute:
$ terraform apply
Kubectl is the CLI tool for interacting with the Kubernetes cluster. Please make sure these tools are installed and available.
To make sure it works, run a simple get nodes command.
$ kubectl get nodes
That’s it you should have a functional Rancher server. Point a browser at the hostname: https://rancher.my.org.
- Miguel Ángel Flores - ([email protected])