This is made to learn & explore new tech & research.
👉 Main Topics
💭 Sub Topics
➡️ Key Points / Components / Categories
The presented architectures are designed based on three factors:
Cloud computing can’t do much if systems are still designed in deployment monolithic approach where software applications are deployed as a single unit. Even though the monolithic approach is easy to understand by developers and has been adopted for decades, it has become a bottleneck with the new technology trends. In the monolithic approach, software systems are developed most likely in the same technology stack, cluster-based replication as a scalability strategy.
Microservices architecture is based on developing software projects into modular services that are: small, self-contained, self-deployable, designed around business capabilities, manage its own data, and communicate with other services over a lightweight protocol (most likely HTTP).
In microservices, every service is designed, developed and operated by a dedicated team, which has almost a full decision on the design and technology of their service. This approach of team structure and management is called DevOps.
A full stack developer is a web developer or engineer who works with both the front and back ends of a website or application—meaning they can tackle projects that involve databases, building user-facing websites, or even work with clients during the planning phase of projects.
➡️ Non-Distributed Monolithic With Server-Side Front-End
In this architecture the application is developed using a 3-layer architecture which runs in a single process. In this approach, the front-end can be developed using Java EE( JSP or JSF), Spring MVC (FreeMarker, Thymeleaf, or JSP), and dynamic HTML rendering using server-side scripting languages such as PHP or Python.
JSP - java server pages is a server-side programming technology that enables the creation of dynamic, platform-independent method for building Web-based applications. JSP have access to the entire family of Java APIs, including the JDBC API to access enterprise databases.
JSF - Java Server Faces (JSF) is a Java-based web application framework intended to simplify development integration of web-based user interfaces. JavaServer Faces is a standardized display technology, which was formalized in a specification through the Java Community Process.
The Spring Web MVC framework provides Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture and ready components that can be used to develop flexible and loosely coupled web applications.
The Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) API provides universal data access from the Java programming language.
Advantage is development simplicity and convenience. scalability, maintainability, and security are the main concerns. In addition, support for modern front-end technologies (such as smartphones apps) may be challenging as well.
➡️ Non-Distributed Monolithic With Client-Side Front-End
This design is similar to the previous one, except that the frontend and the backend are separated into two subsystems. In this approach, the front-end will be fully running on the client side while the backend will run as a server-side process.
Potential technologies to be used in the front-end, in this case, could be
- Traditional web frontend technologies, including HTML, Bootstrap, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Javascript based client-side frameworks such as Angular or React.
- Native client applications such as Android, iOS, or desktop apps.
- Hybrid applications, such as Cordova, PhoneGap, or Xamarin.
This approach enables technology separation between the front-end and backend, where a new front-end can be supported easily without any modifications to the backend.
➡️ Distributed Monolithic With Client-Side Front-End
The application is divided into 4-tiers (separate processes), where each tier communicates with the tier next to it over the network.
In this architecture, even though extra complexity is added to development, deployment, and operations, it enables more levels of modularity and reusability of every tier, where any tier can be easily replaced with another one. In addition, it is considered more secure than the one-tier architecture presented in the previous two approaches. Moreover, it allows more efficient scalability, especially if asynchronous communication is implemented (maybe by using event-driven reactive techniques or traditional messaging such as Java messaging service).
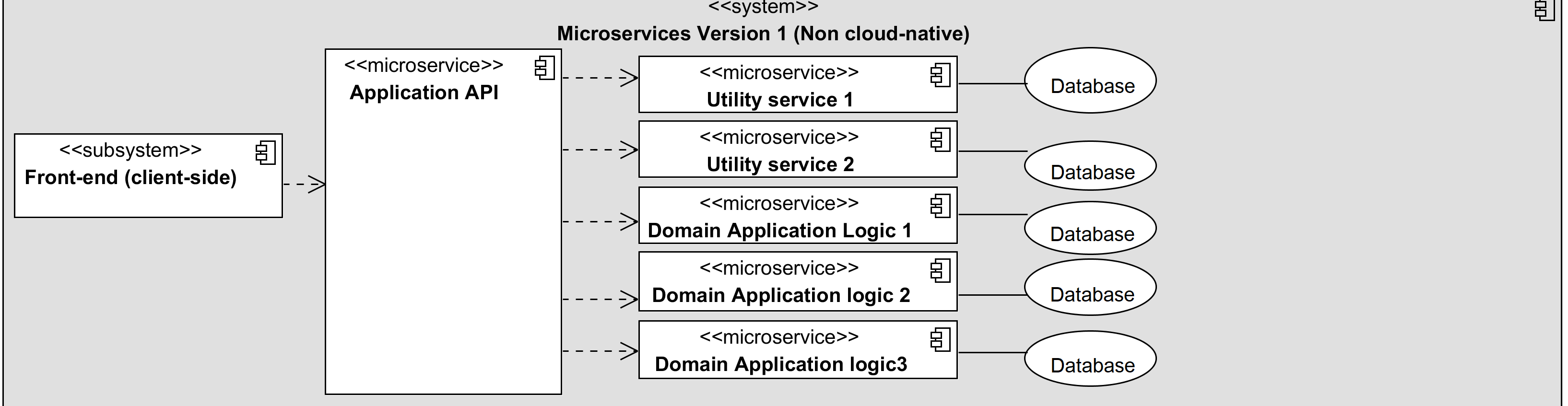
➡️ Non-Cloud Native Microservices
This design utilizes the microservices architectural style. In particular, the application is modulized into self-contained services that can be deployed independently. In microservices architecture, every service shall be designed around business capabilities and manage its own database.
Microservices enables evolutionary approach of software development, where services and features can be developed and deployed incrementally without affecting other services. In addition, it enables more efficient scalability with its lightweight horizontal scalability on the microservice level (not the application level).
Potential technology for microservices implementation includes:
- Spring Boot.
- Drop Wizard.
- Java Micro profile.
- NodeJS.
- Python.
Theoretically, any technology talks HTTP can be used to develop microservices.
➡️ Cloud-Native Microservices
In this approach, a microservices-based application will exploit the full benefits of cloud computing based on the 12-Factors concepts. This design might be sufficient for small-medium scale cloud-based applications. However, for more complex and larger scale applications, more infrastructure microservices should be considered, such as the components provided out of the box by Spring Cloud project.
In addition, other opensource projects may be useful to explore, such as Spring Boot Admin for real-time web-based application monitoring and JHipster project which provides a nice generator for cloud-based applications.
JHipster is a fully Open Source, widely used application generator. Easily create high-quality Spring Boot + Angular/React projects!
The purpose of software development processes is to deliver primary functionality expected by the end users and external stakeholders ,this category of functionality is known as functional requirements
Most of the time, functional requirements can be achieved without following best practices or having a good architecture. For example, implementing a full-featured wire-transfer functionality (including security, validation, integration, and auditing), can be implemented in a single file (maybe tens of hundreds of lines of code).
However, in the last example, the application will not survive for a long time. Problems will start to be visible in many stages, starting with the internal testing, user acceptance testing, to the going-live. Main concerns will be reliability (achieving the required functionality as expected all the time) and maintainability (the ability to maintain and apply changes to this functionality). Also, other potential issues include scalability and security. This leads to a different type of requirements: non-functional requirement (i.e. quality attributes).
SOA services communicate over heavyweight smart-pipes (ESB), microservices communicate over dump pipes with smart-end points. SOA aims to integrate enterprise large complex monolithic applications into enterprise-wide processes, while microservices aims to integrate small microservices into a single project. SOA is enterprise-wide based, microservices is project based. In SOA, a business process is created as orchestration and managed by the platform, in microservices, a business process is written as another microservice on the application level, which can be replaced by another service if the process changed.
An enterprise service bus(ESB) is a middleware tool used to distribute work among connected components of an application. ESBs are designed to provide a uniform means of moving work, offering applications the ability to connect to the bus and subscribe to messages based on simple structural and business policy rules.
Orchestration is the automated configuration, coordination, and management of computer systems and software.

For Example:- The 5G Core Network has been designed around services that are invoked using a standard API. On the surface, the 5G architecture looks very different from the 4G EPC but on close inspection, you can see the evolution from the 4G architecture to the 5G architecture.
The CI/CD pipeline is one of the best practices for devops teams to implement, for delivering code changes more frequently and reliably. CI/CD is a devops best practice because it addresses the misalignment between developers who want to push changes frequently, with operations that want stable applications.
Continuous integration are set of practices that drive development teams to implement small changes and check in code to version control repositories frequently. Because most modern applications require developing code in different platforms and tools, the team needs a mechanism to integrate and validate its changes.The technical goal of CI is to establish a consistent and automated way to build, package, and test applications. With consistency in the integration process in place, teams are more likely to commit code changes more frequently, which leads to better collaboration and software quality.
Continuous delivery picks up where continuous integration ends. CD automates the delivery of applications to selected infrastructure environments. Most teams work with multiple environments other than the production, such as development and testing environments, and CD ensures there is an automated way to push code changes to them. CD automation then performs any necessary service calls to web servers, databases, and other services that may need to be restarted or follow other procedures when applications are deployed.
➡️ One technique is to use version-control branching. A branching strategy such as Gitflow ![]() is selected to define protocols over how new code is merged into standard branches for development, testing and production. Additional feature branches are created for ones that will take longer development cycles. When the feature is complete, the developers can then merge the changes from feature branches into the primary development branch. This approach works well, but it can become difficult to manage if there are many features being developed concurrently.
is selected to define protocols over how new code is merged into standard branches for development, testing and production. Additional feature branches are created for ones that will take longer development cycles. When the feature is complete, the developers can then merge the changes from feature branches into the primary development branch. This approach works well, but it can become difficult to manage if there are many features being developed concurrently.
➡️ There are other techniques for managing features. Some teams also use feature flags, a configuration mechanism to turn on or off features and code at run time. Features that are still under development are wrapped with feature flags in the code, deployed with the master branch to production, and turned off until they are ready to be used.
For example if you were developing a Java application, CI would package all the static web server files such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript along with the Java application and any database scripts. CI not only packages all the software and database components, but the automation will also execute unit tests and other testing. This testing provides feedback to developers that their code changes didn’t break any existing unit tests.
A CI/CD tool such as Jenkins or Travis CI is used to automate the steps and provide reporting.
- Pulling code from version control and executing a build.
- Executing any required infrastructure steps that are automated as code to stand up or tear down cloud infrastructure.
- Moving code to the target compute environment.
- Managing the environment variables and configuring them for the target environment.
- Pushing application components to their appropriate services, such as web servers, API services, and database services.
- Executing any steps required to restarts services or call service endpoints that are needed for new code pushes.
- Executing continuous tests and rollback environments if tests fail.
- Providing log data and alerts on the state of the delivery.
Once a CI/CD tool is selected, development teams must make sure that all environment variables are configured outside the application. CI/CD tools allow setting these variables, masking variables such as passwords and account keys, and configuring them at time of deployment for the target environment.
Many teams implementing CI/CD pipelines on cloud environments also use containers such as Docker and Kubernetes. Containers allow packaging and shipping applications in standard, portable ways. The containers can then be used to scale up or tear down environments that have variable workloads.
CD tools also provide dashboard and reporting functions. If builds or deliveries fail, they alert developers with information on the failed builds. They integrate with version control and agile tools, so they can be used to look up what code changes and user stories made up a build.
It is an architectural pattern that separates an application into three main logical components: the model, the view, and the controller. Each of these components are built to handle specific development aspects of an application. MVC is one of the most frequently used industry-standard web development framework to create scalable and extensible projects.
Following are the components of MVC −
The Model component corresponds to all the data-related logic that the user works with. This can represent either the data that is being transferred between the View and Controller components or any other business logic-related data. For example a Customer object will retrieve the customer information from the database, manipulate it and update it data back to the database or use it to render data.
The View component is used for all the UI logic of the application. For example the Customer view will include all the UI components such as text boxes, dropdowns, etc. that the final user interacts with.
Controllers act as an interface between Model and View components to process all the business logic and incoming requests, manipulate data using the Model component and interact with the Views to render the final output. For example the Customer controller will handle all the interactions and inputs from the Customer View and update the database using the Customer Model. The same controller will be used to view the Customer data.
PMD is a source code analyzer. It finds common programming flaws like unused variables, empty catch blocks, unnecessary object creation, and so forth. It supports Apex, Java, JavaScript, XML, XSL. Additionally it includes CPD, the copy-paste-detector. CPD finds duplicated code in Java, C, C++, C#, PHP, Ruby, Fortran, JavaScript, Matlab, Swift.
There have been many operating systems that were significant in their day but are no longer so, such as AmigaOS, OS/2 from IBM and Microsoft; classic Mac OS, the non-Unix precursor to Apple's macOS; BeOS; XTS-300; RISC OS; MorphOS; Haiku; BareMetal and FreeMint. Some are still used in niche markets and continue to be developed as minority platforms for enthusiast communities and specialist applications. OpenVMS, formerly from DEC, is still under active development by Hewlett-Packard.
Example- MINIX (used for academics & research) & Singularity (purely for research).
Unix was originally written in assembly language by Ken Thompson. The Unix-like family is a diverse group of operating systems, with several major sub-categories including System V, BSD, and Linux. The name "UNIX" is a trademark of The Open Group which licenses it for use with any operating system that has been shown to conform to their definitions. "UNIX-like" is commonly used to refer to the large set of operating systems which resemble the original UNIX.
Unix-like systems run on a wide variety of computer architectures. They are used heavily for servers in business, as well as workstations in academic and engineering environments. Free UNIX variants, such as Linux and BSD, are popular in these areas.
Four operating systems are certified by The Open Group (holder of the Unix trademark) as Unix. HP's HP-UX and IBM's AIX are both descendants of the original System V Unix and are designed to run only on their respective vendor's hardware. In contrast, Sun Microsystems's Solaris can run on multiple types of hardware, including x86 and Sparc servers, and PCs. Apple's macOS, a replacement for Apple's earlier (non-Unix) Mac OS, is a hybrid kernel-based BSD variant derived from NeXTSTEP, Mach, and FreeBSD.
Unix interoperability was sought by establishing the POSIX standard. The POSIX standard can be applied to any operating system, although it was originally created for various Unix variants.
POSIX- Portable Operating Systems Interface
BSD- Berkeley Software Distribution (which includes FreeBSD, NetBSD, and OpenBSD. These operating systems are most commonly found on webservers, although they can also function as a personal computer OS.)
macOS (formerly "Mac OS X" and later "OS X") is a line of open core graphical operating systems developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc., the latest of which is pre-loaded on all currently shipping Macintosh computers. macOS is a UNIX operating system built on technology that had been developed at NeXT.
NeXT- formed by Steve jobs, a company that manufactured high-end computers running on a variation of BSD called NeXTSTEP. One of these computers was used by Tim Berners-Lee as the first webserver to create the World Wide Web.
The Linux kernel originated in 1991, as a project of Linus Torvalds (university student in Finland). He posted information about his project on a newsgroup for computer students and programmers, and received support and assistance from volunteers who succeeded in creating a complete and functional kernel.
Linux is Unix-like, but was developed without any Unix code, unlike BSD and its variants. Because of its open license model, the Linux kernel code is available for study and modification, which resulted in its use on a wide range of computing machinery from supercomputers to smart-watches. Linux is used on only 1.82% of all "desktop" (or laptop) PCs, it has been widely adopted for use in servers and embedded systems such as cell phones. Linux has superseded Unix on many platforms and is used on most supercomputers. Linux kernel is used in some popular distributions,such as Red Hat, Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Google's Android, Chrome OS &Chromium OS.
Server editions of Windows are widely used. In recent years, Microsoft has expended significant capital in an effort to promote the use of Windows as a server operating system. However, Windows' usage on servers is not as widespread as on personal computers as Windows competes against Linux and BSD for server market share.
ReactOS is a Windows-alternative operating system, which is being developed on the principles of Windows – without using any of Microsoft's code.
A Kernel is the central part of an operating system. It manages the operations of the computer and the hardware, most notably memory and CPU time.
- A micro kernel, which only contains basic functionality.
- A monolithic kernel, which contains many device drivers.
- Hybrid Kernel
- Exo Kernel
- Nano Kernel
A computer user never interacts directly with the kernel. It runs behind the scenes and cannot be seen, except for the text logs that it prints.The kernel provides services so programs can request the use of the network card, the disk or other pieces of hardware. The kernel forwards the request to special programs called device drivers which control the hardware. It also manages the file system and sets interrupts for the CPU to enable multitasking.
The Kernel can also talk to hardware on a secure line. So companies can develop a Kernel which can talk to their hardware through a set of buttons. Take the washing machine for an example, Depending on the knobs you move, and time you set – a basic level of Kernel should be enough. That said, Kernel themselves grow complicated with time, which results in types of Kernel.
Here, the OS and Kernel both run in the same memory space and suitable where security is not a significant concern. It results in faster access, but if there is a bug in the device driver, the entire system crashes.
Its a stripped-down version of Monolithic Kernel where the Kernel itself can do most of the job done, and there is no need of an extra GUI. They should be used where security and the crashing system isn’t or will not happen.
This Kernel is what we see most. Windows, Apple’s macOS. They are a mix of Monolithic Kernel and Microkernel. It moves out drivers but keeps system services inside the Kernel – similar to how drivers are loaded when Windows Starts the bootup process.
If you need to have a kernel, but its majority of function is set up outside, then this comes into the picture.
This kernel only offers process protection and resource handling. However it is mostly used when you are testing out an inhouse project, and you upgrade to a better Kernel type.