FlexML is an easy-to-use and flexible AutoML library for Python that simplifies the process of building machine learning models. It automates model selection and hyperparameter tuning, offering users the flexibility to customize the size of their experiments by allowing to train all available models in the library or only a subset of them for faster results, FlexML adapts to your needs!
At the moment, FlexML supports only regression and classification tasks and offers two experiment modes; 'quick' and 'wide' allowing users to choose between fitting a few of machine learning models or the full range of models available in the library. This flexibility extends to hyperparameter tuning as well, enabling a balance between speed and thoroughness.
To install FlexML, you can use pip:
pip install flexml# Experiment for a Regression problem for California House Value Prediction dataset
from flexml import Regression
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
# Load the California House Value Prediction dataset as a Pandas dataframe
df = fetch_california_housing(as_frame=True)['frame']
# Setup a regression experiment with 'quick' experiment_size for faster results by using less ml models, "wide" for all
# (check flexml/config/ml_models.py to check out to all ml models available in the library)
reg_exp = Regression(df, target_col="MedHouseVal", experiment_size="quick")
# Start the experiment with r2 evaluation metric (default)
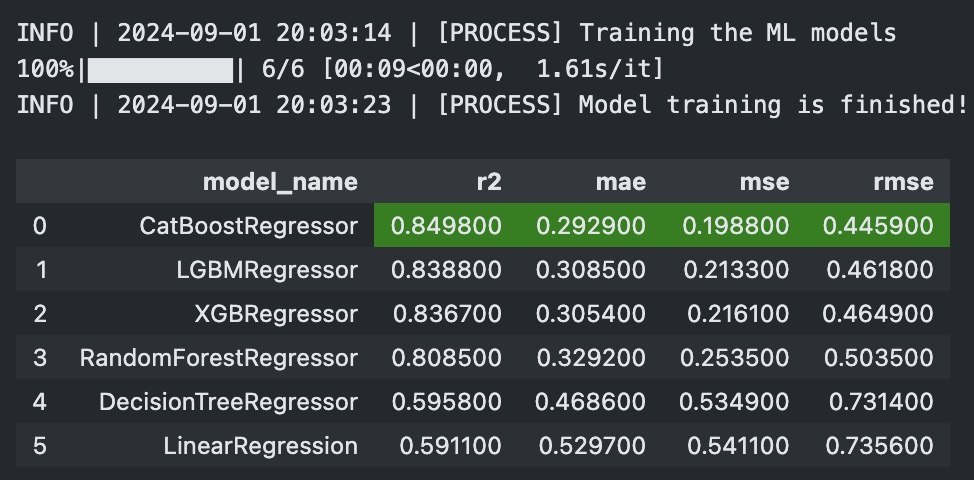
reg_exp.start_experiment(eval_metric="r2")--> Once start_experiment() process finishes, you will see the model leaderboard as below:
# Get the best model, you can pass 'eval_metric' param as well
best_model = reg_exp.get_best_models()
# Get the best model by name (Alternative)
_temp_ = reg_exp.get_model_by_name("LGBMRegressor")
print(best_model) # >>> <catboost.core.CatBoostRegressor object>
# Tune the best model with Randomized Search or pass a model object as param to the beginning
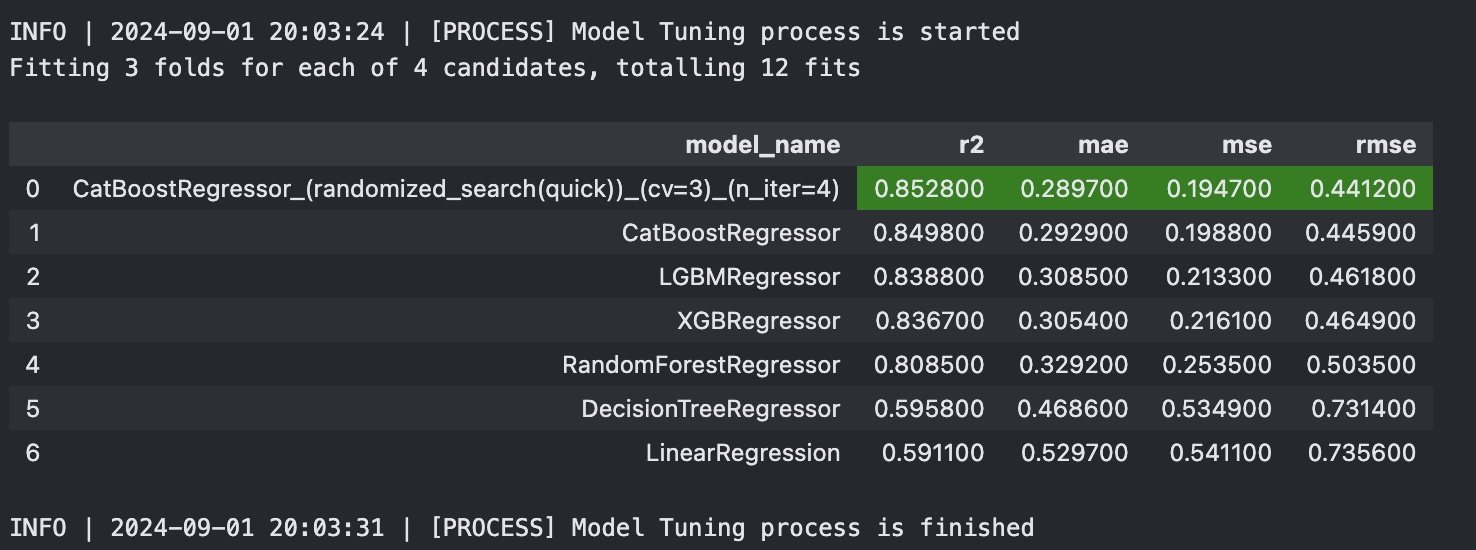
reg_exp.tune_model(tuning_method="randomized_search", tuning_size="quick", eval_metric="r2", n_iter=4)--> Once tune_model() process finishes, you will see the updated model leaderboard as below:
# Get the latest tuned model
tuned_model = reg_exp.tuned_model
# Alternatively, get it via get_model_by_name()
_temp_ = reg_exp.get_model_by_name("CatBoostRegressor_(randomized_search(quick))_(cv=3)_(n_iter=4)")
print(tuned_model) # >>> <catboost.core.CatBoostRegressor object>You can also take a look to jupyter notebook files in the 'notebooks' folder in the repository for more detailed explanations of the usage
- Fork the repository: Click on the 'Fork' button at the top right corner of the GitHub repository page
- Create a new branch: Name your branch descriptively based on the feature or fix you're working on
- Make your changes: Write code and tests to add your feature or fix the issue.
- You can take a look to tests folder in the repository to reach the current unittests
- Run tests: Ensure all existing and new tests pass.
- Submit a pull request: Open a pull request with a clear description of your changes.
- Regression
- Classification
- Model Tuning
- Automatic Data Labelling & Feature Engineering
- Time Series