Built with Git Tutor
This tutorial will walk you through the process of building of a simple todo-list with Flutter
Make sure to complete flutter installation
Execute in your terminal
flutter create todo_listFirst line is an import of material library provided by Flutter. This library is an implementation of various android components
📄 lib/main.dart
+ import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
This function is an entry point of flutter application. It calls just runApp, but we can do more in this function (like making your application full-screen).
📄 lib/main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
+
+ void main() => runApp(MyApp());
Let's actually do this 😏
📄 lib/main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
+ import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
- void main() => runApp(MyApp());
+ void main() {
+ SystemChrome.setEnabledSystemUIOverlays([]);
+ runApp(MyApp());
+ }
Every component in flutter is called widget. It could be either stateless (read - pure) or stateful (container for some state). Top-level app component should be a stateless components, so let's create one
📄 lib/main.dart
SystemChrome.setEnabledSystemUIOverlays([]);
runApp(MyApp());
}
+
+ class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {}
Every widget should override build function. It returns a hierarchy of your layout widgets (Container, Padding, Flex, etc) or your stateful widgets which contain some business logic
📄 lib/main.dart
runApp(MyApp());
}
- class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {}
+ class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
+ @override
+ Widget build(BuildContext context) {
+ return Container();
+ }
+ }
But in case of top-level App widget, it should return either CupertinoApp from 'package:flutter/material.dart', or MaterialApp from 'package:flutter/material.dart'
We'll use material in this tutorial
📄 lib/main.dart
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
- return Container();
+ return MaterialApp();
}
}
Let's add title
📄 lib/main.dart
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
- return MaterialApp();
+ return MaterialApp(
+ title: 'Todo List',
+ );
}
}
Let's also make a Scaffold a home of our application
Scaffold is a helper class from material library which implements basic app layout (app bar, floating action button)
📄 lib/main.dart
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Todo List',
+ home: Scaffold(
+ ),
);
}
}
Now we need to add an application header which will display our app title
📄 lib/main.dart
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Todo List',
home: Scaffold(
+ appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Todo List')),
),
);
}
And finally the body of our app is todolist itself. Let's just add this line and implement the class later
📄 lib/main.dart
title: 'Todo List',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Todo List')),
+ body: TodoList(),
),
);
}
Basic statefull widget will look like this
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class TodoList extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_TodoListState createState() => _TodoListState();
}
class _TodoListState extends State<TodoList> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container();
}
}
We also need to import our TodoList widget
📄 lib/main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
+ import 'package:todo_list/todo_list.dart';
+
void main() {
SystemChrome.setEnabledSystemUIOverlays([]);
runApp(MyApp());
Now let's describe Todo entity as class
📄 lib/todo.dart
class Todo {
Todo({this.title, this.isDone = false});
String title;
bool isDone;
}
and import it to TodoList
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
+ import 'package:todo_list/todo.dart';
class TodoList extends StatefulWidget {
@override
Now we need to extend our TodoList state and add a list of todos
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
}
class _TodoListState extends State<TodoList> {
+ List<Todo> todos = [];
+
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container();
Let's use ListView to render our todo items.
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
class _TodoListState extends State<TodoList> {
List<Todo> todos = [];
+ _buildItem() {}
+
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
- return Container();
+ return ListView.builder(
+ itemBuilder: _buildItem,
+ itemCount: todos.length,
+ );
}
}
Now we're going to implement _buildItem which will be called each time todo has to be rendered
We'll use CheckboxListTile from material library as it has everything we need (checkbox indicating whether todo is completed and title)
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
class _TodoListState extends State<TodoList> {
List<Todo> todos = [];
- _buildItem() {}
+ Widget _buildItem(BuildContext context, int index) {
+ final todo = todos[index];
+
+ return CheckboxListTile(
+ );
+ }
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
Value indicates if list item should be checked
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
final todo = todos[index];
return CheckboxListTile(
+ value: todo.isDone,
);
}
Title is a widget which should be rendered in first row. Typically it is a Text widget
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
return CheckboxListTile(
value: todo.isDone,
+ title: Text(todo.title),
);
}
Finally we need to handle taps on every list item
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
return CheckboxListTile(
value: todo.isDone,
title: Text(todo.title),
+ onChanged: (bool isChecked) {
+ _toggleTodo(todo, isChecked);
+ },
);
}
_toggleTodo implementation is pretty straightforward
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
class _TodoListState extends State<TodoList> {
List<Todo> todos = [];
+ _toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
+ todo.isDone = isChecked;
+ }
+
Widget _buildItem(BuildContext context, int index) {
final todo = todos[index];
Let's try to add some mock todos and see if they are rendered correctly
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
}
class _TodoListState extends State<TodoList> {
- List<Todo> todos = [];
+ List<Todo> todos = [
+ Todo(title: 'Learn Dart'),
+ Todo(title: 'Try Flutter'),
+ Todo(title: 'Be amazed'),
+ ];
_toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
todo.isDone = isChecked;
Ok, everything is rendered correctly, but nothing happens when we tap on items, weird..
Let's add a debug print and see if the handler even called
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
];
_toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
+ print('${todo.title} ${todo.isDone}');
+
todo.isDone = isChecked;
}
Console shows items are checked, value isChecked is true, but checkbox is never rendered
The problem is that we modify our entities, but flutter has no idea this happened, so we need to call setState. (Hi there, react fans! 😏)
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
];
_toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
- print('${todo.title} ${todo.isDone}');
-
- todo.isDone = isChecked;
+ setState(() {
+ todo.isDone = isChecked;
+ });
}
Widget _buildItem(BuildContext context, int index) {
Now we're good with rendering and updates, time to get rid of mock items and add some ui to add new todos.
Let's add a FloatingActionButton
📄 lib/main.dart
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Todo List')),
body: TodoList(),
+ floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
+ child: Icon(Icons.add),
+ ),
),
);
}
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
}
class _TodoListState extends State<TodoList> {
- List<Todo> todos = [
- Todo(title: 'Learn Dart'),
- Todo(title: 'Try Flutter'),
- Todo(title: 'Be amazed'),
- ];
+ List<Todo> todos = [];
_toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
setState(() {
Ok, but what should we do in onPressed? We need to access a state of TodoList and messing with children state directly from parent statelsess widget doesn't sound like a good idea
📄 lib/main.dart
body: TodoList(),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
child: Icon(Icons.add),
+ onPressed: () {
+ // 😢
+ },
),
),
);
So let's just move Scaffold widget down to TodoList
📄 lib/main.dart
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Todo List',
- home: Scaffold(
- appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Todo List')),
- body: TodoList(),
- floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
- child: Icon(Icons.add),
- onPressed: () {
- // 😢
- },
- ),
- ),
+ home: TodoList(),
);
}
}
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
);
}
+ _addTodo() {}
+
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
- return ListView.builder(
- itemBuilder: _buildItem,
- itemCount: todos.length,
+ return Scaffold(
+ appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Todo List')),
+ body: ListView.builder(
+ itemBuilder: _buildItem,
+ itemCount: todos.length,
+ ),
+ floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
+ child: Icon(Icons.add),
+ onPressed: _addTodo,
+ ),
);
}
}
Now we can show a dialog when user taps on FloatingActionButton
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
);
}
- _addTodo() {}
+ _addTodo() {
+ showDialog(
+ context: context,
+ builder: (BuildContext context) {
+ return AlertDialog(
+ title: Text('New todo'),
+ );
+ },
+ );
+ }
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
Dialog will contain a text input:
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return AlertDialog(
title: Text('New todo'),
+ content: TextField(),
);
},
);
and two action buttons: Cancel and Add
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
return AlertDialog(
title: Text('New todo'),
content: TextField(),
+ actions: <Widget>[
+ FlatButton(
+ child: Text('Cancel'),
+ ),
+ FlatButton(
+ child: Text('Add'),
+ ),
+ ],
);
},
);
Dialogs are not just overlays, but actually a routes, so to handle Cancel action we can just call .pop on Navigator of current context
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
actions: <Widget>[
FlatButton(
child: Text('Cancel'),
+ onPressed: () {
+ Navigator.of(context).pop();
+ },
),
FlatButton(
child: Text('Add'),
Now we need to access the value of a TextField to create a Todo
To do this we need to create a TextEditingController
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
class _TodoListState extends State<TodoList> {
List<Todo> todos = [];
+ TextEditingController controller = new TextEditingController();
+
_toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
setState(() {
todo.isDone = isChecked;
and supply it to the TextField
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return AlertDialog(
title: Text('New todo'),
- content: TextField(),
+ content: TextField(controller: controller),
actions: <Widget>[
FlatButton(
child: Text('Cancel'),
now in onPressed of Add action we can log the value of a TextField and clear it
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
),
FlatButton(
child: Text('Add'),
+ onPressed: () {
+ print(controller.value.text);
+ controller.clear();
+ },
),
],
);
Finally let's actually create new todo and add it to the list of existing todos (don't forget to wrap the code with setState)
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
FlatButton(
child: Text('Add'),
onPressed: () {
- print(controller.value.text);
- controller.clear();
+ setState(() {
+ final todo = new Todo(title: controller.value.text);
+
+ todos.add(todo);
+ controller.clear();
+
+ Navigator.of(context).pop();
+ });
},
),
],
Tiny UX improvement: make keyboard pop automatically by passing autofocus: true to a TextField
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return AlertDialog(
title: Text('New todo'),
- content: TextField(controller: controller),
+ content: TextField(
+ controller: controller,
+ autofocus: true,
+ ),
actions: <Widget>[
FlatButton(
child: Text('Cancel'),
TodoListis working, but todo_list.dart is kinda messy and hard to read. The most complex method is _addTodo, so let's start with rewriting it. It seems like we can move the AlertDialog to a separate widget, but we can't do this right now, as we rely on setState from parent widget. Instead we can pass a freshly created todo to a Navigator.pop
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
}
_addTodo() {
- showDialog(
+ showDialog<Todo>(
context: context,
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return AlertDialog(
FlatButton(
child: Text('Add'),
onPressed: () {
- setState(() {
- final todo = new Todo(title: controller.value.text);
+ final todo = new Todo(title: controller.value.text);
+ controller.clear();
- todos.add(todo);
- controller.clear();
-
- Navigator.of(context).pop();
- });
+ Navigator.of(context).pop(todo);
},
),
],
In order to be able to receive the Todo in _addTodo method we need to make it async and await showDialog function result (which will be null in case it was dismissed and instance of Todo otherwise)
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
);
}
- _addTodo() {
- showDialog<Todo>(
+ _addTodo() async {
+ final todo = await showDialog<Todo>(
context: context,
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return AlertDialog(
And move back the logic with state update
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
);
},
);
+
+ if (todo != null) {
+ setState(() {
+ todos.add(todo);
+ });
+ }
}
@override
Now we don't have any dependencies on a parent widget, so we can extract AlertDialog to a separate widget
📄 lib/new_todo_dialog.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:todo_list/todo.dart';
class NewTodoDialog extends StatelessWidget {
final controller = new TextEditingController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return AlertDialog(
title: Text('New todo'),
content: TextField(
controller: controller,
autofocus: true,
),
actions: <Widget>[
FlatButton(
child: Text('Cancel'),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).pop();
},
),
FlatButton(
child: Text('Add'),
onPressed: () {
final todo = new Todo(title: controller.value.text);
controller.clear();
Navigator.of(context).pop(todo);
},
),
],
);
}
}
and use it inside TodoList
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:todo_list/todo.dart';
+ import 'package:todo_list/new_todo_dialog.dart';
+
class TodoList extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_TodoListState createState() => _TodoListState();
class _TodoListState extends State<TodoList> {
List<Todo> todos = [];
- TextEditingController controller = new TextEditingController();
-
_toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
setState(() {
todo.isDone = isChecked;
final todo = await showDialog<Todo>(
context: context,
builder: (BuildContext context) {
- return AlertDialog(
- title: Text('New todo'),
- content: TextField(
- controller: controller,
- autofocus: true,
- ),
- actions: <Widget>[
- FlatButton(
- child: Text('Cancel'),
- onPressed: () {
- Navigator.of(context).pop();
- },
- ),
- FlatButton(
- child: Text('Add'),
- onPressed: () {
- final todo = new Todo(title: controller.value.text);
- controller.clear();
-
- Navigator.of(context).pop(todo);
- },
- ),
- ],
- );
+ return NewTodoDialog();
},
);
Next step – extract todo list component
List istself could also be treated as stateless widget, state related logic could be handled by parent
So let's first rename TodoList to TodoListScreen
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
import 'package:todo_list/new_todo_dialog.dart';
- class TodoList extends StatefulWidget {
+ class TodoListScreen extends StatefulWidget {
@override
- _TodoListState createState() => _TodoListState();
+ _TodoListScreenState createState() => _TodoListScreenState();
}
- class _TodoListState extends State<TodoList> {
+ class _TodoListScreenState extends State<TodoListScreen> {
List<Todo> todos = [];
_toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
rename file
📄 lib/todo_list_screen.dart => lib/todo_list.dart
and fix import
📄 lib/main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
- import 'package:todo_list/todo_list.dart';
+ import 'package:todo_list/todo_list_screen.dart';
void main() {
SystemChrome.setEnabledSystemUIOverlays([]);
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Todo List',
- home: TodoList(),
+ home: TodoListScreen(),
);
}
}
Let's move list related logic to a separate stateless widget
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class TodoList extends StatelessWidget {
_toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
setState(() {
todo.isDone = isChecked;
});
}
Widget _buildItem(BuildContext context, int index) {
final todo = todos[index];
return CheckboxListTile(
value: todo.isDone,
title: Text(todo.title),
onChanged: (bool isChecked) {
_toggleTodo(todo, isChecked);
},
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return ListView.builder(
itemBuilder: _buildItem,
itemCount: todos.length,
);
}
}
and remove this logic from TodoListScreen
📄 lib/todo_list_screen.dart
import 'package:todo_list/todo.dart';
import 'package:todo_list/new_todo_dialog.dart';
+ import 'package:todo_list/todo_list.dart';
class TodoListScreen extends StatefulWidget {
@override
class _TodoListScreenState extends State<TodoListScreen> {
List<Todo> todos = [];
- _toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
- setState(() {
- todo.isDone = isChecked;
- });
- }
-
- Widget _buildItem(BuildContext context, int index) {
- final todo = todos[index];
-
- return CheckboxListTile(
- value: todo.isDone,
- title: Text(todo.title),
- onChanged: (bool isChecked) {
- _toggleTodo(todo, isChecked);
- },
- );
- }
-
_addTodo() async {
final todo = await showDialog<Todo>(
context: context,
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Todo List')),
- body: ListView.builder(
- itemBuilder: _buildItem,
- itemCount: todos.length,
- ),
+ body: TodoList(),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
child: Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: _addTodo,
Now let's review our TodoList widget
It is missing Todo class import
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
+ import 'package:todo_list/todo.dart';
+
class TodoList extends StatelessWidget {
_toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
setState(() {
It also doesn't have todos, so let's pass them from parent widget
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
import 'package:todo_list/todo.dart';
class TodoList extends StatelessWidget {
+ TodoList({@required this.todos});
+
+ final List<Todo> todos;
+
_toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
setState(() {
todo.isDone = isChecked;
📄 lib/todo_list_screen.dart
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Todo List')),
- body: TodoList(),
+ body: TodoList(
+ todos: todos,
+ ),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
child: Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: _addTodo,
_toggleTodo method relies on setState, so let's move it back to parent
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
final List<Todo> todos;
- _toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
- setState(() {
- todo.isDone = isChecked;
- });
- }
-
Widget _buildItem(BuildContext context, int index) {
final todo = todos[index];
📄 lib/todo_list_screen.dart
class _TodoListScreenState extends State<TodoListScreen> {
List<Todo> todos = [];
+ _toggleTodo(Todo todo, bool isChecked) {
+ setState(() {
+ todo.isDone = isChecked;
+ });
+ }
+
_addTodo() async {
final todo = await showDialog<Todo>(
context: context,
and pass it down to TodoList as a property
📄 lib/todo_list.dart
import 'package:todo_list/todo.dart';
+ typedef ToggleTodoCallback = void Function(Todo, bool);
+
class TodoList extends StatelessWidget {
- TodoList({@required this.todos});
+ TodoList({@required this.todos, this.onTodoToggle});
final List<Todo> todos;
+ final ToggleTodoCallback onTodoToggle;
Widget _buildItem(BuildContext context, int index) {
final todo = todos[index];
value: todo.isDone,
title: Text(todo.title),
onChanged: (bool isChecked) {
- _toggleTodo(todo, isChecked);
+ onTodoToggle(todo, isChecked);
},
);
}
📄 lib/todo_list_screen.dart
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Todo List')),
body: TodoList(
todos: todos,
+ onTodoToggle: _toggleTodo,
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
child: Icon(Icons.add),
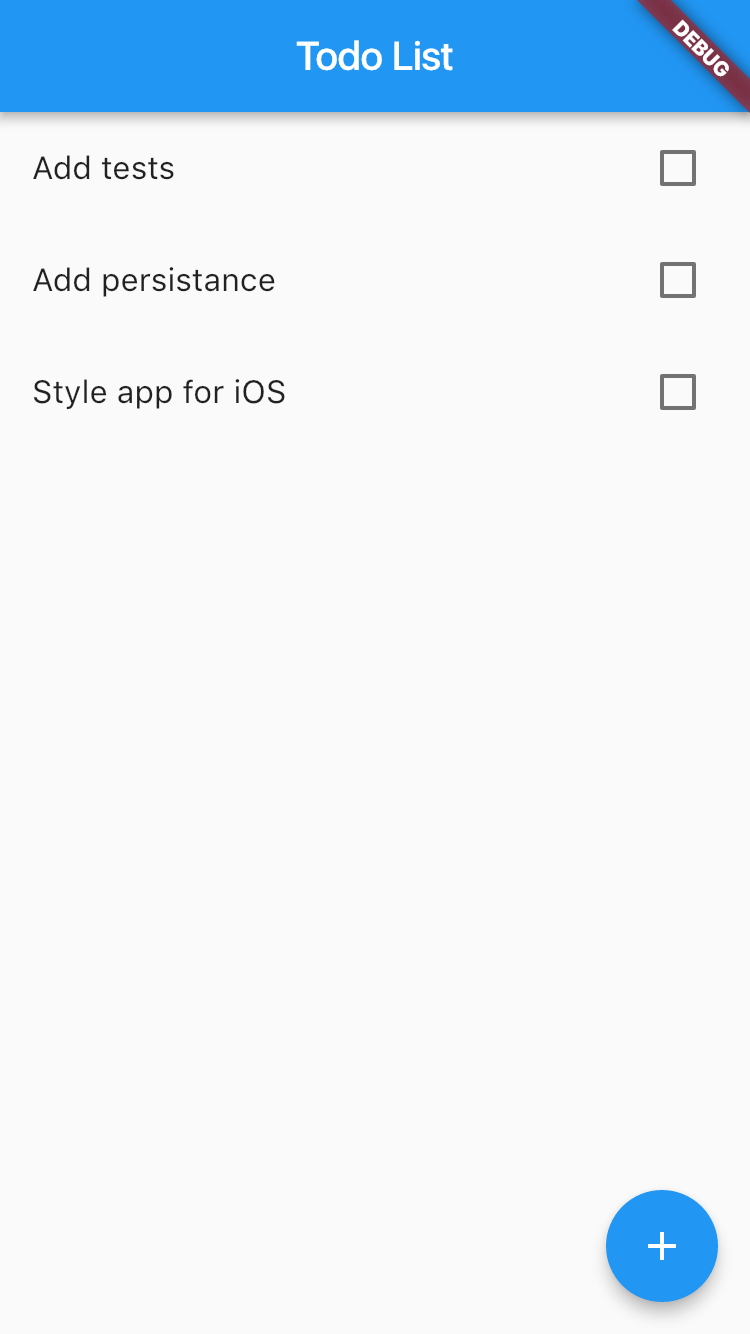
Yay! We have working and kinda well-structured Todo List application written in Flutter 🎉
But there is still a lot of work to do:
See you in next tutorials! 👋
Built with Git Tutor