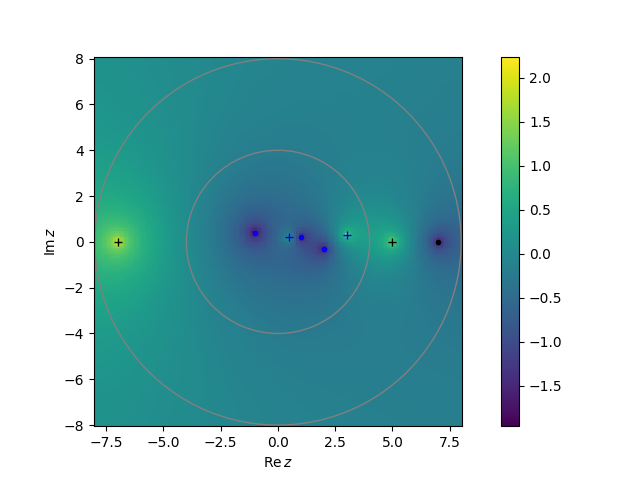
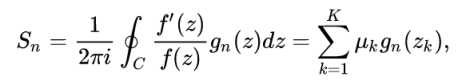This python package aims at finding poles and zeros of a meromorphic function with their multiplicities inside a closed contour in the complex plane. All the roots can be found without initial guess.
For convenience we denote by root a pole or a zero. The method is based on the generalized argument principle :
where
The method applies to meromorphic (and also to holomorphic) functions, assuming there is no root on the path
Theoretical development can be found in Refs. [1, 2] and the references therein.
The approach used here is closer to [2] where the probe functions are
The main advantage of the contour splitting is its robustness and its simplicity, but the price to pay is the increase of the number of function evaluations, since the integral need to be evaluated for each contour. The overhead appears only for significant number of roots (say more than 10). This bound depends on the roots distribution [2]. The ideal case is when the roots are uniformly distributed around the integration contour.
For this kind of solver, it is generally better to increase the number of contour splits than the number of integration points.
- Compute the moments
- Solve the generalized eigenvalue problem involving Hankel matrix [1, 2] to get the roots
- Solve the Vandermonde system to recover the multiplicity
- Remove the spurious roots. If the rank is not well determined, we get the genuine roots and some spurious ones [2]. Spurious ones have a ~0 multiplicity.
[1] Kravanja, Peter, Marc Van Barel, and Ann Haegemans. "On computing zeros and poles of meromorphic functions." Series in Approximations and Decompositions 11 (1999): 359-370.
[2] Chen, Hao-Tian. "On locating the zeros and poles of a meromorphic function." (2018).
polze is based on numpy, scipy and matplotlib.
polze is designed as a standard python package. The installation can be done after cloning or downloading the repos, using
pip3 install path/to/polze [--user]
or in editable mode if you want to modify the sources
pip3 install -e path/to/polze
Note that on some systems (like ubuntu), python3 or pip3 should be use to call python v3.x
Tests are handled with doctest and unittest. To call the test procedure, simply execute the test module
python -m polze.test
The doctrings are compatible with several Auto-generate API documentation, like pdoc3. Once the package has been installed or the at polze location run,
pdoc3 --html --force --config latex_math=True polze
The html files are generated in place. Then open the polze/index.html file. This interactive doc is particularly useful to see latex includes.
# Definition of the function
f = lambda z: np.tan(z)
df = lambda z: np.tan(z)**2 + 1 # [df is optional]
# Initialization of the solver
pz = PZ((f, df), Rmax=5, Npz=10, Ni=1024)
# Solve with moment method
pz.solve()
# Get the poles p and the zeros z
p, z = pz.dispatch()
# plot the roots
pz.plot()
# Performed an iterative refinement with Newton-Raphson method
pr, info = pz.iterative_ref()For now, polze use only circular integration contours in z and a single kind of probe function. The contour splitting is done a priori using the estimate of the number of roots (Npz), ie no error estimators are used.
cxroots is a Python package for finding all the roots of a function, f(z), of a single complex variable within a given contour, C, in the complex plane.
This approach has he same theoretical basis than polze but is (now) limited to analytic functions.
If you want to contribute to polze, your are welcomed! Don't hesitate to
- report bugs, installation problems or ask questions on issues;
- propose some enhancements in the code or in the documentation through pull requests (PR);
- suggest or report some possible new usages and why not start a scientific collaboration ;-)
- ...
To ensure code homogeneity among contributors, we use a source-code analyzer (eg. pylint). Before submitting a PR, run the tests suite. New tests should be added if new functionnalies are added.
polze is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
polze is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with polze. If not, see https://www.gnu.org/licenses/.