forked from pyecharts/pyecharts
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Merge pull request pyecharts#754 from pyecharts/dev
Dev -> Master -> Release v0.5.11
- Loading branch information
Showing
32 changed files
with
6,712 additions
and
2,911 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,285 @@ | ||
| > Advanced Usage: This document describes advanced usage of the pyecharts library. | ||
| ## Overview | ||
|
|
||
| Starting with v0.5.0, pyecharts supports the *javascript callback function* and the *echarts event handler*, further covering the [ECharts](http://echarts.baidu.com/) related features. Inject new vitality into the development of the project. | ||
|
|
||
| In the field of Python-To-Javascript language translation, [javascripthon](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/javascripthon) is a simple Python 3.5+ to Javascript language translator; [dukpy](https:/ /github.com/amol-/dukpy) Supports language translation for Python 2.7 and Python 3.4. | ||
|
|
||
| Based above, the pyecharts team developed [pyecharts-javascripthon] (https://github.com/pyecharts/pyecharts-javascripthon) as the underlying Python-To-Javascript language translation library, which encapsulated the above two different translators. Several Javascript data type adaptation modules are also available. For more on the translator, please go to [Translator] (en-us/translator). | ||
|
|
||
| pyecharts currently only uses and encapsulates some of Javascripthon's translation rules, mainly **Function Translate**. Use pseudo code to indicate the following: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| input:a Python function objection | ||
| output:a multi-line unicode string | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| For example, input the following Python functions: | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| def add(x, y): | ||
| return x + y | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Translated into the following Javascript functions. | ||
|
|
||
| ```js | ||
| function add(x, y) { | ||
| return (x + y); | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| For pyecharts users, there is no need to understand how the translator works. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Installation | ||
|
|
||
| ### Basic installation | ||
|
|
||
| pyecharts has pyecharts-javascripthon installed by default and can also be installed via pip. | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| $ pip install pyecharts-javascripthon | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### Environment restrictions | ||
|
|
||
| Since Javascripthon requires a version of Python of at least 3.5+ and pyecharts users of python 2.7, 3.4, 3.5 and 3.6, pyecharts-javascripthon uses a two-track system: python 3.5+ users directly use Javascripthon; python 2.7 and 3.4 users call network translation services (software as a service). At the same time, I hope that everyone will support the operating expenses of this network service. | ||
|
|
||
| > Note: Make sure the system is networked when using Python 2.7-3.4 users. | ||
|
|
||
| ## JavaScript callback function | ||
|
|
||
| ### Basic usage | ||
|
|
||
| pyecharts has encapsulated the underlying related logic and is transparent to the user. So you can use it as before. The callback function is assigned to the echarts configuration dictionary via the `add` method. The callback function here must satisfy one of the following conditions: | ||
|
|
||
| - Defined function with `def` | ||
|
|
||
| Note that the `lambda` expression is currently not supported. | ||
|
|
||
| Example: | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from pyecharts import Bar | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| def label_formatter(params): | ||
| return params.value + ' [Good!]' | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| attr = ["Jan", "Feb"] | ||
| v1 = [2.0, 4.9] | ||
| bar = Bar("Bar chart", "precipitation and evaporation one year") | ||
| bar.add("precipitation", attr, v1, is_label_show=True, label_formatter=label_formatter) | ||
| bar.render() | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| > Callback function format reference [series[i]-bar.label.formatter](http://echarts.baidu.com/option.html#series-bar.label.formatter) 。 | ||
| Rendering | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ### Tooltip example | ||
|
|
||
| For example, pyecharts users often ask questions in the Geo diagram how to display only the map coordinate names and values in the tooltip without the latitude and longitude. | ||
|
|
||
| Like this: | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| def test_geo_shantou_city(): | ||
| data = [('澄海区', 30), ('南澳县', 40), ('龙湖区', 50), ('金平区', 60)] | ||
| geo = Geo("汕头市地图示例", **style.init_style) | ||
| attr, value = geo.cast(data) | ||
| geo.add( | ||
| "", | ||
| attr, | ||
| value, | ||
| maptype="汕头", | ||
| is_visualmap=True, | ||
| is_legend_show=False, | ||
| label_emphasis_textsize=15, | ||
| label_emphasis_pos='right', | ||
| ) | ||
| geo.render() | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| Now, you can do this by defining a `geo_formatter` function firstly. | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| def geo_formatter(params): | ||
| return params.name + ' : ' + params.value[2] | ||
|
|
||
| def test_geo_shantou_city(): | ||
| data = [('澄海区', 30), ('南澳县', 40), ('龙湖区', 50), ('金平区', 60)] | ||
| geo = Geo("汕头市地图示例", **style.init_style) | ||
| attr, value = geo.cast(data) | ||
| geo.add( | ||
| "", | ||
| attr, | ||
| value, | ||
| maptype="汕头", | ||
| is_visualmap=True, | ||
| is_legend_show=False, | ||
| tooltip_formatter=geo_formatter, # The point is here to pass the function directly as a parameter. | ||
| label_emphasis_textsize=15, | ||
| label_emphasis_pos='right', | ||
| ) | ||
| geo.render() | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ### Label example | ||
|
|
||
| Use the callback function to set float type | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from pyecharts_javascripthon.dom import window | ||
| from pyecharts import Bar, Grid | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| def custom_formatter(params): | ||
| return window.parseFloat(params.value).toFixed(2) | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| attr = ["aa", "bb", "Diabetes Mellitus Requiring Medication", "d", "e", "fff"] | ||
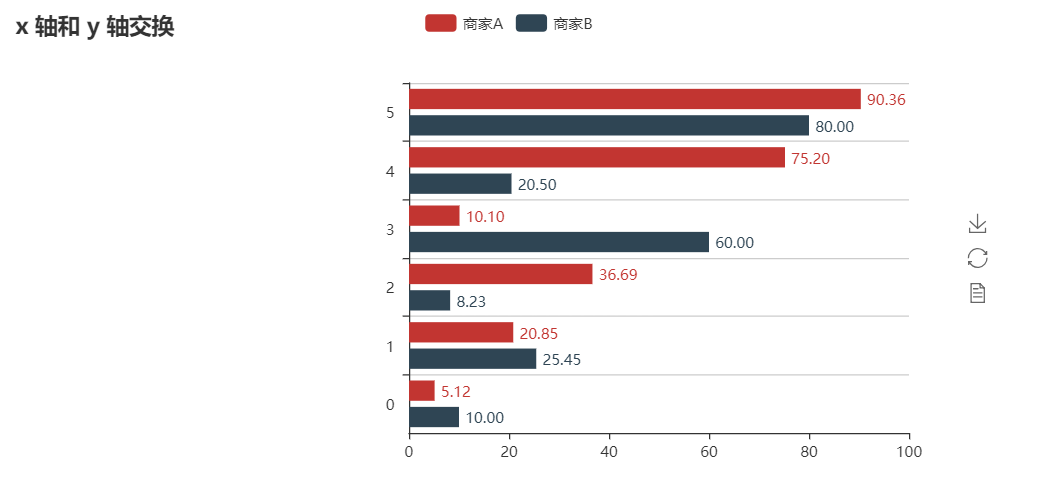
| v1 = [5.12, 20.85, 36.69, 10.10, 75.20, 90.36] | ||
| v2 = [10.00, 25.45, 8.23, 60.00, 20.50, 80.00] | ||
| bar = Bar("x 轴和 y 轴交换") | ||
| bar.add( | ||
| "商家A", | ||
| attr, | ||
| v1, | ||
| is_label_show=True, | ||
| label_pos="right", | ||
| label_formatter=custom_formatter, | ||
| ) | ||
| bar.add( | ||
| "商家B", | ||
| attr, | ||
| v2, | ||
| is_convert=True, | ||
| is_label_show=True, | ||
| label_pos="right", | ||
| label_formatter=custom_formatter, | ||
| ) | ||
| grid = Grid() | ||
| grid.add(bar, grid_left="40%") | ||
| grid.render() | ||
| ``` | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## JavaScript event handlers | ||
|
|
||
| Echarts provides [api/events](http://echarts.baidu.com/api.html#events) event handlers, mainly via 'on' method. | ||
|
|
||
| pyecharts provides the following global event name variables based on the official list of events. Located in the `pyecharts.echarts.events` module. | ||
|
|
||
| ``` python | ||
| # Mouse Events | ||
| MOUSE_CLICK = "click" | ||
| MOUSE_DBCLICK = "dbclick" | ||
| MOUSE_DOWN = "mousedown" | ||
| MOUSE_OVER = "mouseover" | ||
| MOUSE_GLOBALOUT = "globalout" | ||
|
|
||
| # Other Events | ||
| LEGEND_SELECT_CHANGED = "legendselectchanged" | ||
| LEGEND_SELECTED = "legendselected" | ||
| LEGEND_UNSELECTAED = "legendunselected" | ||
| LEGEND_SCROLL = "legendscroll" | ||
| DATA_ZOOM = "datazoom" | ||
| DATA_RANGE_SELECTED = "datarangeselected" | ||
| TIMELINE_CHANGED = "timelinechanged" | ||
| TIMELINE_PLAY_CHANGED = "timelineplaychanged" | ||
| RESTORE = "restore" | ||
| DATA_VIEW_CHANGED = "dataviewchanged" | ||
| MAGIC_TYPE_CHANGED = "magictypechanged" | ||
| GEO_SELECT_CHANGED = "geoselectchanged" | ||
| GEO_SELECTED = "geoselected" | ||
| GEO_UNSELECTED = "geounselected" | ||
| PIE_SELECT_CHANGED = "pieselectchanged" | ||
| PIE_SELECTED = "pieselected" | ||
| PIE_UNSELECTED = "pieunselected" | ||
| MAP_SELECT_CHANGED = "mapselectchanged" | ||
| MAP_SELECTED = "mapselected" | ||
| MAP_UNSELECTED = "mapunselected" | ||
| AXIS_AREA_SELECTED = "axisareaselected" | ||
| FOCUS_NODE_ADJACENCY = "focusnodeadjacency" | ||
| UNFOCUS_NODE_ADJACENCY = "unfocusnodeadjacency" | ||
| BRUSH = "brush" | ||
| BRUSH_SELECTED = "brushselected" | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| The usage is as follows: | ||
| ```python | ||
| #!/usr/bin/env python | ||
| # coding=utf-8 | ||
| from __future__ import unicode_literals | ||
|
|
||
| import pyecharts.echarts.events as events | ||
| from pyecharts import Bar | ||
| from pyecharts_javascripthon.dom import alert | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
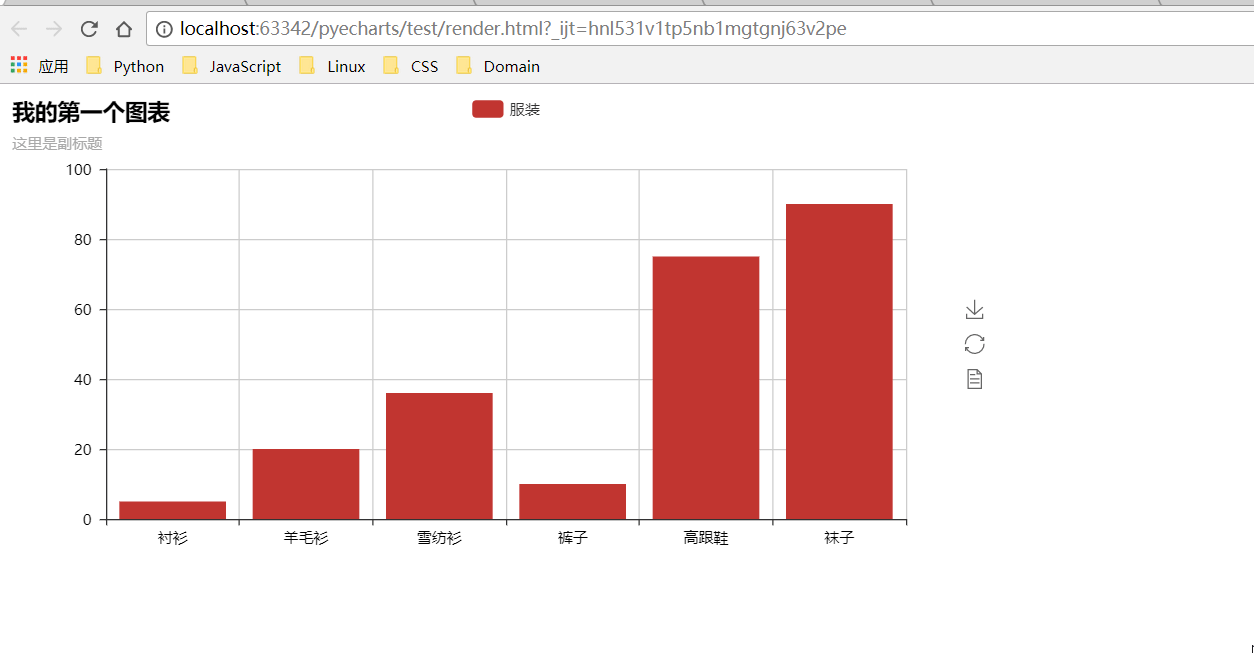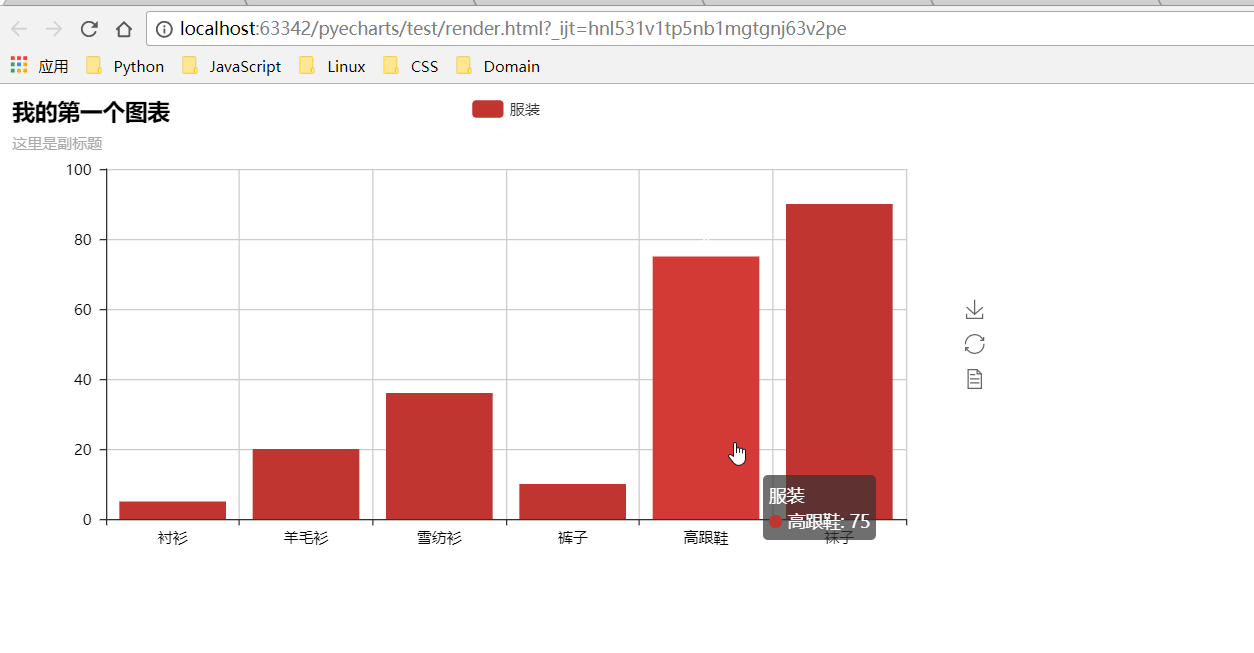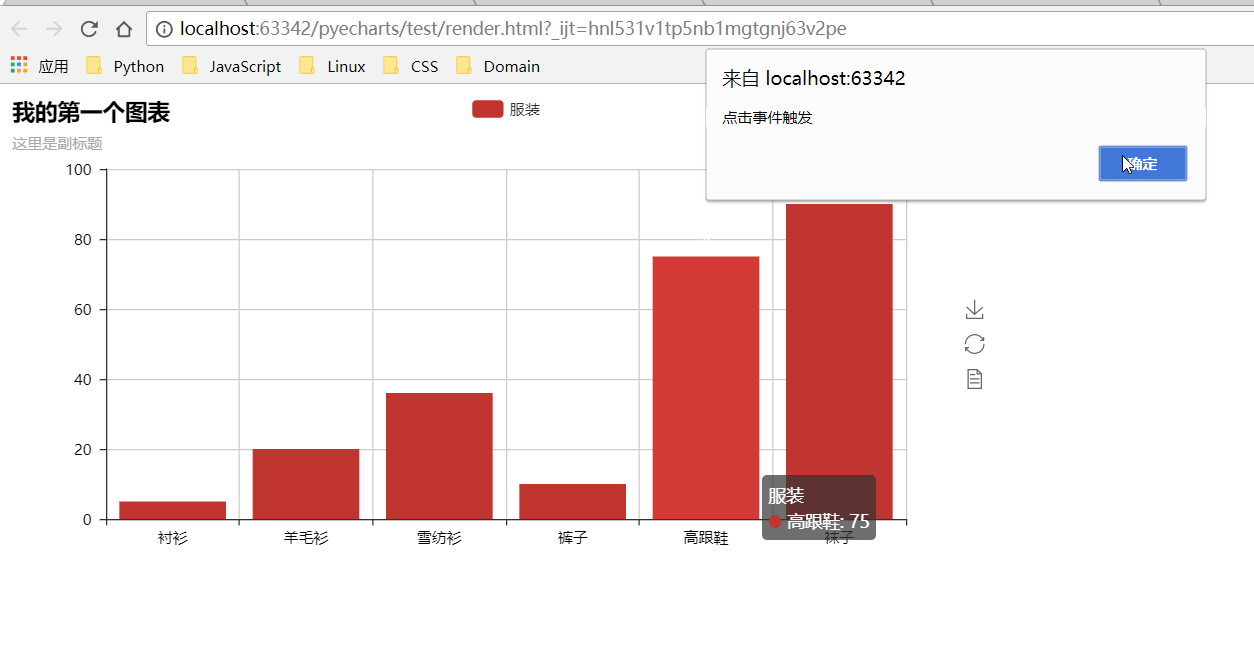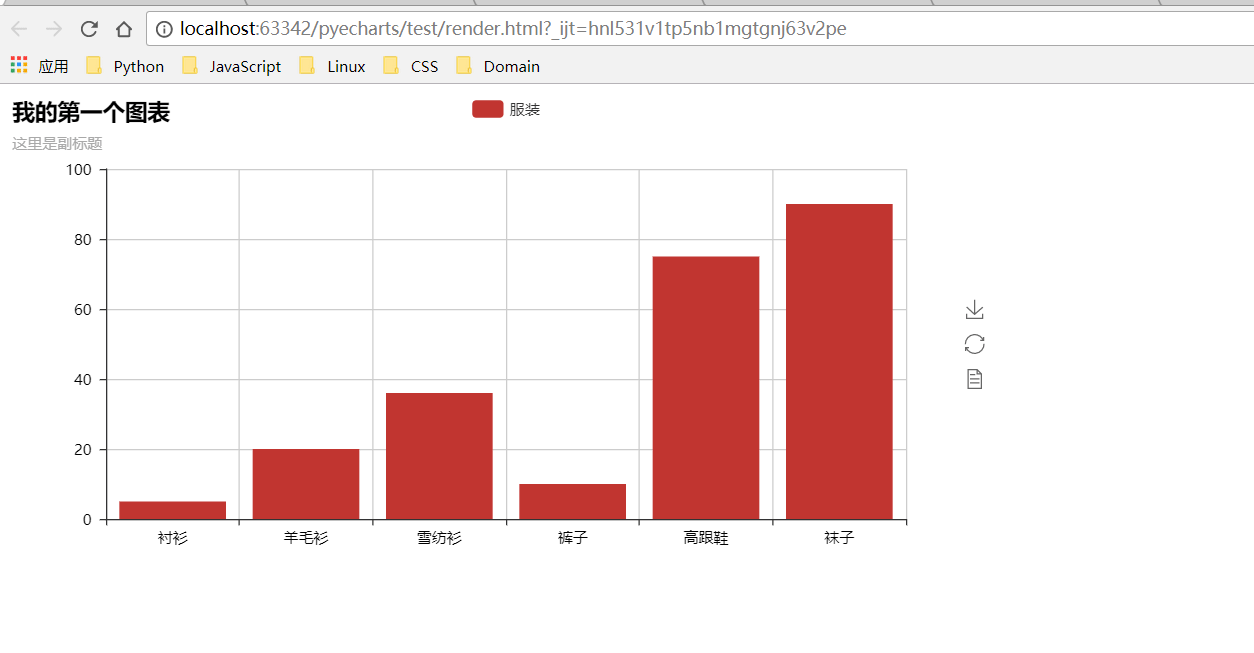
| def on_click(): | ||
| alert("点击事件触发") | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| def test_mouse_click(): | ||
| bar = Bar("我的第一个图表", "这里是副标题") | ||
| bar.add( | ||
| "服装", ["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"], [5, 20, 36, 10, 75, 90] | ||
| ) | ||
| bar.on(events.MOUSE_CLICK, on_click) | ||
| bar.render() | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ## Note | ||
|
|
||
| First, pyecharts does not check if the echarts chart configuration option supports callback functions. See the ECharts documentation for this section. | ||
|
|
||
| This refers to whether the options parameter itself supports callback functions, such as : | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| def my_title(): | ||
| return 'my_title' | ||
| bar.add(my_title, [], []) | ||
| ``` | ||
| There are no rendering errors in pyecharts, but it does not meet the requirements for title in ECharts. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Second, in order to improve performance, pyecharts did the following: | ||
|
|
||
| - The actual execution of a function translation is when the `render` function is called, not the `add` function. | ||
| - Cache the function that has been translated with the **function name** as an index to avoid rendering the function of the same name multiple times. | ||
|
|
||
| Therefore, you should avoid using the same function name. The following situations may not achieve the expected results. | ||
|
|
||
| ```python | ||
| from pyecharts import Bar | ||
|
|
||
| def label_formatter(params): | ||
| return params.name + ' [Good!]' | ||
|
|
||
| attr = ["Jan", "Feb"] | ||
| v1 = [2.0, 4.9] | ||
| bar = Bar("Bar chart", "precipitation and evaporation one year") | ||
| bar.add("precipitation", attr, v1, is_label_show=True, label_formatter=label_formatter) | ||
| bar.render() | ||
|
|
||
| def label_formatter(params): | ||
| return params.name + '[OK!]' | ||
|
|
||
| bar2 = Bar("Bar chart", "precipitation and evaporation one year") | ||
| bar2.add("precipitation", attr, v1, is_label_show=True, label_formatter=label_formatter) | ||
| bar2.render() | ||
| ``` |
Oops, something went wrong.