PostgreSQL Database implementation for A Used Car E-commerce data management.
- Users can offer one or multiple used cars.
- Before offering their used car, users are required to provide their complete data, including their name, phone number, and domicile.
- Users can offer their used car through advertisements on the website.
- The advertisements include information such as brand, car model, car body type, transmission system, model year, color, and mileage of the car being offered.
- Users can search for offered cars based on seller location, car brand, and car body type.
- Users can bid for their desired cars if the price is negotiable.
- Car purchasing transactions are conducted outside the application.
The primary objective of this system is to:
- Design and manage a database that stores user and car details for the e-commerce platform.
- Maintain a comprehensive database of car advertisements.
- Capture and record user bids.
- Provides support for car searching based on seller location, brand, and car body type.
This database consists of following tables.
| table name | description |
|---|---|
| users | storing users information such as name, phone number, and domicile |
| cities | storing cities information such as city name, latitude, and longitude for specifying location |
| ads | storing advertisment information including details about the car, the ad poster, and the time the ad was created |
| bids | storing buyer bids information such as ad of car being bidden, bid price, and bid date |
| cars | storing details about the car including, brand, model, body type, year of manufacture, and price |
CREATE TABLE cars (
car_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
brand VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
model VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
body_type VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
price INT NOT NULL CHECK (price_idr > 0),
year INT NOT NULL
);CREATE TABLE cities (
city_id PRIMARY KEY,
city_name VARCHAR(12) NOT NULL,
latitude NUMERIC(9,6) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
longitude NUMERIC(9,6) NOT NULL UNIQUE
);CREATE TABLE users (
user_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
phone_number VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
city_id INT NOT NULL REFERENCES cities(city_id),
role VARCHAR(6) NOT NULL CHECK (role in ('Seller', 'Buyer'))
);CREATE TABLE ads (
ad_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
user_id INT NOT NULL REFERENCES users(user_id),
car_id INT NOT NULL REFERENCES cars(car_id),
title VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
description TEXT NOT NULL,
color VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
transmission VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL CHECK (transmission in ('Automatic', 'Manual')),
mileage INT NOT NULL,
negotiable BOOLEAN NOT NULL,
post_date TIMESTAMP(0) NOT NULL
);--create trigger function for ensuring that user_id in ads table is "Seller"
CREATE FUNCTION validate_seller_role()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
BEGIN
IF EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM users
WHERE user_id = NEW.user_id AND role = 'Seller'
) THEN
RETURN NEW;
ELSE
RAISE EXCEPTION 'User must have role "Seller"';
END IF;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
--create trigger object for validate_seller_role()
CREATE TRIGGER ads_seller_role_trigger
BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE ON ads
FOR EACH ROW
EXECUTE FUNCTION validate_seller_role();CREATE TABLE bids (
bid_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
user_id INT NOT NULL REFERENCES users(user_id),
ad_id INT NOT NULL REFERENCES ads(ad_id),
bid_price INT NOT NULL CHECK (bid_price > 0),
bid_date TIMESTAMP(0) NOT NULL
);--create trigger function for ensuring that user_id in bids table is "Buyer"
CREATE FUNCTION validate_buyer_role()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
BEGIN
IF EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM users
WHERE user_id = NEW.user_id AND role = 'Buyer'
) THEN
RETURN NEW;
ELSE
RAISE EXCEPTION 'User must have role "Buyer"';
END IF;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
--create trigger object for validate_buyer_role()
CREATE TRIGGER bids_buyer_role_trigger
BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE ON bids
FOR EACH ROW
EXECUTE FUNCTION validate_buyer_role();--create trigger function for ensuring that ad_id in bids table has value "true" in ads.negotiable field
CREATE FUNCTION validate_negotiable_ad()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
BEGIN
IF EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM ads
WHERE ad_id = NEW.ad_id AND negotiable = true
) THEN
RETURN NEW;
ELSE
RAISE EXCEPTION 'Car price must be negotiable';
END IF;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
--create trigger object for validate_negotiable_ad()
CREATE TRIGGER bids_negotiable_ad_trigger
BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE ON bids
FOR EACH ROW
EXECUTE FUNCTION validate_negotiable_ad();Data in table users, ads, and bids are generated by Python Faker and Python Random Module. Generated data is written into a csv file and imported to postgreSQL database.
def save_to_csv(name, cols, rows):
"""
A function for saving generated data to csv file
Args:
name (str) = csv file name
cols (list) = column name
rows (list) = generated data that will be inputted to table as rows
return:
-
"""
with open(file= name, mode= 'w', newline= '' ) as csvfile:
csv_dict_writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames= cols)
csv_dict_writer.writeheader()
csv_dict_writer.writerows(rows)from faker import Faker
import random
from csv_helper import *
fake = Faker('id_ID')
def generate_dummy_user(n):
"""
A function for generating user data.
name and phone number of the user is generated by Faker.
Args
n (int) : desired number of users to be generated
Return
user_data (list)
"""
city_ids = [
3171,
3172,
3173,
3174,
3175,
3573,
3578,
3471,
3273,
1371,
1375,
6471,
6472,
7371,
5171,
]
user_data = []
for i in range(1,n+1):
user_data.append({
"user_id": i,
"name": fake.name(),
"phone_number": fake.phone_number(),
"city_id": random.choice(city_ids),
"role" :random.choice(["Buyer", "Seller"])
})
return user_data
#define column for user table
user_cols = ['user_id', 'name', 'phone_number', 'city_id', 'role']
#generate rows for user table
user_rows = generate_dummy_user(100)
#save to user.csv
save_to_csv('csv/users.csv', user_cols, user_rows)from faker import Faker
import random
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from csv_helper import *
fake = Faker('id_ID')
#open user.csv to get user id data
with open('csv/users.csv', mode='r') as file:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(file)
user_ids = [row["user_id"] for row in csv_reader if row["role"] == "Seller"]
#open car_product.csv to get car data
with open('csv/car_product.csv', mode='r') as file:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(file)
cars_data = []
for row in csv_reader:
cars_data.append({
"product_id": row["product_id"],
"brand" : row["brand"],
"model" : row["model"],
"body_type" : row["body_type"],
"year" : row["year"],
"price" : row["price"]
})
def generate_dummy_ads(n, cars_data, users_data):
"""
A function for generating advertisment data.
Args
n (int) : desired number of ads to be generated
users_data (list) : list of user id
cars_data (list) : list of cars data
Return
ads_data (list)
"""
ads_data = []
for i in range(1, n+1):
ad_id = i
user_id = random.choice(users_data)
index_car_data = random.randint(0, (len(cars_data)-1))
car_id = cars_data[index_car_data]["product_id"]
title = f'{cars_data[index_car_data]["year"]} {cars_data[index_car_data]["model"]} {cars_data[index_car_data]["body_type"]}'
color = random.choice(["Merah", "Hitam", "Silver", "Putih", "Biru", "Abu-abu", "Hijau", "Oranye", "Coklat", "Kuning"])
mileage = random.randint(10000, 80000)
transmission = random.choice(["Automatic", "Manual"])
negotiable = random.choice([True, False])
desc = f'Warna: {color} Jarak tempuh: {mileage} Tipe mobil: {transmission} Harga: {cars_data[index_car_data]["price"]} Bisa nego: {"Iya" if negotiable else "Tidak"}'
post_date = fake.date_time_between_dates(datetime_start =datetime(2022, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0), datetime_end =datetime(2023, 1, 1, 23, 59, 59)).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
ads_data.append({
"ad_id" : ad_id,
"user_id" : user_id,
"car_id" : car_id,
"title" : title,
"description" : desc,
"color": color,
"transmission" : transmission,
"mileage" : mileage,
"negotiable" : negotiable,
"post_date" : post_date,
})
return ads_data
#define columns for ads table
ad_cols = ["ad_id", "user_id", "car_id", "title", "description", "color", "transmission", "mileage", "negotiable", "post_date"]
#generate rows for ads table
ad_rows = generate_dummy_ads(200, cars_data, user_ids)
#save to ads.csv
save_to_csv("csv/ads.csv", ad_cols, ad_rows)import csv
import random
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from csv_helper import *
#open user.csv to get user id data
with open('csv/users.csv', mode='r') as file:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(file)
list_user_id = [row["user_id"] for row in csv_reader if row["role"] == "Buyer"]
#open ads.csv to get ads data. Only retrieve needed information for further processing
with open('csv/ads.csv', mode='r') as file:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(file)
ads_data = []
for row in csv_reader:
ads_data.append(
{
"ad_id" : row["ad_id"],
"car_id" : row["car_id"],
"negotiable" : row["negotiable"],
"post_date" : row["post_date"]
}
)
#open car_product.csv to get car data. Only retrieve needed information for further processing
with open('csv/car_product.csv', mode='r') as file:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(file)
cars_data = []
for row in csv_reader:
cars_data.append({
"product_id": row["product_id"],
"price" : row["price"]
})
def generate_price_bid(ad_id, ads, cars_data):
"""
A function for generating bid price lower or same as car price
Args
ad_id (str)
cars_data(list) :list of cars data
ads(list): list of ads data
Return
bid price (int)
"""
car_id = ""
for item in ads:
if item["ad_id"] == ad_id:
car_id = item["car_id"]
break
car_price = 0
for item in cars_data:
if item["product_id"] == car_id:
car_price = int(item["price"])
return random.randint(car_price - 30_000_000, car_price)
def generate_bids_date(ads, ad_id):
"""
A function for generating bid date after ad post date
Args
ad_id (str)
ads(list): list of ads data
Return
bid date (str)
"""
post_datetime = ""
for item in ads:
if item["ad_id"] == ad_id:
post_datetime = item["post_date"]
break
base_date = datetime.strptime(post_datetime, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
random_date = base_date + timedelta(days=random.randint(1,120), hours=random.randint(0,23), minutes=random.randint(0,59), seconds=random.randint(0,59))
return random_date.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
def generate_dummy_bids(n, users, ads):
"""
A function for generating bids data.
Args
n (int) : desired number of bids to be generated
users (list) : list of user id
ads (list) : list of ads data
Return
bids_data (list)
"""
negotiable_cars = [item for item in ads if item["negotiable"] == 'True']
if len(negotiable_cars) == 0:
print("No negotiable car available")
return
bids_data = []
for i in range(1, n+1):
bid_id = i
ad_id = random.choice(negotiable_cars)["ad_id"]
user_id = random.choice(users)
bid_price = generate_price_bid(ad_id, negotiable_cars, cars_data)
bid_date = generate_bids_date(negotiable_cars, ad_id)
bids_data.append({
"bid_id" : bid_id,
"user_id" : user_id,
"ad_id" : ad_id,
"bid_price" : bid_price,
"bid_date" : bid_date,
})
return bids_data
#define columns for bids table
bid_cols = ["bid_id", "user_id", "ad_id", "bid_price", "bid_date"]
#generate rows for bids table
bid_rows = generate_dummy_bids(400, list_user_id, ads_data)
#save to bids.csv
save_to_csv("csv/bids.csv", bid_cols, bid_rows)import csv
import psycopg2
from psycopg2 import Error
#connect to postgreSQL database
try:
connection = psycopg2.connect(
#change the value according to your pgAdmin settings
user="user",
password="password",
host="host",
port="port",
database="database_name"
)
cursor = connection.cursor()
except (Exception, Error) as error:
print("Error while connecting to PostgreSQL", error)
def insert_user_dummy(filename):
"""
A function for inputing user data from csv file to posgreSQL database.
Args:
filename (str)
Return:
-
"""
with open(f'{filename}', 'r') as file:
csv_data = csv.reader(file)
next(csv_data)
for row in csv_data:
name = row[1]
phone = row[2]
city_id = row[3]
role = row[4]
insert_query = f"INSERT INTO users (name, phone_number, city_id, role) VALUES ('{name}', '{phone}', '{city_id}', '{role}');"
cursor.execute(insert_query)
connection.commit()
def insert_ads_dummy(filename):
"""
A function for inputing ads data from csv file to posgreSQL database.
Args:
filename (str)
Return:
-
"""
with open(f'{filename}', 'r') as file:
csv_data = csv.reader(file)
next(csv_data)
for row in csv_data:
user_id = row[1]
car_id = row[2]
title = row[3]
description = row[4]
color = row[5]
transmission = row[6]
mileage = row[7]
negotiable = row[8]
post_date = row[9]
insert_query = f"INSERT INTO ads (user_id, car_id, title, negotiable, description, post_date, color, transmission, mileage) VALUES ('{user_id}', '{car_id}', '{title}', '{negotiable}', '{description}', '{post_date}', '{color}', '{transmission}', {mileage});"
cursor.execute(insert_query)
connection.commit()
def insert_bids_dummy(filename):
"""
A function for inputing bids data from csv file to posgreSQL database.
Args:
filename (str)
Return:
-
"""
with open(f'{filename}', 'r') as file:
csv_data = csv.reader(file)
next(csv_data)
for row in csv_data:
user_id = row[1]
ad_id = row[2]
bid_price = row[3]
bid_date = row[4]
insert_query = f"INSERT INTO bids (user_id, ad_id, bid_price, bid_date) VALUES ('{user_id}', '{ad_id}', '{bid_price}', '{bid_date}');"
cursor.execute(insert_query)
connection.commit()
insert_user_dummy("csv/users.csv")
insert_ads_dummy("csv/ads.csv")
insert_bids_dummy("csv/bids.csv")Following are example of transactional queries you can do on this database.
SELECT
car_id,
brand,
model,
year,
price
FROM cars
WHERE year >= '2015'
ORDER BY year;INSERT INTO bids (user_id, ad_id, bid_price, bid_date)
VALUES (19, 86, 90000000, current_timestamp);Viewing all cars from one user with name Ibrani Usada and ordering the result from most recent posted car
SELECT
c.car_id,
c.brand,
c.model,
c.year,
c.price,
a.post_date
FROM cars c
INNER JOIN ads a
USING(car_id)
INNER JOIN users u
USING(user_id)
WHERE u.name = 'Ibrani Usada'
ORDER BY a.post_date DESC;SELECT
car_id,
brand,
model,
year,
price
FROM cars
WHERE model ILIKE '%yaris%'
ORDER BY price;--create function for calculaing haversine distance
CREATE FUNCTION haversine_distance(lat1 NUMERIC, lon1 NUMERIC, lat2 NUMERIC, lon2 NUMERIC)
RETURNS FLOAT AS $$
DECLARE
rad_lat1 float := radians(lat1);
rad_lon1 float := radians(lon1);
rad_lat2 float := radians(lat2);
rad_lon2 float := radians(lon2);
dlon float := rad_lon2 - rad_lon1;
dlat float := rad_lat2 - rad_lat1;
a float;
b float;
r float := 6371;
distance float;
BEGIN
a := sin(dlat/2)^2 + cos(rad_lat1) * cos(rad_lat2) * sin(dlon/2)^2;
b := 2 * asin(sqrt(a));
distance := r * b;
RETURN distance;
END;
$$
LANGUAGE plpgsql;
--search nearest car from city with id 3173
SELECT ca.car_id, ca.brand, ca.model, ca.year, ca.price, haversine_distance(
(SELECT latitude FROM cities WHERE city_id = 3173),
(SELECT longitude FROM cities WHERE city_id = 3173),
ci.latitude,
ci.longitude) AS distance
FROM cities ci
INNER JOIN users u
USING (city_id)
INNER JOIN ads a
USING (user_id)
INNER JOIN cars ca
USING (car_id)
ORDER BY distance;Following are example of Analytical queries you can do on this database.
SELECT c.model AS model, COUNT(DISTINCT ad_id) AS count_product, COUNT(bid_id) AS count_bid
FROM ads a
LEFT JOIN cars c
USING (car_id)
LEFT JOIN bids b
USING (ad_id)
GROUP BY model
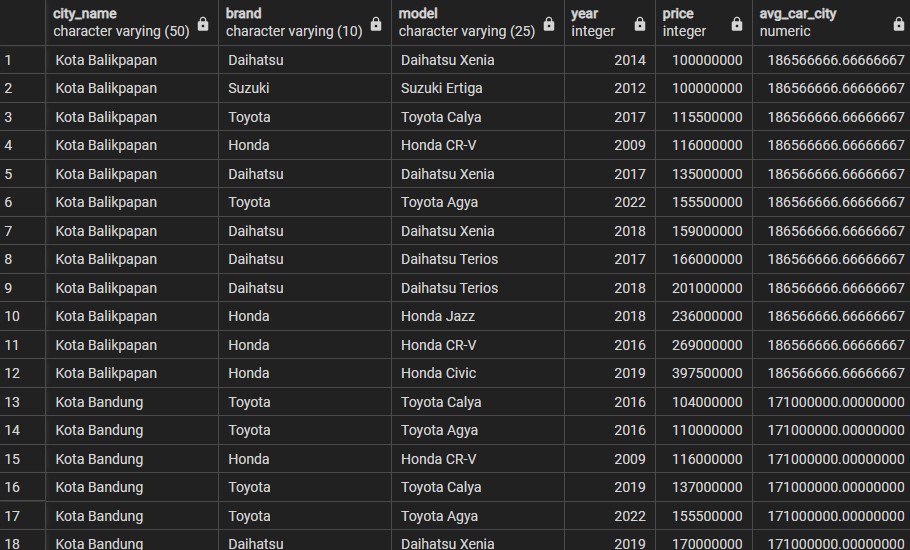
ORDER BY count_bid DESC;with price_and_avg_price as (
SELECT ci.city_name, c.brand, c.model, c.year, c.price,
AVG(c.price) OVER(PARTITION BY ci.city_name ORDER BY c.price ASC RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING)
AS avg_car_city,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY city_name, brand, model, year, price) AS rn
FROM cars c
INNER JOIN ads a
USING (car_id)
INNER JOIN users u
USING (user_id)
INNER JOIN cities ci
USING (city_id)
)
--select row number 1 only to avoid duplicated car data
SELECT city_name, brand, model, year, price, avg_car_city
FROM price_and_avg_price
WHERE rn = 1;WITH bids_data AS (
SELECT
c.model,
b.user_id,
b.bid_date,
b.bid_price
FROM bids b
INNER JOIN ads a
USING (ad_id)
INNER JOIN cars c
USING (car_id)
WHERE c.model = 'Daihatsu Xenia'
)
SELECT
model,
user_id,
bid_date AS previous_bid_date,
LEAD(bid_date) OVER (PARTITION BY user_id ORDER BY bid_date) AS next_bid_date,
bid_price AS previous_bid_price,
LEAD(bid_price) OVER (PARTITION BY user_id ORDER BY bid_date) AS next_bid_price
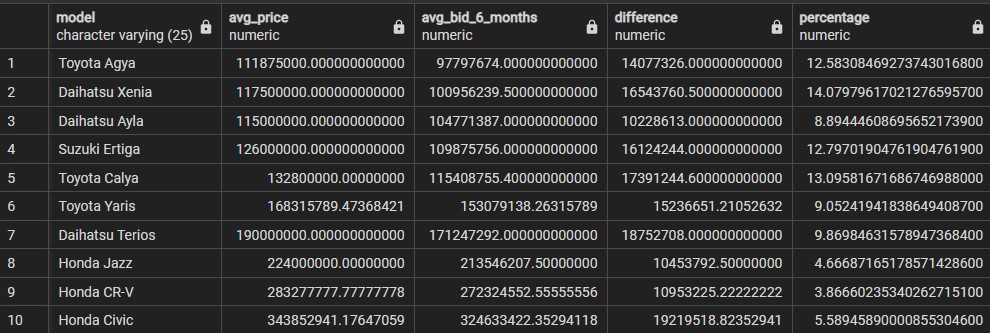
FROM bids_data;WITH avg_price_data AS (
SELECT
c.model,
AVG(c.price) AS avg_price,
AVG(b.bid_price) AS avg_bid_6_months
FROM bids b
INNER JOIN ads a
USING (ad_id)
INNER JOIN cars c
USING (car_id)
WHERE b.bid_date >= CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL '6 months'
GROUP BY c.model
)
SELECT
model,
avg_price,
avg_bid_6_months,
(avg_price - avg_bid_6_months) AS difference,
(avg_price - avg_bid_6_months)/avg_price * 100 AS percentage
FROM avg_price_data
ORDER BY avg_bid_6_months;Average bid price of one car model from last one to six months (using window function). i.e average bid price of Honda CR-V.
WITH avg_bid_price_data AS (
SELECT
c.brand,
c.model,
b.bid_date,
b.bid_price,
AVG(b.bid_price) OVER (PARTITION BY c.brand, c.model ORDER BY DATE_TRUNC('month', b.bid_date) ASC) AS avg_price,
EXTRACT(MONTH FROM CURRENT_DATE) - EXTRACT(MONTH FROM DATE_TRUNC('month', b.bid_date)) AS month_diff
FROM bids b
INNER JOIN ads a
USING (ad_id)
INNER JOIN cars c
USING (car_id)
WHERE b.bid_date >= CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL '6 months' AND c.model = 'Honda CR-V'
)
SELECT
brand,
model,
MAX(CASE WHEN month_diff = 6 THEN avg_price ELSE NULL END) AS avg_bid_price_m_6,
MAX(CASE WHEN month_diff = 5 THEN avg_price ELSE NULL END) AS avg_bid_price_m_5,
MAX(CASE WHEN month_diff = 4 THEN avg_price ELSE NULL END) AS avg_bid_price_m_4,
MAX(CASE WHEN month_diff = 3 THEN avg_price ELSE NULL END) AS avg_bid_price_m_3,
MAX(CASE WHEN month_diff = 2 THEN avg_price ELSE NULL END) AS avg_bid_price_m_2,
MAX(CASE WHEN month_diff = 1 THEN avg_price ELSE NULL END) AS avg_bid_price_m_1
FROM avg_bid_price_data
GROUP BY brand, model;- Clone/download this repository
- Install PostgreSQL and pgAdmin 4
- Create database via pgAdmin4
- run DDL.sql from query tool pgAdmin 4
- run python scripts for generating and inserting dummy data to PostgreSQL database