📘 Documentation | Demo | Website | Discord
Stack is an open-source, self-hostable, and highly customizable authentication and user management system.
We provide frontend and backend libraries for Next.js, React, and JavaScript. You can set it up in one minute and scale with the project as it grows. Think of it as Supabase Auth or next-auth, but better.
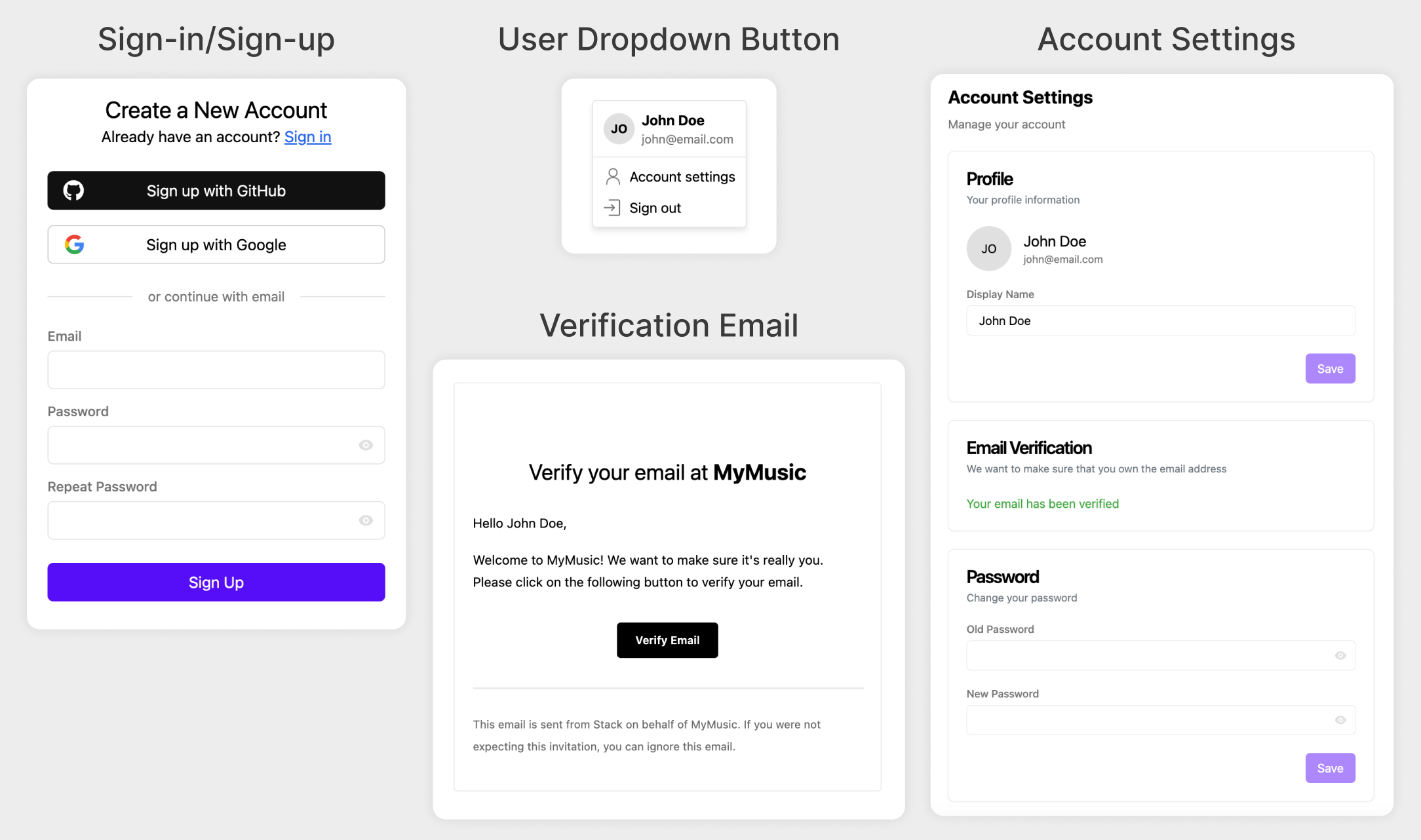
Here are some of the components you get out-of-the-box:
- Composable React components & hooks
- OAuth (Google, Facebook, GitHub, etc.)
- Email and password authentication (with email verification and password reset)
- Easy to set up with proxied providers (no need to sign up and create OAuth endpoints yourself on all the providers)
- User management & analytics
- User-associated metadata with client-/server-specific permissions
- Out-of-the-box Dark/Light mode support
- suports switching out the underlying UI library, support MUI Joy out of the box
- 100% open-source!
Currently, only Next.js is supported, but we are working on adding other frameworks.
We all know how much overhead there is when starting a new project. Developers need to handle so many things that aren't even part of their core business, like user authentication, user profiles, payments, dashboards, hosting, and more. Our vision is to build a full-stack framework that handles all of this out-of-the-box with less than 10 minutes of setup, so developers can focus on what they really want to build. Authentication is the first step towards this vision.
- Organization, groups, and roles
- More pre-built UI components (user profile display/edit, onboarding page)
- Fraud/bot prevention
- Feature-rich email/notification system
- Cross-platform/language supports
To get started with Stack, you need to create a Next.js project using the App router. Then, you can install Stack by running the following command:
npm install @stackframe/stackFor setup, refer to our documentation.
This is for you if you want to contribute to the Stack project.
Make sure you have pnpm installed alongside Node v20. Next, ensure you created .env.local files by copying .env in each sub-package in the packages folder and filling out the variables. You will need to start a Postgres database; you can do this with the following command:
docker run -it --rm -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=password -p "5432:5432" postgresThen:
pnpm install
# Run code generation (repeat this after eg. changing the Prisma schema)
pnpm run codegen
# After starting a Postgres database and filling the corresponding variables in .env.local, push the schema to the database:
# for production databases, use `deploy` instead. See: https://www.prisma.io/docs/orm/prisma-migrate/understanding-prisma-migrate/mental-model#prisma-migrate-in-a-staging-and-production-environment
pnpm run prisma:server migrate reset
# Start the dev server
pnpm run devYou can also open Prisma Studio to see the database interface and edit data directly:
pnpm run prisma:server studioIf you make changes to the Prisma schema, you need to run the following command to create a migration:
pnpm run prisma:server migrate dev