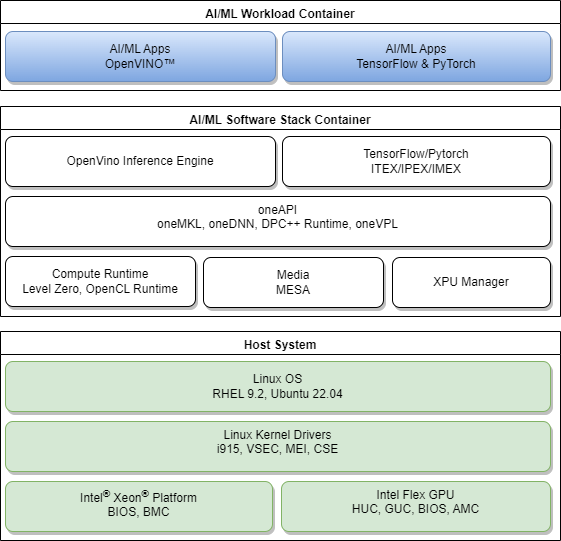
The following diagram illustrates a high-level discrete GPU-based Linux software stack to run High Performance Computing and AI/ML workloads on Intel® Xeon® platforms with Intel® Data Center Flex Series GPUs. This document provides a sample dockerfile with build instructions to automate installations of the recommended base GPU/media user space modules and AI/ML software components on the Intel® Edge Server platform with Intel® Data Center Flex Series GPUs.
Host Development platforms validated in this setup guide include:
- Emerald Rapids - SP (EMR-SP)
- Sapphire Rapids - EEC (SPR-EEC)
- Ice Lake - D (ICX-D)
Intel® Data Center GPU validated in this setup guide include:
- Intel® Data Center GPU Flex Series 170
- Intel® Data Center GPU Flex Series 140
- Please refer to RHEL 9 Installation for Host Operating System installation setup
- Please refer to FLEX GPU Drivers for RHEL for FLEX GPU Drivers Installation
- Please refer to Ubuntu 22.04 OS Installation for Host Operating System installation setup
- Please refer to FLEX GPU Drivers for Ubuntu for FLEX GPU Drivers Installation
Please refer to the sample Dockerfile and build instructions below to build a docker image that contains the base GPU/media user space components, Intel® OneAPI, Intel® OpenVINO, Intel® Extension for PyTorch* (IPEX) and Intel® Extension for TensorFlow* (ITEX) AI software components to run AI/ML workloads with Docker.
For example for ubuntu 22.04
FROM ubuntu:22.04
ARG PROXY ""
ARG NO_PROXY ""
ENV http_proxy ${PROXY}
ENV https_proxy ${PROXY}
ENV ftp_proxy ${PROXY}
ENV no_proxy ${NO_PROXY}
RUN env -u no_proxy apt-get update
RUN env -u no_proxy apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends wget gpg ca-certificates \
apt-utils curl gpg-agent
RUN env -u no_proxy -u NO_PROXY wget -qO - \
https://repositories.intel.com/graphics/intel-graphics.key \
| gpg --dearmor --output /usr/share/keyrings/intel-graphics.gpg
RUN echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/intel-graphics.gpg] \
https://repositories.intel.com/gpu/ubuntu \
jammy/production/2328 unified" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/intel.gpu.jammy.list
RUN env -u no_proxy -u NO_PROXY apt update
RUN env -u no_proxy -u NO_PROXY apt-get install -y \
intel-opencl-icd intel-level-zero-gpu level-zero \
intel-media-va-driver-non-free libmfx1 libmfxgen1 libvpl2 \
libegl-mesa0 libegl1-mesa libegl1-mesa-dev libgbm1 libgl1-mesa-dev libgl1-mesa-dri \
libglapi-mesa libgles2-mesa-dev libglx-mesa0 libigdgmm12 libxatracker2 mesa-va-drivers \
mesa-vdpau-drivers mesa-vulkan-drivers va-driver-all vainfo \
intel-metrics-library \
clinfo
#Optional 1.0: install openapi dpcpp mkl
ARG mkl_version=2024.0.0-49656
ARG dpcpp_version=2024.0
RUN env -u no_proxy -u NO_PROXY curl -fsSL \
https://apt.repos.intel.com/intel-gpg-keys/GPG-PUB-KEY-INTEL-SW-PRODUCTS.PUB | apt-key add -
RUN echo "deb https://apt.repos.intel.com/oneapi all main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/intel-oneapi.list
RUN env -u no_proxy -u NO_PROXY apt update
RUN env -u no_proxy -u NO_PROXY apt-get install -y intel-oneapi-mkl=${mkl_version} \
intel-oneapi-compiler-dpcpp-cpp-runtime-${dpcpp_version} \
intel-oneapi-runtime-libs
#Optional 1.1: install openvino runtime, Please specify --build-arg=ov_url=xxx to install specific version of openvino
ENV INTEL_OPENVINO_DIR=/opt/intel/openvino
ARG ov_url=https://storage.openvinotoolkit.org/repositories/openvino/packages/2023.0/linux/l_openvino_toolkit_ubuntu22_2023.0.0.10926.b4452d56304_x86_64.tgz
WORKDIR /tmp
RUN wget ${ov_url}
RUN tar -xzf /tmp/*.tgz && \
OV_BUILD="$(find . -maxdepth 1 -type d -name "*openvino*" | grep -oP '(?<=_)\d+.\d+.\d.\d+')" && \
OV_YEAR="$(echo "$OV_BUILD" | grep -oP '^[^\d]*(\d+)')" && \
OV_FOLDER="$(find . -maxdepth 1 -type d -name "*openvino*")" && \
mkdir -p /opt/intel/openvino_"$OV_BUILD"/ && \
cp -rf "$OV_FOLDER"/* /opt/intel/openvino_"$OV_BUILD"/ && \
rm -rf /tmp/"$OV_FOLDER" && \
ln --symbolic /opt/intel/openvino_"$OV_BUILD"/ /opt/intel/openvino && \
rm -rf "${INTEL_OPENVINO_DIR}/tools/workbench" && rm -rf /tmp
RUN chmod 1777 /tmp
RUN ${INTEL_OPENVINO_DIR}/install_dependencies/install_openvino_dependencies.sh -y \
-c=python -c=core
#Optional 2.0: install ipex & itex
ARG tf_version=2.14.0
ARG itex_version=v2.13.0.0
ARG torch_version=2.1.0a0
ARG ipex_version=2.1.10+xpu
ARG torchvision=0.16.0a0
RUN pip3 install tensorflow==${tf_version} intel-extension-for-tensorflow[gpu];
RUN env -u no_proxy -u NO_PROXY python3 -m pip install \
torch==${torch_version} torchvision==${torchvision} \
intel_extension_for_pytorch==${ipex_version} \
--extra-index-url https://pytorch-extension.intel.com/release-whl/stable/xpu/us/
- Get Docker for your host OS
- Kindly duplicate the aforementioned Dockerfile and save as
Dockerfile.ubuntu
#Example build command
$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
#in the same directory as the dockerfile
$ docker build -t image:tag -f Dockerfile.ubuntu [--build-arg=<PROXY=xxx>] .
If Dockerfile method is not desired, you may install the AI software toolchains following the installation guides below.
- Intel® oneAPI Installation Guide
- OpenVINO™ Toolkit Installation Guide
- Intel® Extension for TensorFlow Installation Guide
- Intel® Extension for PyTorch Installation Guide
The user can run AI/ML workload on the installed software stack now.
Submit your questions, issues, bugs on the GitHub issues page.
See Intel's Security Center for information on how to report a potential security issue or vulnerability.